Welcome to our “Ransomware Trends in 2023: A Live Blog of Insights and Analysis.” This live blog delves into the intricate world of ransomware, providing timely updates and valuable statistics on the prevailing trends shaping the threat landscape. As ransomware continues to wreak havoc on individuals and industries alike, it is imperative to remain vigilant and well-informed.
Our meticulous examination of ransomware attack counts, breached data, paid ransoms, victim counts, and targeted industries aims to shed light on cybercriminals’ evolving tactics and strategies. Join us as we navigate the intricate maze of ransomware in 2023, equipping you with the knowledge to fortify your defenses and protect against these ever-evolving threats.
Ransomware Statistics of the First Half of 2023
Ransomware attacks maintain their prevalence in 2023 and continue to show growth trends. This year, in which CL0p ransomware has recently announced dozens of victims at once and LockBit has been continuing its steady ransomware attacks since 2022, has already been recorded as an important year for the concept of ransomware. In this post, we will evaluate the situation by reviewing various statistics.
- Ransomware attacks occupy almost a quarter of cyberattacks, with 24%. This number amounts to millions. (IBM, Verizon)
Although this figure corresponded to 10% for 2022, it was possible to mention near 500 million ransomware attacks. (Statista) Looking at the number of Ransomware operators alone, it can be misconstrued that they are limited to the thousands. However, ransomware attacks can be attempted every year, even on small businesses and personal users.
- Judging by organized cybercrime alone, ransomware attacks account for 62% of all attacks. (Verizon)
Ransomware, which occupies a quarter of all cyber malicious actions, finds a place in 62% of the attacks made by more dangerous and ambitious organized cybercrime organizations and qualifies this as the main problem.
- Ransomware attack costs have increased by 13% in the last one year. (IBM)
While increases in damage in terms of cost from all cyberattacks can be observed, ransomware has risen the most. According to IBM’s 2023 report, the average ransomware attack cost reached USD 5.13 million, showing a 13% increase from the previous year’s average cost of USD 4.54 million in the 2022 report.
- The average cost of a ransomware attack is up to 5 million dollars. (IBM)
According to IBM, Out of the ransomware victims, 37% chose not to involve law enforcement in containing a ransomware breach. However, the ones who decided to involve law enforcement experienced a less expensive ransomware breach overall. Specifically, the average ransomware breach cost was USD 5.11 million when law enforcement wasn’t interested, whereas it was reduced to USD 4.64 million when law enforcement was engaged. This difference of 9.6% accounts for USD 470,000.
- It takes almost one year on average to identify and contain ransomware.(IBM)
It takes almost one year on average to identify and contain ransomware. Ransomware attacks are not only financially costly but also time-consuming, thus causing further financial costs and disrupting operations. Again, according to the IBM report, working with the security forces can significantly reduce this time. With law enforcement involvement, the total time taken to identify and contain a ransomware breach was 11.4% or 33 days shorter, amounting to 273 days in total, as opposed to 306 days without their assistance. Furthermore, the mean time to contain a ransomware breach was 63 days, 23.8% shorter when law enforcement was engaged, compared to 80 days without their involvement. These findings indicate that collaborating with law enforcement can significantly reduce the cost and duration of a ransomware breach.
- After being identified, it can take up to 80 days to be completely contained.(IBM)
The most significant solution to reduce this time is incident response and recovery plans. Organizations that encountered a ransomware attack and had implemented automated response playbooks or workflows tailored for such incidents were able to contain the attacks in just 68 days. This was 16% faster compared to the average containment time of 80 days for organizations without automated response playbooks or workflows. (IBM)
- Paying for the ransomware does not create any cost savings in the end. (IBM)
Based on IBM’s report, organizations that opted to pay the ransom during a ransomware attack experienced only a slight variation in total cost, amounting to USD 5.06 million, compared to USD 5.17 million for those who did not pay. This cost difference was USD 110,000, equivalent to 2.2%. However, it’s important to note that this calculation excludes the actual cost of the ransom itself. Considering the typically high amounts demanded in ransomware attacks, organizations that paid the ransom likely incurred higher overall expenses than those that refused to pay.
