Reverse Engineering New Variant of Ransomware seen in 2021

Introduction
Babuk Ransom is the newly discovered ransomware that targets enterprises as the operation called Big Game Hunting. Babuk threat actors first and the foremost seen in 2021 as being lurking as part of double extortion groups. In this blog i will be revering latest sample of Babuk ransom.
The sample analyzed in this report has hash as:
18e299d4331ccff805275b21f33be0a3bd3d1d9ce72a79ba78d2f32dd657bfbb .
Analysis
Static Analysis (Basic)
 Signature Overview.
Signature Overview. Information Gathering using PE Studio on Babuk Ransom.
Information Gathering using PE Studio on Babuk Ransom.Static Analysis (Advanced)
Starting off with exports in Babuk( babyk ) ransom which is neither protected nor obfuscated payload of 8096 bytes targeting 32-bit systems.
 export in Babyk ransom.
export in Babyk ransom.Here is the disassembly call graph of Babuk ransom.
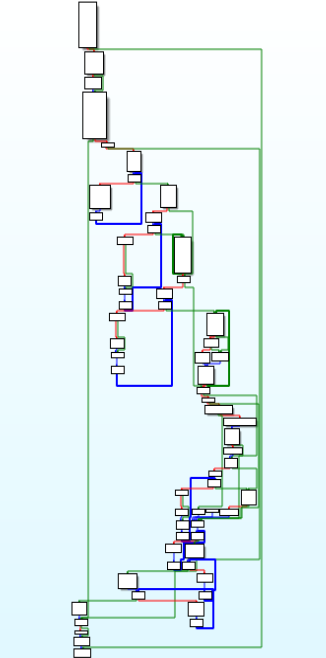 Call Graph of Babyk Ransom.
Call Graph of Babyk Ransom.Firstly in the babyk ransom heap information is being gathered in start function.
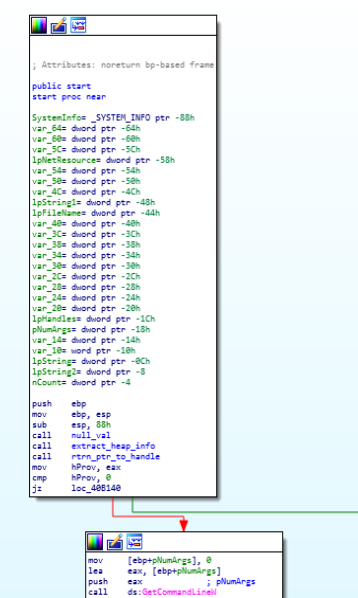 heap information gathering in start (entrypoint) function.
heap information gathering in start (entrypoint) function.then after that command line string is being retrieved using GetCommandLineW and soon after that the string fetched are being parsed using the CommandLineToArgvW function and after that the Shutdown level is set to zero so that the user cannot be able to shutdown the system and warning is being shown to user that malware process can’t be stopped which is quiet often not being seen in the Ransomware as due to that feature in Babyk ransom user had to manually shutdown the system.
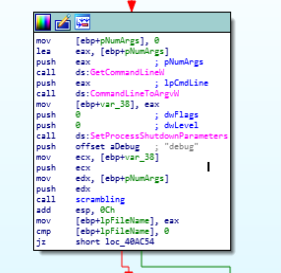 CmdLine args ops and Shutdown process halting.
CmdLine args ops and Shutdown process halting.Next up after saving the public key on disk calling function “save_pub_key_on_disk” , services operations are being performed using “service_ops” function, following up on that the system information is being recorded calling “record_sys_activities” .

