The digital landscape is continually evolving, marked by the constant emergence of new security loopholes that serve as potential gateways for attackers to infiltrate our most vital assets. This highlights the critical need to strengthen the security of both personal and business environments. In this blog post, we will shed light on the latest critical vulnerabilities, impacting GitLab, Apple’s Magic Keyboard firmware, and Juniper Networks’ Junos OS.
GitLab Has Patched Critical Vulnerabilities, Including a Zero-Click Leading to Account Takeover (CVE-2023-7028, CVE-2023-5356)
GitLab has recently rolled out security updates for both Community Edition (CE) and Enterprise Edition (EE). These updates aim to address several vulnerabilities, with the most severe among them being a zero-click exploit.
CVE-2023-7028 (CVSS v3: 10.0, Critical):
CVE-2023-7028 stems from an issue in the email verification process, allowing an attacker to deliver password reset requests to an unverified email address. Successful exploitation does not require user interaction, and could lead to account takeover; the vulnerability carries the maximum severity score of 10.0, representing the urgency of mitigating this potential threat.
 SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence: CVE-2023-7028
SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence: CVE-2023-7028
Takeover of a GitLab account poses significant risks for an organization. Attackers could compromise sensitive data and API keys; furthermore, they could inject malicious code into repositories. Importantly, even if an attacker successfully changes the password by exploiting the vulnerability, the use of Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) can prevent their attempts to log in to the GitLab account.
Currently, there are no reports of exploitation related to the vulnerability. GitLab reports that the critical security vulnerability affects self-managed instances that are running the following versions:
- 16.1 prior to 16.1.6
- 16.2 prior to 16.2.9
- 16.3 prior to 16.3.7
- 16.4 prior to 16.4.5
- 16.5 prior to 16.5.6
- 16.6 prior to 16.6.4
- 16.7 prior to 16.7.2
GitLab recommends taking the following steps to identify if you have been compromised:
- Check gitlab-rails/production_json.log for HTTP requests to the /users/password path with params.value.email consisting of a JSON array with multiple email addresses.
- Check gitlab-rails/audit_json.log for entries with meta.caller.id of PasswordsController#create and target_details consisting of a JSON array with multiple email addresses.
CVE-2023-5356 (CVSS v3: 9.6, Critical):
Stemming from incorrect authorization checks, the second critical vulnerability patched by GitLab is tracked as CVE-2023-5356, which could allow an attacker to misuse Slack and Mattermost integrations integrations for the execution of slash commands. Slash commands serve as a convenient method for utilizing and integrating applications within the workspace, and this vulnerability permits such actions to be executed as another user.
 SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence: CVE-2023-5356
SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence: CVE-2023-5356
GitLab CE/EE is susceptible to CVE-2023-5356 across various versions, including those from 8.13 before 16.5.6, 16.6 before 16.6.4, and 16.7 before 16.7.2. Organizations operating GitLab instances within these version ranges should take immediate action to address this security concern.
Additional Vulnerabilities in the GitLab Security Update
In the same security update, GitLab addressed additional vulnerabilities, namely CVE-2023-4812 (CVSS v3: 7.6, High),CVE-2023-6955 (CVSS v3: 6.6, Medium) andCVE-2023-2030 (CVSS v3: 3.5, Low).
Due to the high-severity vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2023-4812, an attacker can bypass the required CODEOWNERS approval by modifying an already approved merge request.
The issue affects GitLab across various versions, including those from 15.3 before 16.5.5, 16.6 before 16.6.4, and 16.7 before 16.7.2. Organizations utilizing GitLab instances within these version ranges are urged to take immediate action to mitigate the potential risks associated with this security vulnerability.
CVE-2023-6955 allows an attacker to create a workspace in one group associated with an agent from another group, essentially leading to the creation of workspaces under different root namespaces, due to an improper access control.
On the other hand, CVE-2023-2030 highlights a low-severity vulnerability where commit signature validation ignores headers after the signature. Exploiting this vulnerability could potentially allow an attacker to modify the metadata of signed commits.
How to Secure Your GitLab; Apply the Updates and Enable 2FA
GitLab has addressed these security vulnerabilities in versions 16.5.6, 16.6.4, and 16.7.2, the fix has also been backported to versions 16.1.6, 16.2.9, 16.3.7, and 16.4.5. To strengthen security and mitigate potential threats, it is strongly recommended to promptly upgrade your GitLab instances to the patched versions.
Additionally, users, especially those with elevated privileges, are advised to enable 2FA. For detailed information, refer to the security release on GitLab.
Apple Has Fixed a Bluetooth Keyboard Injection Vulnerability in Magic Keyboard Firmware Update (CVE-2024-0230)
Apple has released a Magic Keyboard firmware update to fix a recently disclosed vulnerability related to Bluetooth keyboard injection. The vulnerability, identified as CVE-2024-0230, is currently awaiting assignment of a severity score.
According to Apple’s advisory, an attacker with physical access to the equipment could potentially extract its Bluetooth pairing key and monitor Bluetooth traffic. The company has effectively addressed this vulnerability by implementing enhanced checks in version 2.0.6.
How Does the Vulnerability Work?