- The percentage of ransomware attacks that resulted in the victim paying, fell to a record low of 34% (Coveware)
The good news is that in ransomware attacks, paying is becoming less and less; although non-payment obviously turns out to be the most logical way, sometimes desperation or a lack of cybersecurity awareness can lead to the opposite.
- About 1 in 3 attacks start with email phishing. (Coveware)
Ransomware is, of course, no exception, as phishing is at the forefront of every cyberattack; other attack vectors include RDP accesses and Software Vulnerability. Especially due to the Cl0p group and the MOVEit incident, the importance of Software Vulnerability is increasing this year, and it can be thought that it will increase in the future.
- With 45% of total ransomware attacks in the first half of 2023, almost half of the attacks belong to one group: LockBit. (SOCRadar)
LockBit group maintains its throne as the most active ransomware group since the 2nd half of 2022 with its constantly updated variants. Other ranks are followed by ALPHV BlackCat and Cl0p Ransomware, respectively.
- The most targeted industry is Professional, Scientific, and Technical Services (29%). (SOCRadar)
Professional, Scientific, and Technical Services can be at the top of the lists as it is a broad sectoral definition. However, the 2nd place Manufacturing has been targeted a high number alone, with 20%. Immediately after, the Healthcare, Education, and Information sectors occur, respectively.
- The US alone has been the target of up to 70% of ransomware attacks. (SOCRadar)
The fact that the US is both an economic giant and the threat actors are predominantly from Russia justifies this high figure. While the UK takes second place with 10%, Germany, France, and Canada are on the list with very close numbers. This again means that almost all of the targeted countries are Western-affiliated countries.
- Database leaks occur in ransomware blogs in as much as 34% of victim announcements. (SOCRadar)
