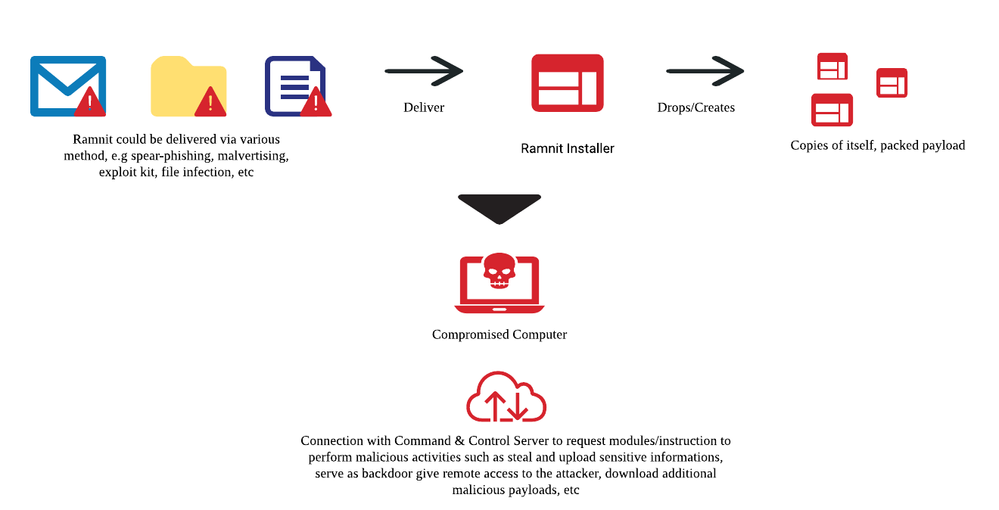
Ramnit Banking Trojan was first discovered in 2010 and is still evolving and staying actively as the second rank on the top banking trojan list in October 2019 as from the source post. It may be distributing via malvertising, exploit kit, spear-phishing campaign or others method to infect on the victim’s machines.
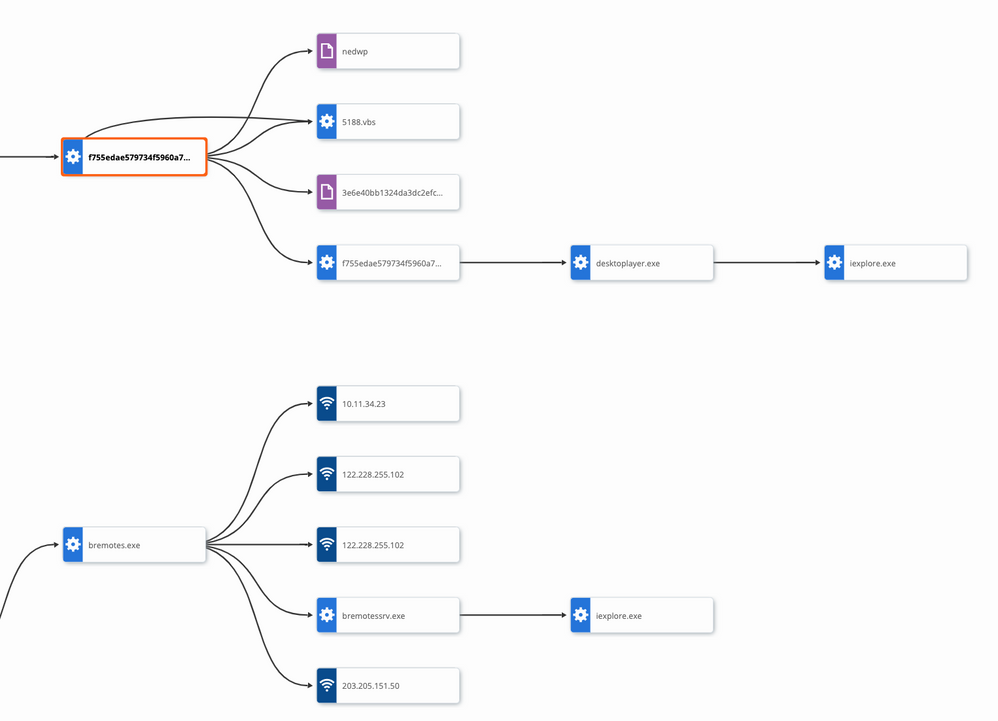
Figure1: Ramnit overall process
This post serves to inform our customers about detection and protection capabilities within the Carbon Black suite of products against Ramnit.
Behavioral Summary
Upon execution of Ramnit, it will create copies of itself, randomly renamed and store under %WINDIR% (C:\Windows) or %ProgramsFiles% directory, for example “%ProgramFiles%\Microsoft\desktoplayer.exe”.
It may also create additional payload by adding ‘srv’ at the end of the original filename, for example “[malware filename]srv.exe”.