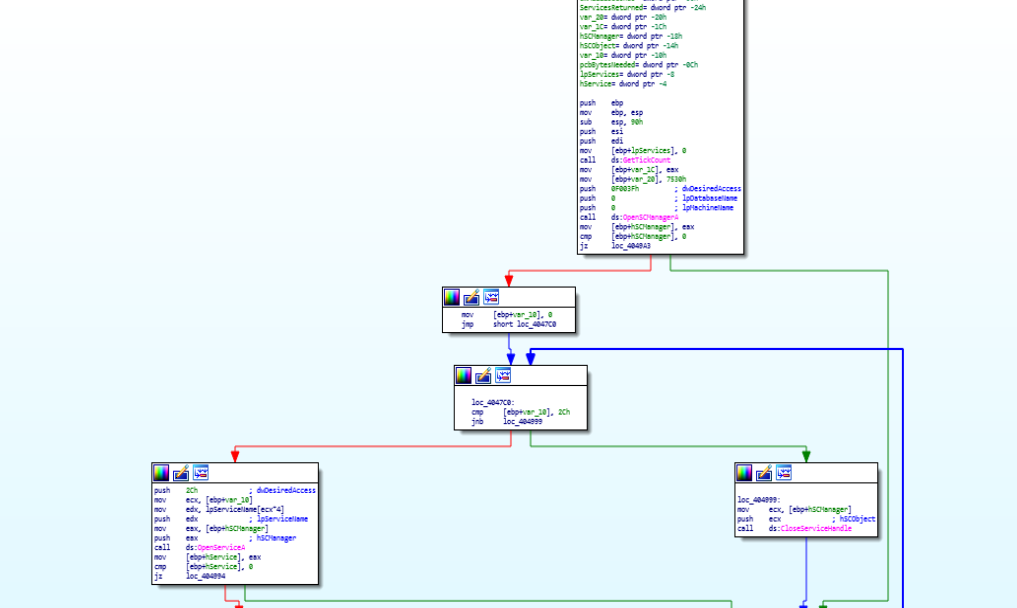 service_ops function disassembly call graph.
service_ops function disassembly call graph.And then recycle bin is being freed up by calling “SHEmptyRecycleBinA” function. Then the information on system is being gathered using “GetSystemInfo“ and then the heap allocation and access operations on victim system are being performed using “heap_alloc” & “create_access”.
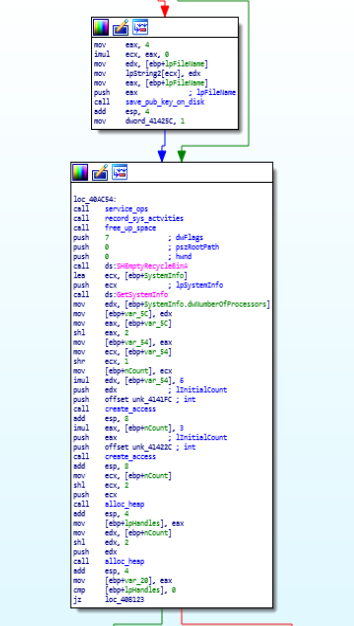 calling of service_ops function and freeing up space in recycle bin.
calling of service_ops function and freeing up space in recycle bin.As we move further in the start function , firstly the modification of arguments is being done then using the “CreateThread” function thread is being created.
 further reversed code of entry ( start ) function of babyk ransom.
further reversed code of entry ( start ) function of babyk ransom.Then the scrambling is being done on three variables a1, a2 and a3 by calling “scrambling” function. In this function mainly the modification of values is being done.

 code and call graph of scrambling function.
code and call graph of scrambling function.As we move further in start function, check for heap allocation is being done using “alloc_heap” and then check for admin privileges is being done calling “check_for_admin_prv “ function.