The vulnerability, discovered by Marc Newlin of SkySafe, reveals a potential threat where a nearby attacker can connect to a vulnerable device through unauthenticated Bluetooth and inject keystrokes for malicious purposes. These actions include installing apps, executing arbitrary commands, and forwarding messages.
Newlin explained that such vulnerabilities work by deceiving the Bluetooth host state-machine into pairing with a fraudulent keyboard without user confirmation. The inherent unauthenticated pairing mechanism, as defined in the Bluetooth specification, becomes susceptible to exploitation due to implementation-specific bugs.
Physical access to the device poses a challenging exploitation prerequisite and Apple has not reported any instances of exploitation in the wild. On the other hand, the attack does not demand specialized hardware and can be executed from a Linux computer employing a standard Bluetooth adapter. Newlin also highlighted that Lockdown Mode does not prevent attacks from exploiting this vulnerability.
Unpatched devices are vulnerable under specific conditions. Android devices are susceptible whenever Bluetooth is enabled. For Linux/BlueZ, vulnerability arises when Bluetooth is in a discoverable/connectable state. In the case of iOS and macOS, the risk is present when Bluetooth is enabled, and a Magic Keyboard has been paired with the respective phone or computer.
Critical Vulnerability in Juniper Could Lead to DoS, RCE, and Enable Root Privileges (CVE-2024-21591)
Juniper Networks has released security updates to fix a critical vulnerability affecting Junos OS in SRX Series firewalls and EX Series switches.
Tracked as CVE-2024-21591 (CVSS v3: 9.8), the vulnerability resides in the J-Web configuration interfaces of these devices and could be exploited by unauthenticated, network-based threat actors. It is attributed to the use of an insecure function allowing attackers to overwrite arbitrary memory.
Successful exploitation of this vulnerability could lead to Denial-of-Service (DoS), Remote Code Execution (RCE), and the acquisition of root privileges on the compromised device.
Juniper Networks reports no evidence of exploitation in the wild, but a Shodan search reveals over 9,000 accessible J-Web interfaces on the internet, underscoring the expansive range of potentially vulnerable devices.
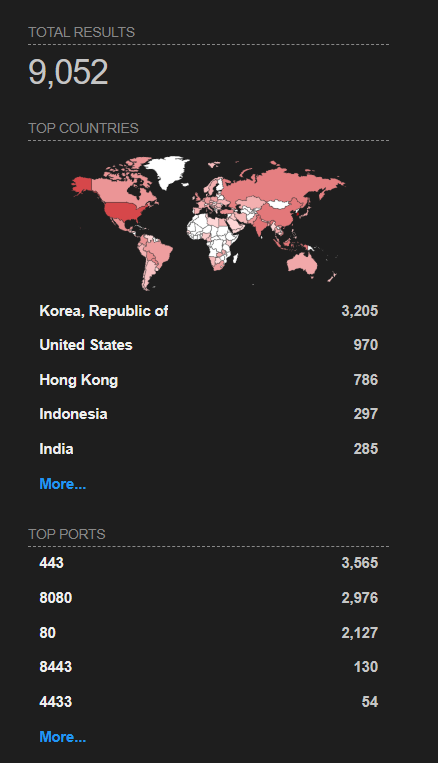 Shodan search results for exposed J-Web interfaces
Shodan search results for exposed J-Web interfaces
Which Products/Versions Are Affected?
The vulnerability affects Juniper Networks Junos OS SRX Series and EX Series in various versions:
- Junos OS versions earlier than 20.4R3-S9
- Junos OS 21.2 versions earlier than 21.2R3-S7
- Junos OS 21.3 versions earlier than 21.3R3-S5
- Junos OS 21.4 versions earlier than 21.4R3-S5
- Junos OS 22.1 versions earlier than 22.1R3-S4
- Junos OS 22.2 versions earlier than 22.2R3-S3
- Junos OS 22.3 versions earlier than 22.3R3-S2
- Junos OS 22.4 versions earlier than 22.4R2-S2, 22.4R3
It is strongly advised to apply the security updates to prevent potential exploitation. If immediate updating is not feasible, disabling J-Web or restricting access to trusted hosts is recommended as a workaround.
Proactive Vulnerability Management with SOCRadar
SOCRadar provides tools for quickly identifying, assessing, and mitigating vulnerabilities, as well as insights into potential threats to help you stay on top of the threat landscape.
Utilizing SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module, you can easily monitor potential exposure points in your digital infrastructure. ASM enables organizations to proactively identify and mitigate potential threats by providing real-time insights into your attack surface and emerging vulnerabilities.
 SOCRadar Attack Surface Management
SOCRadar Attack Surface Management
Furthermore, SOCRadar provides comprehensive Vulnerability Intelligence, delivering you the most recent updates on known vulnerabilities and emerging hacker trends.
SOCRadar’s solutions provide organizations with the critical information they need to stay ahead of potential threats and gather insights to quickly respond to threats, effectively assisting their vulnerability management strategies.
Sign up for a free edition to experience the full capabilities of SOCRadar XTI.
 SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence
SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence
The post Latest Critical Vulnerabilities Affecting GitLab, Apple’s Magic Keyboard, and Juniper Networks’ Junos OS appeared first on SOCRadar® Cyber Intelligence Inc..
Article Link: Latest Critical Vulnerabilities Affecting GitLab, Apple's Magic Keyboard, and Juniper Networks’ Junos OS
