Today, we’re proud to announce our Eclypsium Automata binary analysis system, which replicates the knowledge and tooling used by our expert human security research team. This blog post describes the reasons why Automata fills a crucial gap in defenses and how it works to detect previously unknown threats and zero-day vulnerabilities.
Threats Against IT Infrastructure
The threat landscape has changed. Threat actors turned their sights to lower-level components in our IT infrastructure supply chain. A few observations from recent years:
- Management software – Products that have privileged access to important parts of the IT environment are top targets for supply chain attacks, as evidenced by the incidents involving SolarWinds and Kaseya VSA incidents.
- Remote server management systems – Server vendors offer remote management technology that is a tempting target for attackers, as illustrated by implants targeting HPE iLO.
- Virtualization infrastructure such as VMware ESXi – This is business-critical infrastructure and can cause massive damage if compromised, as evidenced by the 10-day system outage that cost MGM casinos $100 million.
- Linux-based OS firmware – As seen by the recent Ivanti Connect Secure and CitrixBleed campaigns, multiple criminal and APT groups are targeting weaknesses in network infrastructure, especially VPNs, firewalls, and other edge devices that must be exposed to the internet to serve their function. IoT devices used in IT networks also often use Linux-based OS firmware that contains many open-source components, which leads us to the next point.
- Open-source software – This category has come under closer scrutiny recently with the xz backdoor, planted by a bad actor who spent two years as a maintainer in a project that affected nearly every Linux distribution.
- Drivers – Malicious or compromised drivers allow attackers to subvert security mechanisms and evade detection.
- UEFI malware – In the past several years, we’ve seen nearly a dozen different types of malware focused on subverting UEFI/BIOS. Contrary to popular belief, this malware can be delivered remotely, even through regular phishing attacks. Examples include MoonBounce, CosmicStrand, FinSpy, Trickboot, Black Lotus, and Glupteba.
These types of attacks used to be primarily the province of nation-states. That’s no longer the case as the well-funded ransomware ecosystem becomes more sophisticated. Just as Metasploit made exploits against Windows systems much easier two decades ago, today there are more examples available to make it easier to target components below the operating system.
An Expert Security Researcher That Never Sleeps
Attackers’ shift toward the lower layers of IT infrastructure has left organizations with a tremendous gap in their defenses—one that’s filled with Eclypsium Automata, the most sophisticated binary analysis system on the market. We’ve encoded Automata with the domain expertise of our expert security research team and orchestrated the same types of tooling that they use to reverse-engineer binaries.
Importantly, Eclypsium Automata runs 24/7 and analyzes 100% of new binaries in our customers’ environments, protecting against previously unknown threats, vulnerabilities, and misconfigurations. It uses multiple methods and ML models, and scales to handle millions of firmware and software binaries without requiring any action from the customer. We’re proud to offer this industry-leading capability to our customers.
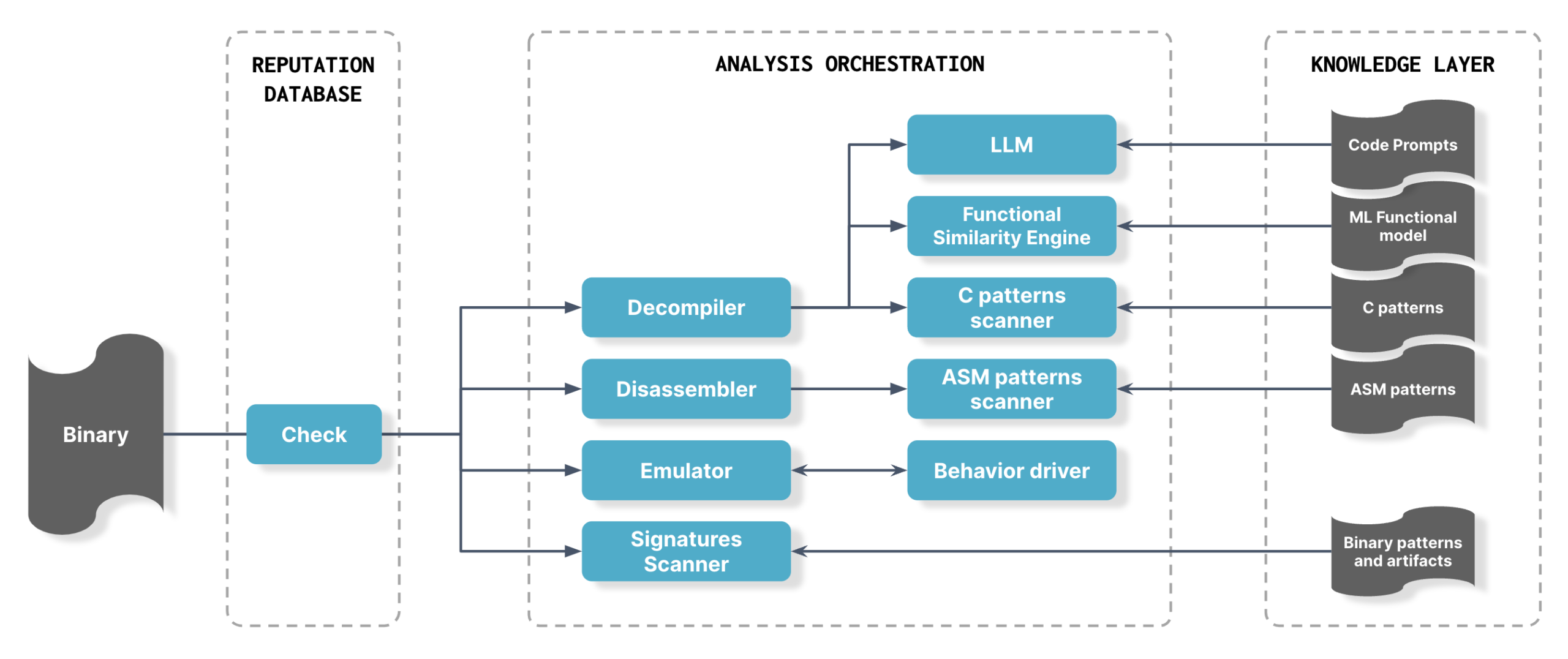
The system employs expert techniques used by human researchers when reverse engineering malware and probing binaries for weaknesses:
- Extraction – The Eclypsium sensor extracts binaries from the system and sends them to the customer tenant for analysis. This scheduled process is customizable.
- Unpacking and integrity check – The binary is decompressed, unpacked, and checked for integrity against the Eclypsium reputation database comprising 12M+ components.