In addition, it will create the following registry key to ensure it will execute on the startup: Key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\Userinit Value: c:\windows\system32\userinit.exe, %ProgramFiles%\Microsoft\desktoplayer.exe
Ramnit will need to connect to command and control (C&C) server then collect and upload sensitive information such as browser cookies, bank credentials, FTP credentials, and more data based on the requested modules which will be downloaded as .dll from C&C server. In addition, depending on the instruction from C&C server, it may download additional malicious payload to the victim’s computer and perform additional malicious activities. Ramnit will inject the malicious DLL modules into the context of legitimate system processes such as svchost.exe or web browser processes such as iexplore.exe (Shown in figure 4).
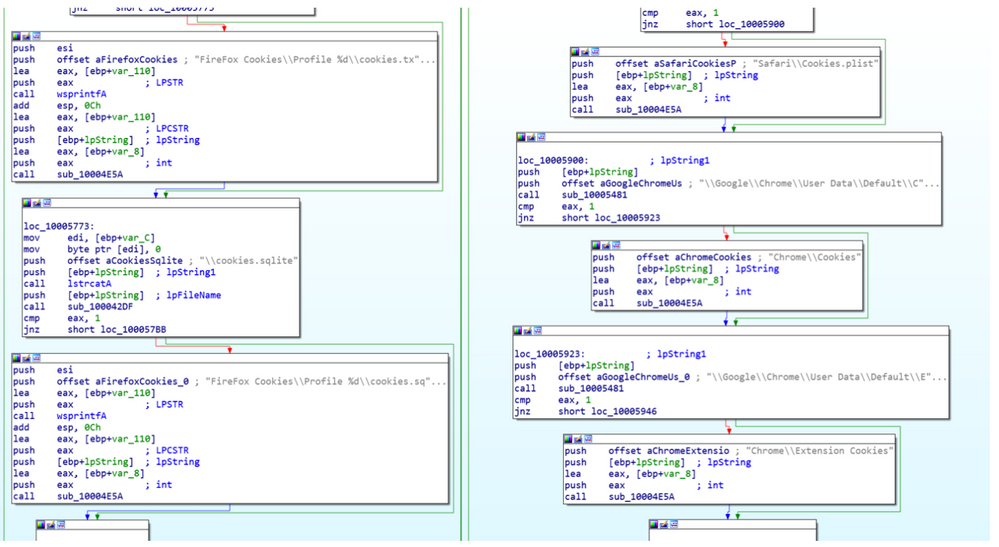
Figure 2: One of the Ramnit modules collecting cookies from IE, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Safari
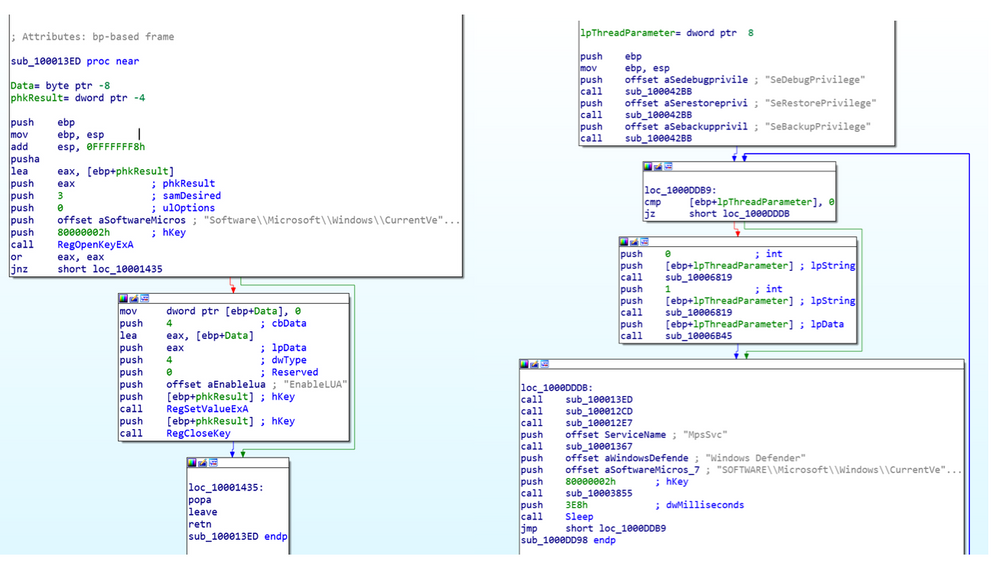
Figure 3: Ramnit will disable security software/services by modifying their registry key.
