Roundcube Vulnerability (CVE-2024-37383) Exploited in Phishing Attacks Targeting Government Agencies for Credential Theft
A vulnerability in the popular open-source Roundcube Webmail, CVE-2024-37383, was observed to be exploited by threat actors to launch phishing attacks aimed at stealing user credentials. Although patched, this stored XSS vulnerability remains a significant concern due to its potential for further exploitation in targeted attacks.
Phishing Campaign Targets Government Organizations Using Exploited Roundcube Flaw
In June 2024, the flaw was exploited in phishing campaigns targeting government organizations in the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) region, using hidden payloads within seemingly harmless email attachments.
Researchers from Positive Technologies have confirmed that the phishing emails tricked recipients into revealing sensitive credentials by injecting fake login forms into Roundcube’s interface.
How Does CVE-2024-37383 Work?
CVE-2024-37383 (CVSS 6.1) is a medium-severity vulnerability impacting Roundcube Webmail versions earlier than 1.5.6 and 1.6.x before 1.6.6. The issue arises from the improper processing of SVG elements within emails, which gives attackers the opportunity to inject and execute malicious JavaScript code in the victim’s browser.
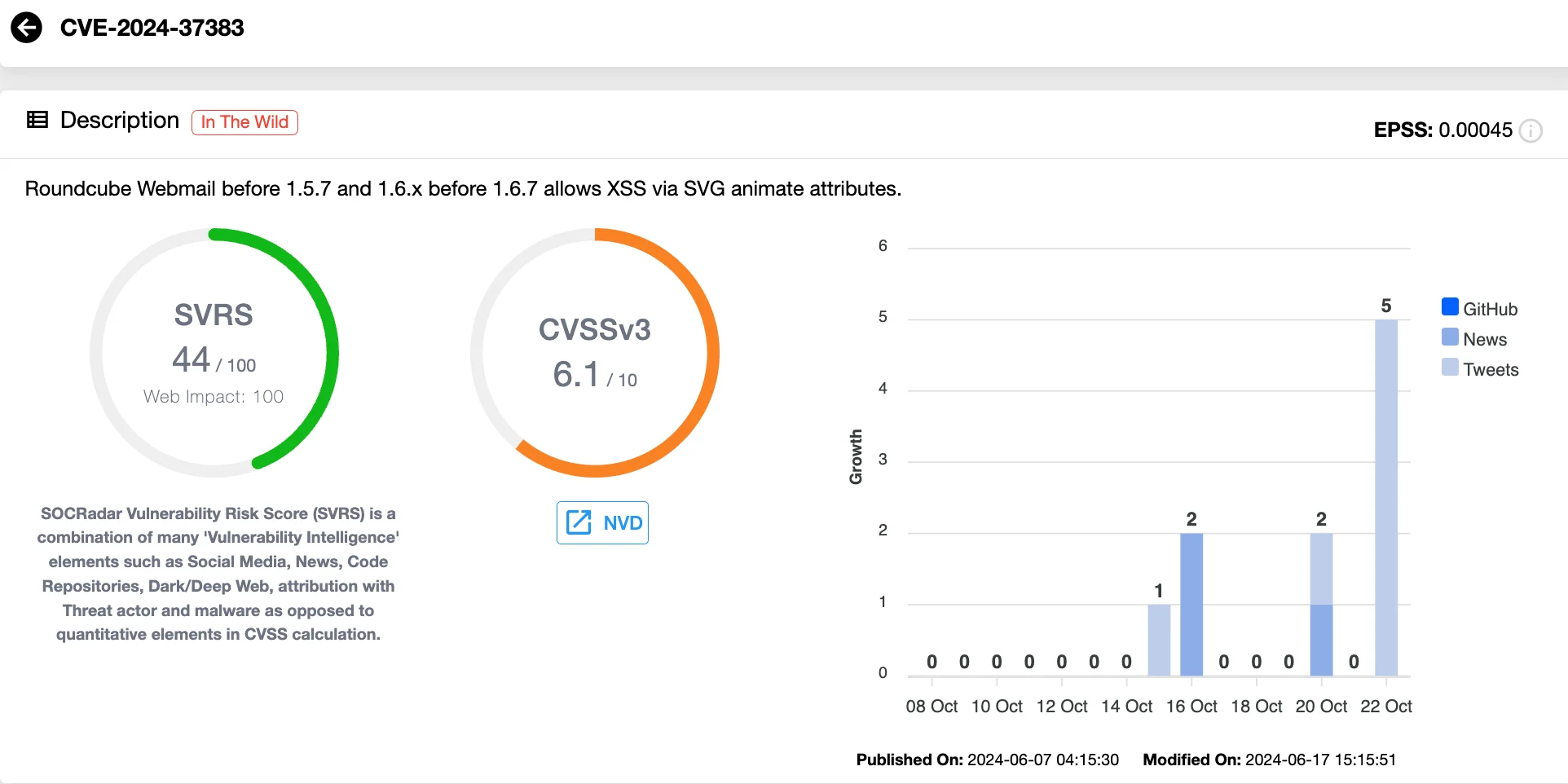
Details of CVE-2024-37383 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Attackers embed JavaScript in what appears to be an empty email, using a malformed href attribute. The extra space in the attribute bypasses Roundcube’s security filters, allowing them to execute arbitrary code. In result, when the recipient opens the malicious email in a vulnerable Roundcube version, the attackers can access sensitive information, such as login credentials.
