Statistics across all threats
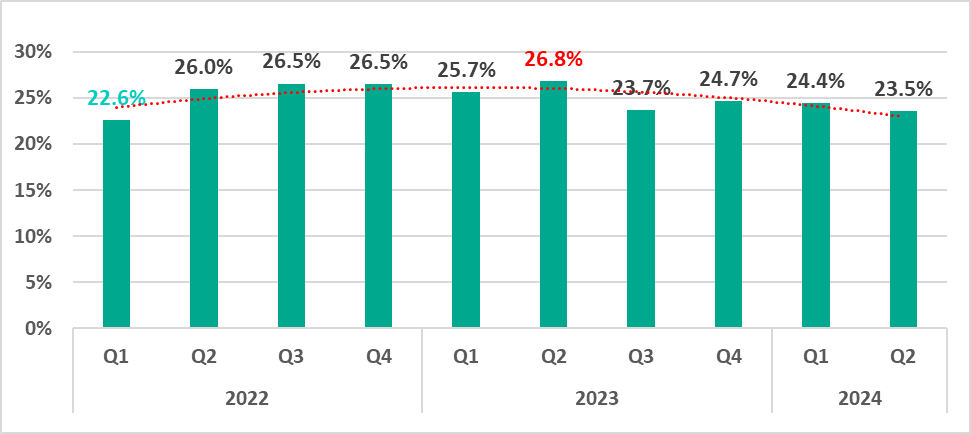
In the second quarter of 2024, the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked decreased by 0.9 pp from the previous quarter to 23.5%.
The percentage has decreased by 3.3 pp compared to the second quarter of 2023, when the indicator reached its highest level since records began in 2022.
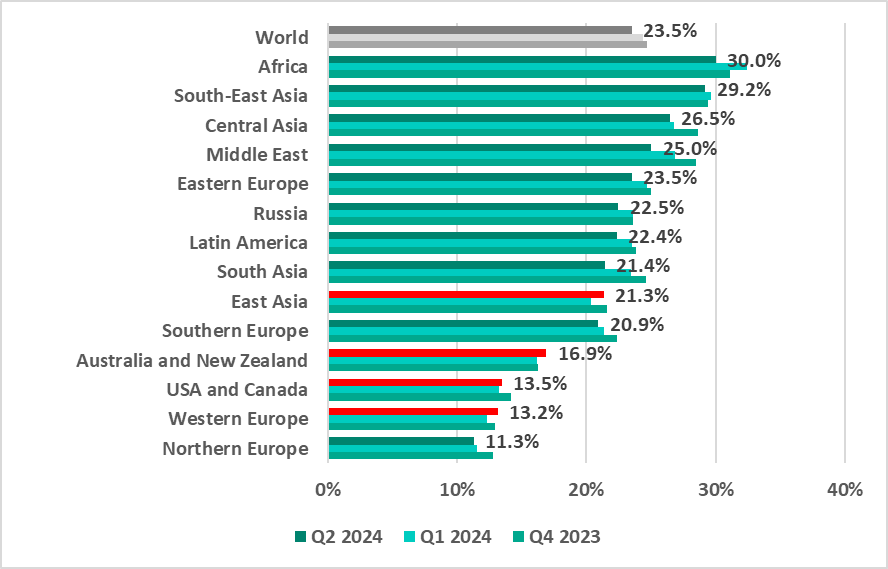
Regions ranking
In most regions, the percentage of ICS computers that blocked malicious objects decreased compared to the first quarter of 2024. The indicator increased only in East Asia (by 1.0 pp), Western Europe (by 0.8 pp), Australia and New Zealand (by 0.7 pp) and the USA and Canada (by 0.2 pp).
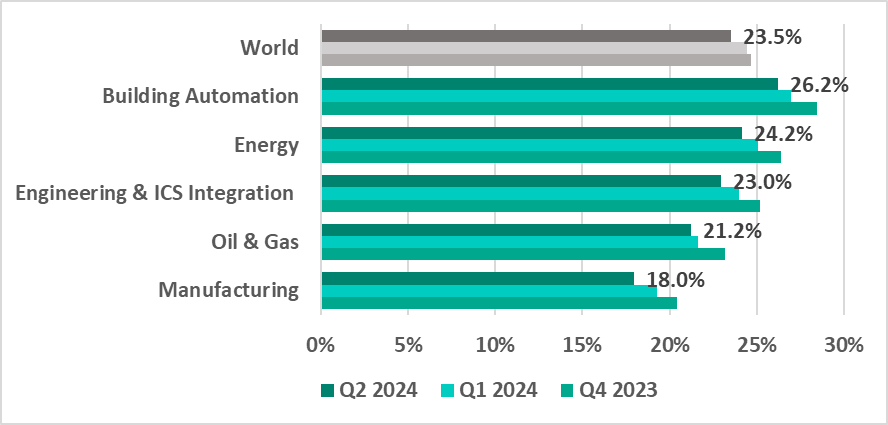
Industries ranking
The building automation sector continues to lead the surveyed industries in terms of the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked. In general, this indicator continues to decrease across all industries for the second quarter in a row.