In the first half of 2023, in addition to 1,461 victim announcements, 500 database leaks were registered in SOCRadar data. This number, which corresponds to around 30%, may indicate that the remaining victims have paid or that the ransom claim is false. Another possibility is that although the databases were not publicly leaked, they may have been sold to other threat actors.
Monthly Update: July 2023
Ransomware events for July started the 2nd half, causing completely different cases from the first half of 2023. The Cl0p group has dethroned the long-standing LockBit, by far ahead. Cl0p group made about 150 ransomware victim announcements in one month, with their collective victim listings up to +70 in one go.
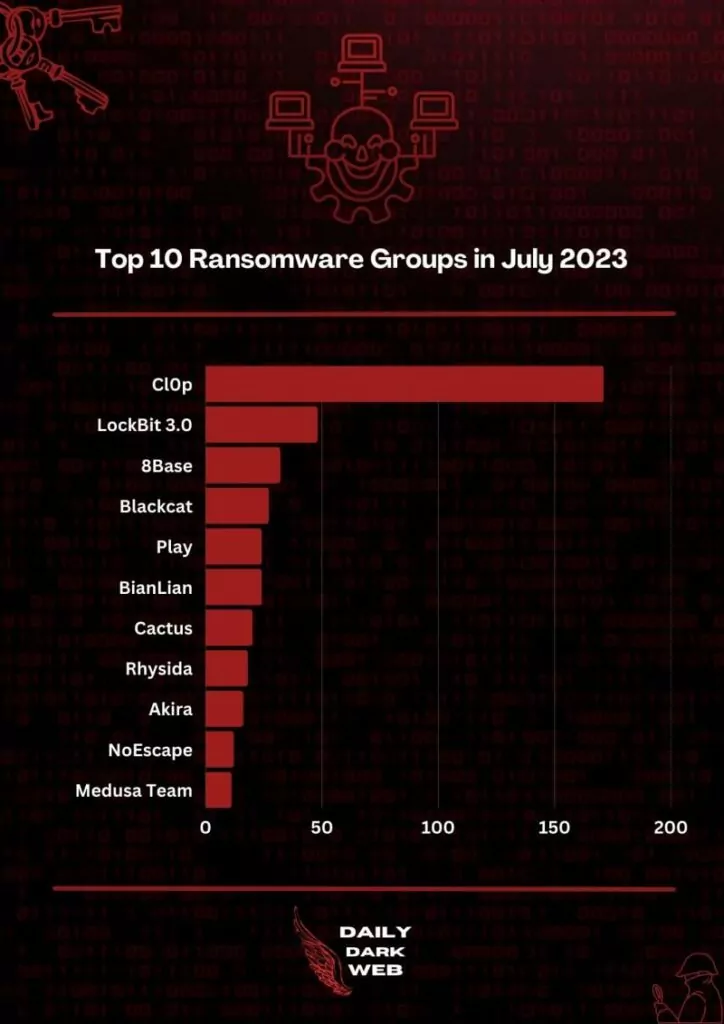 Figure 1. Top Ransomware Groups in July 2023. (DailyDarkWeb)
Figure 1. Top Ransomware Groups in July 2023. (DailyDarkWeb)
A total of 486 victim announcements were recorded on the SOCRadar platform. On the contrary to the first half of the year, Manufacturing ranked first as the most targeted industry this month. While the US is still the most targeted country, the targeting rate dropped from 70% to 63% this month.
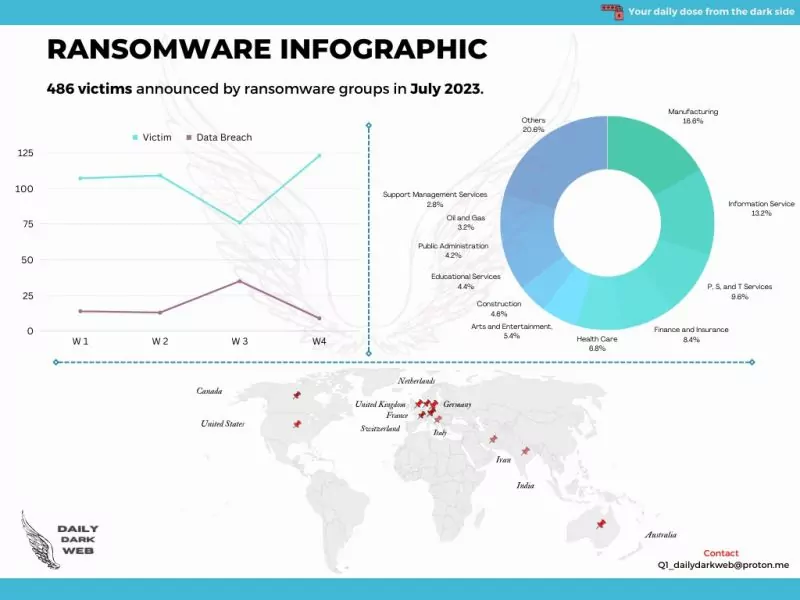 Figure 2. Total victim counts, targeted countries and industries in SOCRadar Platform. (DailyDarkWeb)
Figure 2. Total victim counts, targeted countries and industries in SOCRadar Platform. (DailyDarkWeb)
Trends and Patterns
Ransomware, a costly and adaptive threat, continues transforming alongside technological advancements. To grasp the evolving ransomware landscape in 2023, it’s crucial to identify key trends and patterns that shape its tactics. Reflecting on the trends of 2022 and looking ahead to 2023, here are six notable evolutions and three predicted trends by security researchers that shed light on the ever-changing nature of ransomware attacks.
Shifting Focus to Data Extortion: Ransomware groups have discovered success in extorting victims by posting stolen data online when their demands are not met. This tactic puts additional pressure on organizations to comply, as the potential exposure of sensitive information can lead to reputational damage and legal consequences.