Researchers also released a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit, showing how the vulnerability can allow Cross-site Scripting (XSS) attacks. By embedding fake login forms in Roundcube’s interface, attackers can trick users into entering their credentials, which are then stolen for unauthorized access.
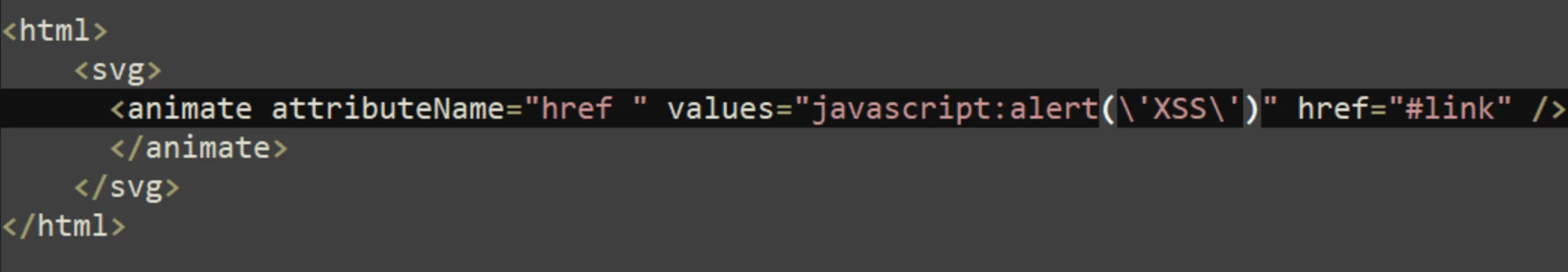
POC exploit for the CVE-2024-37383 vulnerability (PT)
How Do Attackers Exploit CVE-2024-37383?
In September 2024, researchers discovered that threat actors had exploited CVE-2024-37383 in a phishing campaign targeting government organizations in the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) region. The phishing emails, sent in June 2024, contained hidden JavaScript payloads specifically designed to steal credentials from Roundcube users.
These emails appeared to be empty, with an invisible document attachment. However, embedded within the email’s code was a malicious base64-encoded JavaScript that leveraged the Roundcube vulnerability.
The payload distracted victims by downloading a deceptive document while injecting a fake login form into Roundcube’s interface. The attackers intended for users to enter their credentials, which were then sent to the malicious server libcdn.org, registered on June 6, 2024, and hosted on Cloudflare infrastructure.
Also notably, the attackers used the ManageSieve plugin to retrieve emails from compromised accounts.
Update Roundcube to Prevent Exploitation
The most effective way to secure your Roundcube installation is to upgrade to the latest patched versions. The CVE-2024-37383 vulnerability has been addressed inversion 1.5.7 andversion 1.6.7, with the most recent release,version 1.6.9, available as of last month. These updates resolve the stored XSS vulnerability, preventing attackers from exploiting it.
As your digital footprint expands, so does your exposure to potential threats. Unmonitored or forgotten assets can become entry points for attackers, putting your business at risk. SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module helps you discover and monitor all your external-facing assets, ensuring nothing slips through the cracks. It continuously tracks your organization’s attack surface and highlights exposed or vulnerable areas.
Take control of your digital assets and fortify your defenses with SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management.
With SOCRadar’s ASM, you can actively manage your digital footprint, gaining visibility into all exposed assets across your network. This real-time monitoring allows you to address potential risks quickly, shutting down attack vectors before they can be exploited by cybercriminals.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
Researchers have identified the following as network indicators:
- libcdn.org – Sending access credentials to the mail server account
- rcm.codes – Sending mailbox content
Tactics, Techniques, Procedures (TTPs)
| ID | Name | Description |
| T059.007 | JavaScript Execution | Cybercriminals use JavaScript code to execute payloads within the victim’s email session in their browser. |
| T1114.003 | Remote Email Collection | Cybercriminals collect the contents of the victim’s mailbox using the ManageSieve plugin |
| T1056.004 | Web Portal Capture | Cybercriminals insert the login and password input fields into an email webpage and send the entered data to a remote server |