- Signature scanning – If the binary is new (does not match anything in our reputation database), Automata engages and uses YARA rules to check for strings and other known implant artifacts. This is highly effective for known threats but does not protect against new threats, which is why Automata goes further with advanced AI-assisted analysis.
- Disassembly – Automata disassembles the binary so that the machine code can be scanned for patterns.
- Decompilation – Automata decompiles the binary and applies proprietary static code analysis techniques and LLM technology to look for zero-day vulnerabilities and unknown implants in the code. Notably, Automata uses a functional similarity engine to determine the function of unknown binaries. Machine learning models classify the functionality of files, then the functions are analyzed in context to identify malicious behavior—for example, binaries writing to an NTFS file system or hooking to APIs.
- Emulation – Automata identifies new examples of malicious behavior by dynamically analyzing the code and emulating its behavior.
The end result is that Automata can detect previously unknown malware, malicious behavior, and vulnerabilities. Importantly, Eclypsium Automata encodes the collective domain knowledge and expertise of the Eclypsium research team, which over the last 15 years (our founders started at Intel doing both offensive and defensive research) has discovered numerous backdoors and vulnerabilities. In 2023, for example, Eclypsium researchers uncovered a backdoor in Gigabyte firmware and multiple vulnerabilities in AMI MegaRAC BMC software. But, unlike our human researchers, Automata does not need to eat or sleep, and can tirelessly analyze millions of new binaries each day. Our research team provides the knowledge layer to Automata, specifically guidance in the form of new prompts, rules, and models.
As a demonstration of how Automata can automatically discover new (zero-day) vulnerabilities, the system has already uncovered several vulnerabilities in UEFI implementations from major vendors. We are working with these vendors on the disclosure process and will be talking about them as soon as we are able to do so responsibly. Stay tuned!
Eclypsium Automata takes advantage of the computing power of the cloud and uses a single tenant per customer, but can also support self-hosted deployments. This model offers data privacy as well as flexibility where on-premises hosting is a requirement.
Growing Threats Require More Sophisticated Defenses
Below-the-surface threats continue to grow. Both nation-state actors and criminal groups are targeting weaknesses in the IT infrastructure supply chain with tampered components, backdoors, and implants. Without continuous monitoring of your IT infrastructure for vulnerabilities and threats, you are accepting an enormous amount of risk.
It’s time for organizations to start paying attention to the supply chain for their IT infrastructure. Eclypsium’s Automata automated binary analysis system provides a much-needed added layer of defense to your organization. Think of it like part of an immune system for your IT infrastructure, learning about threats and helping your organization to mount the necessary defenses. Automata is one of the ways that Eclypsium is pioneering the space of digital supply chain security. We have built other key parts of a digital supply chain solution, such as the world’s largest reputation database for checking the integrity of components and the only solution that can provide continuous integrity checking of components in production assets.
To learn more about Automata, including how it works and the thinking behind the technology, please register for our webinar on April 30.
The post Multiplying Security Research: How Eclypsium Automates Binary Analysis at Scale appeared first on Eclypsium | Supply Chain Security for the Modern Enterprise.