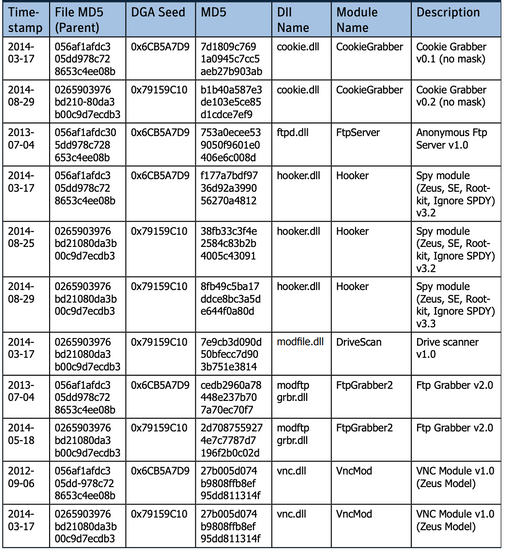
The identified Ramnit modules may refer to the following table: (Reference here)
The following screenshot is of CB Threat Hunter process chart and part of the event logs by Ramnit.
Figure 4: CB Threat Hunter Process Chart
Figure 5: CB Threat Hunter Event Log
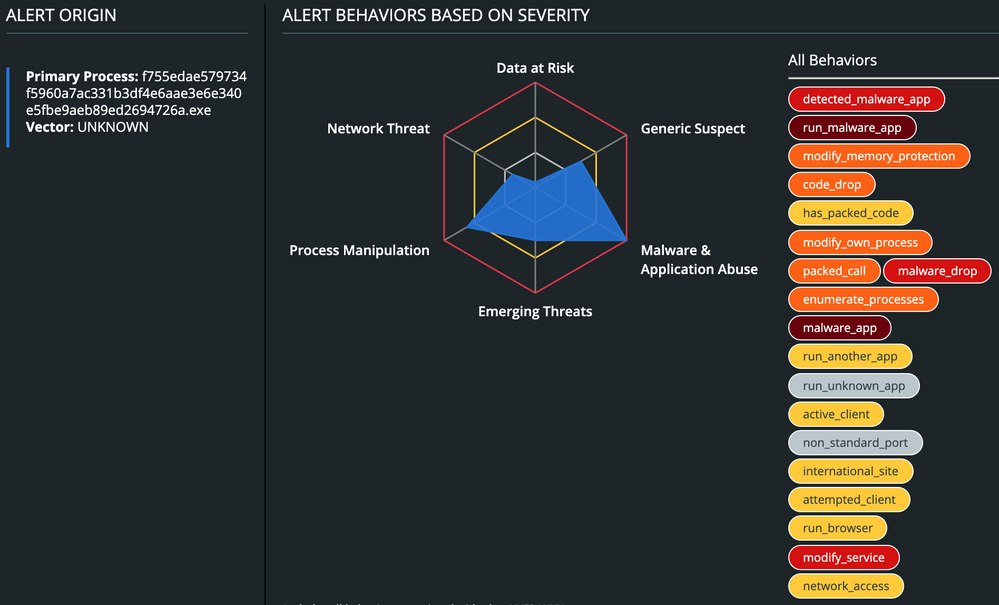
Other than that, CB Defense will display the malware’s overall triggered TTPs.
If you are a VMware Carbon Black customer looking to learn more on how to defend against this attack, click here.
Remediation:
MITRE ATT&CK TIDs
| TID | Tactic | Description |
|---|---|---|
| T1045 | Defense Evasion | Software Packing |
| T1027 | Defense Evasion | Obfuscated Files or Information |
| T1143 | Defense Evasion | Hidden Window |
| T1071 | Command and Control | Standard Application Layer Protocol |
| T1057 | Discovery | Process Discovery |
| T1050 | Privilege Escalation, Persistence | New Service |
| T1058 | Privilege Escalation, Persistence | Service Registry Permissions Weakness |
| T1112 | Defense Evasion | Modify Registry |
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
|
Indicator |
Type |
Context |
|
f755edae579734f5960a7ac331b3df4e6aae3e6e340e5fbe9aeb89ed2694726a bd19c8496017c962b9cd8508346e3878 |
SHA256 MD5 |
Ramnit (Main Installer) |
|
fd6c69c345f1e32924f0a5bb7393e191b393a78d58e2c6413b03ced7482f2320 ff5e1f27193ce51eec318714ef038bef |
SHA256 MD5 |
Ramnit (UPX Packed) |
|
876C5CEA11BBBCBE4089A3D0E8F95244CF855D3668E9BF06A97D8E20C1FF237C 44e92c4b5f440b756f8fb0c9eeb460b2 |
SHA256 MD5 |
Ramnit (Unpacked) |
|
4742490b011ca40fec59604bad953d32eae08512c513166f2cbd652f7fd6d2cb ed362f56ad7cd9d5c4e2415436c1c129 |
SHA256 MD5 |
Ramnit (DLL) |
|
160726b05e49f6f86983b2d945f7d691d1d9797078e4b7da4c0d7d7cba95c1d7 606215cf65fab017cff76463402a15e2 |
SHA256 MD5 |
Ramnit (DLL) |
The post Threat Analysis Unit (TAU) Threat Intelligence Notification: Ramnit Banking Trojan appeared first on VMware Carbon Black.
Article Link: https://www.carbonblack.com/2019/11/18/threat-analysis-unit-tau-threat-intelligence-notification-ramnit-banking-trojan/