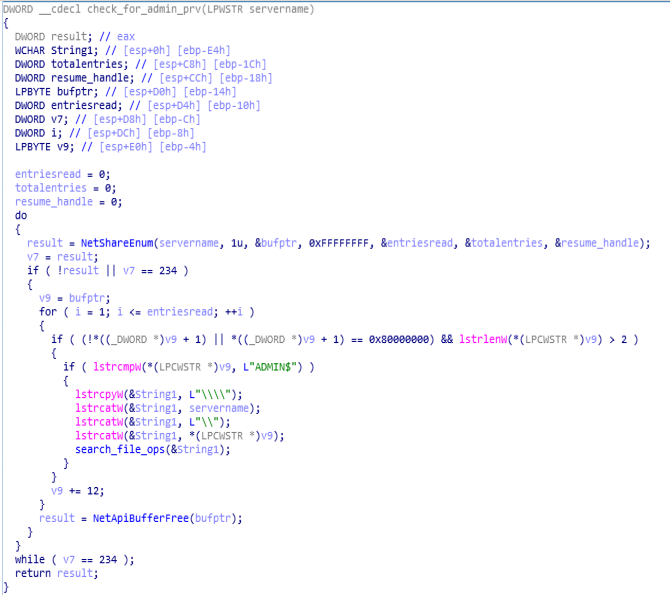
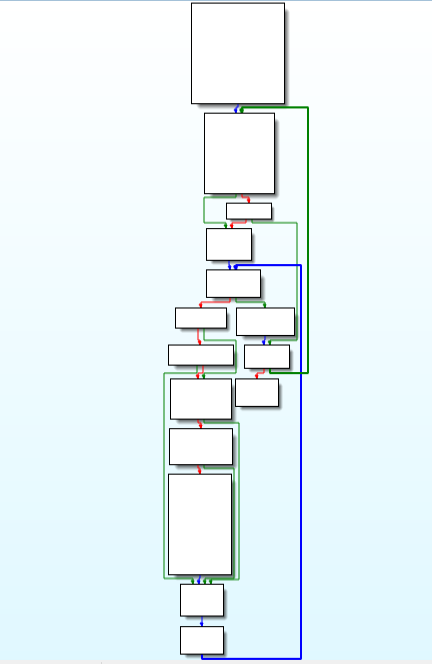 code and call graph of check_for_admin_prv function.
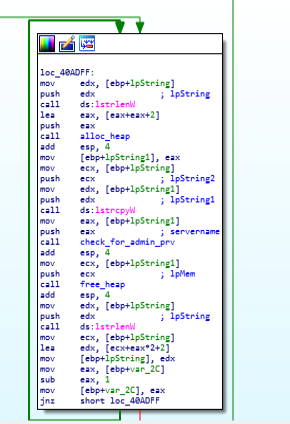
code and call graph of check_for_admin_prv function.Here is the disassembly call graph view of start function during moving to location “loc_40ADFF”.
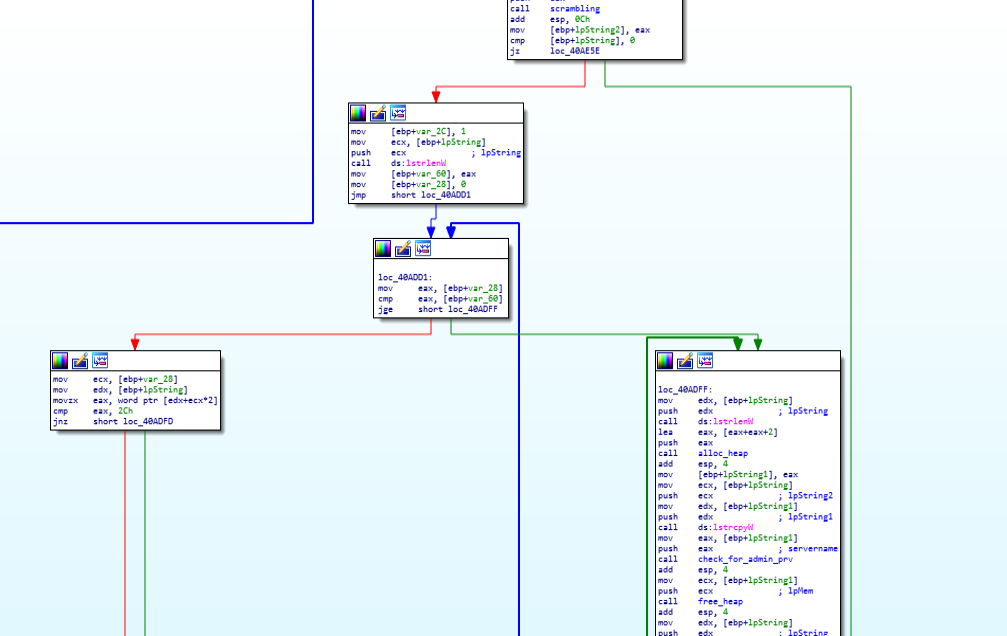 Disassembly view of start function during calling free_heap function.