Percentage of ICS computers on which the activity of malicious objects of various categories was prevented
Diversity of detected malware
In the second quarter of 2024, Kaspersky’s protection solutions blocked malware from 11,349 different malware families of various categories on industrial automation systems.
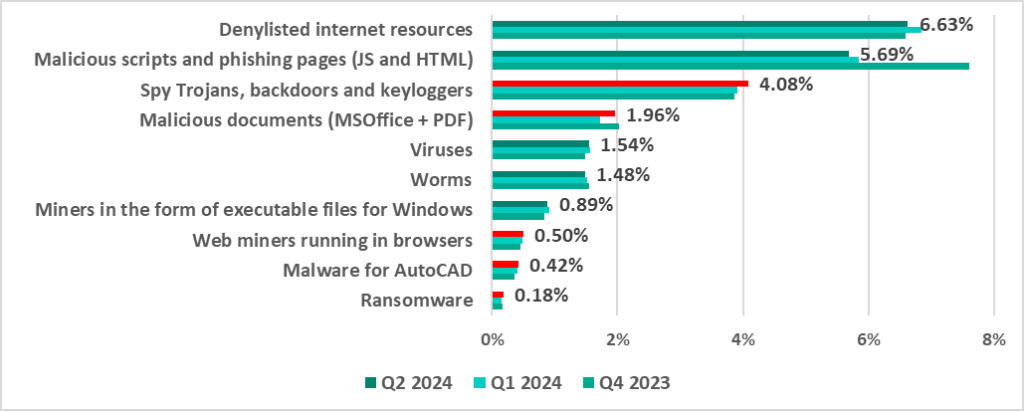
Percentage of ICS computers on which the activity of malicious objects of various categories was prevented
Compared to the previous quarter, the most noticeable proportional increase in the second quarter of 2024 was in the percentage of ICS computers on which ransomware was blocked – a 1.2-fold increase.
Malicious object categories in numbers
Malicious objects used for initial infection
This category includes dangerous web resources, malicious scripts and malicious documents.
- Denylisted internet resources – 6.63% (-0.21 pp compared to the first quarter of 2024);
- Malicious scripts and phishing pages (JS and HTML) – 5.69% (-0.15 pp);
- Malicious documents (MSOffice+PDF) – 1.96% (+0.24 pp).
Next-stage malware
Malicious objects used to initially infect computers deliver next-stage malware – spyware, ransomware, and miners – to victims’ computers. As a rule, the higher the percentage of ICS computers on which the initial infection malware is blocked, the higher the percentage for next-stage malware.
- Spyware (spy Trojans, backdoors and keyloggers) – 4.08% (+0.18 pp);
- Ransomware – 0.18% (+0.03 pp);
- Miners (in the form of executable files for Windows) – 0.89% (-0.03 pp).
Self-propagating malware
These are worms and viruses. Worms and virus-infected files were originally used for initial infection, but as botnet functionality evolved, they took on next-stage characteristics.
To spread across ICS networks, viruses and worms rely on removable media, network folders, infected files including backups, and network attacks on outdated software.
- Worms – 1.48% (-0.03 pp);
- Viruses – 1.54% (-0.02 pp).
AutoCAD malware
This category of malware is typically a low-level threat, coming last in the malware category rankings in terms of the percentage of ICS computers on which it was blocked.
- AutoCAD malware – 0.42% (+0.01 pp).
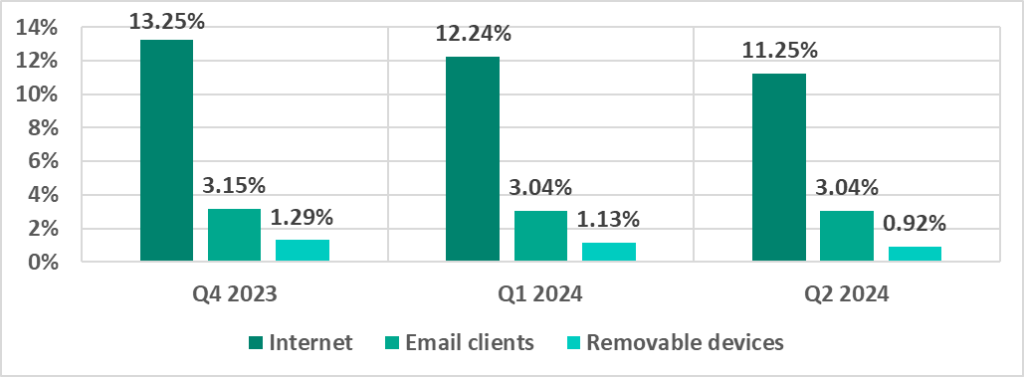
Main threat sources
The internet, email clients and removable storage devices remain the primary sources of threats to computers in an organization’s technology infrastructure. (Note that the sources of blocked threats cannot be reliably identified in all cases.)
The full global report is available on the Kaspersky ICS CERT website.
Article Link: Threat landscape for industrial automation systems, Q2 2024 | Securelist