Exploiting Data Monetization Opportunities: Stolen data is valuable to its rightful owners and to cyber criminals who can sell it to other malicious actors, creating an underground market. The rise of cryptocurrencies facilitates anonymous transactions, making it easier for ransomware groups to profit from their illicit activities.
Targeting Cloud Environment: With the growing adoption of cloud technology, ransomware groups are exploiting vulnerabilities in cloud resources. They use compromised instances for activities for launching ransomware attacks. Cloud environments’ decentralized and interconnected nature provides new attack vectors for cybercriminals.
Expanding Scope to Uncommon Platforms: Ransomware groups now target business-critical devices and platforms that lack readily available backups, increasing the potential impact of their attacks. Linux, Windows, macOS, FreeBSD, and non-standard processor architectures are all fair game, as demonstrated by the emergence of new ransomware families like RedAlert/N13V and LockBit.
Embracing Automation for Scaling Up: Ransomware groups leverage automation to streamline attacks, reducing costs and increasing operational efficiency. Automated tools enable attackers to propagate malware faster, target multiple platforms simultaneously, and evade detection by security systems. In addition, new ransomware strains have even increased encryption speeds enormously.
Leveraging Zero-Day Vulnerabilities: Adversaries take advantage of unknown software flaws or system vulnerabilities, enabling multiple attacks before patches or fixes are developed. This approach allows ransomware groups to exploit security gaps, making it challenging for organizations to defend against attacks effectively.
Looking ahead to 2023, three additional trends are predicted to shape the ransomware landscape:
Enhanced Functionality: Ransomware groups will continue to develop self-spreading capabilities, expanding their reach. Malware can autonomously infect vulnerable systems by incorporating worm-like features, enabling rapid proliferation and increased infection rates.
Driver Abuse: Vulnerable drivers, particularly in antivirus software, will be exploited by malicious actors. Attackers will focus on compromising device drivers to bypass security measures, rendering traditional defense mechanisms less effective and facilitating successful ransomware attacks.
Code Adoption: Ransomware groups will adopt code from other families, enhancing their capabilities and attracting more affiliates. This trend reflects the industrialization of ransomware, where malicious actors collaborate, share resources, and leverage the expertise of different groups to create more sophisticated and potent attacks.
Most Common TTPs of 2023
TTPs are also changing and varying every year in line with the trends. By examining the trends and insights from 2023, we can identify the top 5 TTPs commonly used by ransomware groups. These TTPs shed light on the evolving strategies employed by threat actors to maximize their impact and financial gains. Let’s delve into the details:
- Phishing Campaigns (T1566) Ransomware groups continue to rely on phishing campaigns to gain initial access to target networks. By sending deceptive emails or messages, they trick unsuspecting users into clicking on malicious links or downloading infected attachments. Vigilance and employee awareness training are crucial in mitigating the risks associated with these phishing attempts.
- Exploiting Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) (T1021.001), Ransomware groups exploit weak or misconfigured Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) connections to gain unauthorized access to systems. Once inside, they can move laterally across the network, escalating privileges and deploying ransomware payloads. Properly securing RDP by implementing strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and limiting access can reduce the attack surface significantly.
- Software Vulnerabilities (T1203) Exploiting software vulnerabilities remains a favored TTP among ransomware groups. They target unpatched or outdated software, utilizing known vulnerabilities to gain a foothold in the target environment. Timely software updates and regular vulnerability assessments are vital for minimizing the risk of successful ransomware attacks.
- Supply Chain Attacks (T1195) Ransomware groups increasingly target supply chains, compromising trusted third-party vendors or software providers to gain access to their client’s networks. By exploiting vulnerabilities in the software supply chain, threat actors can infiltrate multiple organizations through a single entry point. Strengthening supply chain security, including conducting due diligence on vendors and assessing their security practices, is essential for mitigating this risk.
