![]()
New Insikt research highlights an emerging trend where threat actors are increasingly exploiting trusted platforms like Google Drive, OneDrive, Notion, and GitHub to conceal malicious activities within normal internet traffic. This tactic enhances their efficiency in data theft and operations while weakening conventional defenses. Advanced persistent threat (APT) groups are at the forefront of this strategy, with less sophisticated groups following suit. This underscores the need for adaptable defense strategies that evolve alongside threat actor innovations.
The report addresses a crucial gap in understanding by offering a systematic overview of legitimate internet services (LIS) abuse across malware categories. It predicts a further increase in LIS abuse due to advantages enjoyed by threat actors and the challenges faced by defenders. The lack of comprehensive reporting makes it difficult to quantify the trend definitively, but the prevalence of LIS abuse by well-established malware families, the adoption of these methods by newer strains, and the rapid innovation by APT groups all suggest an increasing trend in LIS abuse for adversary infrastructure.
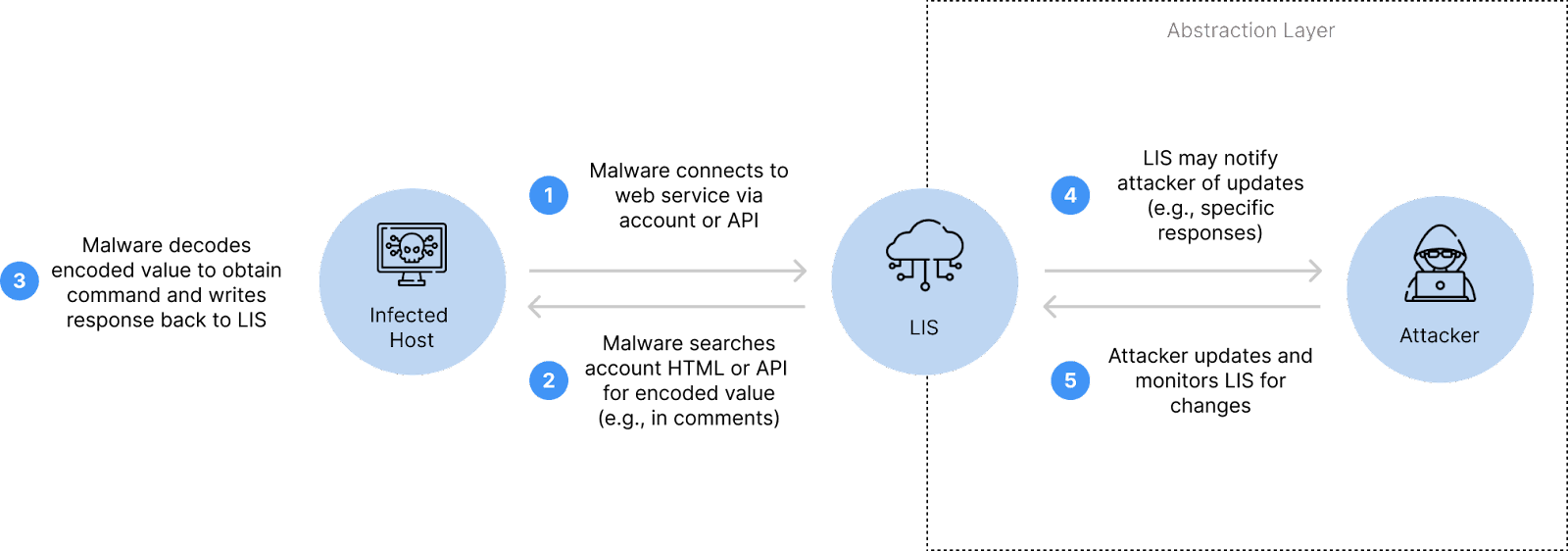 Overview of a full C2 infrastructure setup using LIS
Overview of a full C2 infrastructure setup using LIS
As threat actors continue to evolve their tactics, traditional defenses like indicator of compromise (IOC) blocking and basic detections will become less effective. A multi-faceted approach, encompassing network-, file-, and log-based detection methods, is proposed. Defenders should also proactively identify potentially vulnerable internet services and conduct attack simulations to stay ahead.
The report's analysis of over 400 malware families reveals that 25% of them abuse LIS in some capacity, with 68.5% of those families abusing more than one LIS. Infostealers are the most likely to exploit LIS (37%), driven by their data exfiltration objectives and ease of infrastructure setup. Different malware categories adopt distinct infrastructure schemes. Cloud storage platforms like Google Drive are the most commonly abused, followed by messaging apps like Telegram and Discord.
In the short term, defenders are advised to identify and block LIS that are not used within their environment but are known to be used maliciously. For long-term security, organizations should invest resources in understanding both legitimate and malicious uses of specific services. This understanding will facilitate the development of more effective and nuanced detection methods. Technologies like TLS network interception are gaining relevance for improved visibility, though they also introduce privacy and compliance concerns.
Despite the challenges, defenders can implement measures such as blocking or flagging malicious LIS usage, proactive threat hunting, and focusing on a diverse range of detection methods. Developing a comprehensive understanding of legitimate and malicious service usage is crucial for effective detection mechanisms and overall protection. The next report in the series will delve into the abuse of a specific LIS category used as malicious infrastructure.
To read the entire analysis with endnotes, click here to download the report as a PDF.
Article Link: Threat Actors Leverage Internet Services to Enhance Data Theft and Weaken Security Defenses | Recorded Future