- Living-off-the-Land Techniques (T1218) Ransomware groups often employ “living-off-the-land” techniques, utilizing legitimate tools and processes already within a compromised network to carry out malicious activities. This approach allows them to bypass traditional security defenses and remain undetected for extended periods. Monitoring for suspicious behavior, employing behavioral analysis, and implementing robust endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions can aid in detecting and stopping these stealthy attacks.
Summary
The prevalence of ransomware attacks in 2023 highlights the pressing need for organizations and individuals to prioritize robust cybersecurity measures. It is crucial to implement comprehensive security protocols, including regular software updates, strong password practices, network segmentation, and employee training on identifying phishing attempts and other common attack vectors. Additionally, organizations should consider investing in advanced threat detection and response systems to proactively identify and mitigate potential ransomware threats.
In conclusion, the alarming surge in ransomware attacks in 2023 emphasizes the critical importance of robust cybersecurity practices across organizations and individuals. By staying vigilant, implementing preventive measures, and fostering collaborative efforts, we can work towards mitigating the impact of ransomware and safeguarding our digital ecosystem.
How Can SOCRadar Help to Battle with Ransomware Threats?
SOCRadar offers comprehensive solutions to address the challenges posed by ransomware groups and their most common TTPs. Let’s explore how SOCRadar can help mitigate the risks associated with each technique:
Phishing Campaigns (T1566): SOCRadar provides robust email security capabilities that leverage machine learning algorithms and threat intelligence feeds. By using SOCRadar email analysis, SOC Analysts can analyze incoming emails, identify phishing attempts, and block malicious messages from reaching end users. Additionally, SOCRadar detects potentially fraudulent domains and websites that will enable threat actors to perform a wide range of attacks, such as wire transfer fraud, phishing, and scams against your organization and your customers.
Exploiting Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) (T1021.001): SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management module helps organizations identify and remediate weaknesses in their RDP implementations. It continuously monitors and scans RDP services, detecting misconfigurations or weak credentials. By alerting security teams to potential vulnerabilities, SOCRadar enables them to take proactive measures such as implementing strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and access restrictions to secure RDP connections effectively.
 SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence
SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence
Software Vulnerabilities (T1203): SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Management module is critical in mitigating the risk of software vulnerabilities. It actively scans the environment, identifying outdated or unpatched software components. The platform correlates vulnerability data with threat intelligence, providing security teams with prioritized remediation recommendations. SOCRadar helps organizations stay ahead of threat actors exploiting known vulnerabilities by ensuring timely software updates and patch management.
Supply Chain Attacks (T1195): SOCRadar’s supply chain security module assists organizations in proactively assessing the security posture of their third-party vendors and software providers. It performs due diligence checks, evaluates vendor security practices, and assesses potential risks. With this information, organizations can make informed decisions about engaging with vendors and ensure they maintain adequate security controls throughout the supply chain.
 SOCRadar Supply Chain Intelligence
SOCRadar Supply Chain Intelligence
Living-off-the-Land Techniques (T1218): SOCRadar’s advanced threat detection capabilities, including behavioral analysis and endpoint detection and response (EDR) integration, empower organizations to identify and stop living-off-the-land attacks. By continuously monitoring your external attack surface SOCRadar detects suspicious behavior and alerts security teams in real-time. This enables swift investigation and response, helping organizations minimize the dwell time of threat actors and prevent further damage. Moreover, you can retrieve TTPs of Threat Actor Groups and various IoCs from our campaigns page for further knowledge on this topic.
In summary, SOCRadar offers a comprehensive suite of tools and features to address the most common TTPs of 2023. By leveraging its threat intelligence, vulnerability management, supply chain security, and advanced threat detection capabilities, organizations can strengthen their security posture and effectively defend against evolving cyber threats.
The post Ransomware Chronicles: Unveiling the Monthly Trends in 2023 appeared first on SOCRadar® Cyber Intelligence Inc..
Article Link: Ransomware Chronicles: Unveiling the Monthly Trends in 2023