Disassembly view of start function during calling free_heap function.then afterwards the drive information on network is being fetched by making call to “drive_info_fetch_on_netwrk” function.
 reversed code of start function where the drive_info_fetch_on_netwrk is being called.
reversed code of start function where the drive_info_fetch_on_netwrk is being called.
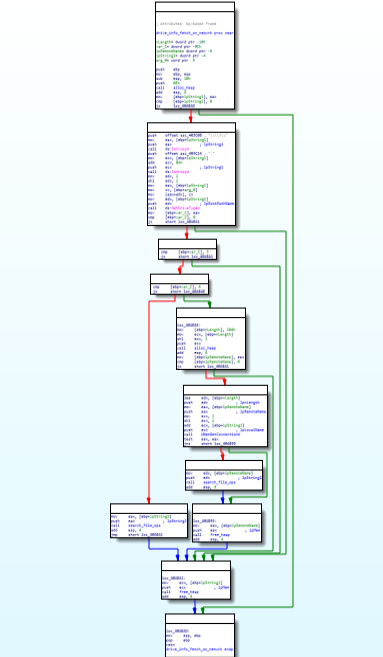 code and disassembly call graph of drive_info_fetch_on_netwrk function.
code and disassembly call graph of drive_info_fetch_on_netwrk function.Then after that by syncing the access and setting up mutex operations.
 disassembly call graph of start function during creating mutex.
disassembly call graph of start function during creating mutex.then the enumeration of resources on network is being done using “enum_netrk_resrcs” function which have to be encrypted.
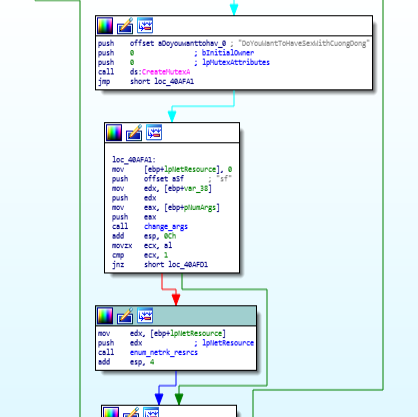 Disassembly view of start function during setting up enum_netwk_resrcs function.
Disassembly view of start function during setting up enum_netwk_resrcs function.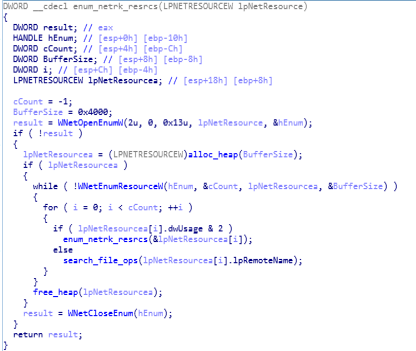 reversed code of enum_netwk_resrcs function.
reversed code of enum_netwk_resrcs function.in the end of start function, freeing up of victim system memory is being done and also the handle of cryptographic service provider (CSP) and a key container is being released which is being created in the starting of the start function calling “rtrn_ptr_to_handle”.
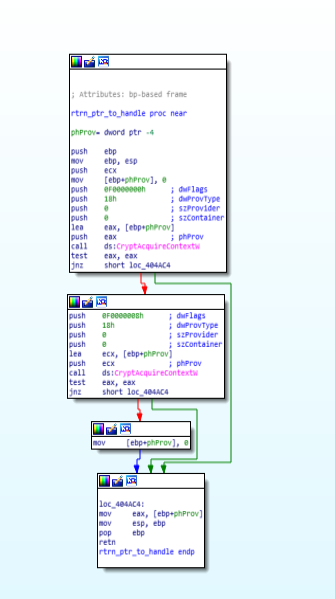
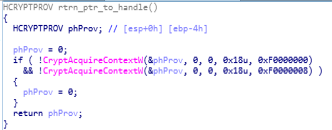 disassembly call graph & code of rtrn_ptr_to_handle function.
disassembly call graph & code of rtrn_ptr_to_handle function. calling function that release CSP and a key container.
calling function that release CSP and a key container.In this Babuk ransom sample , algo. used for protecting encryption keys is ChaCha.

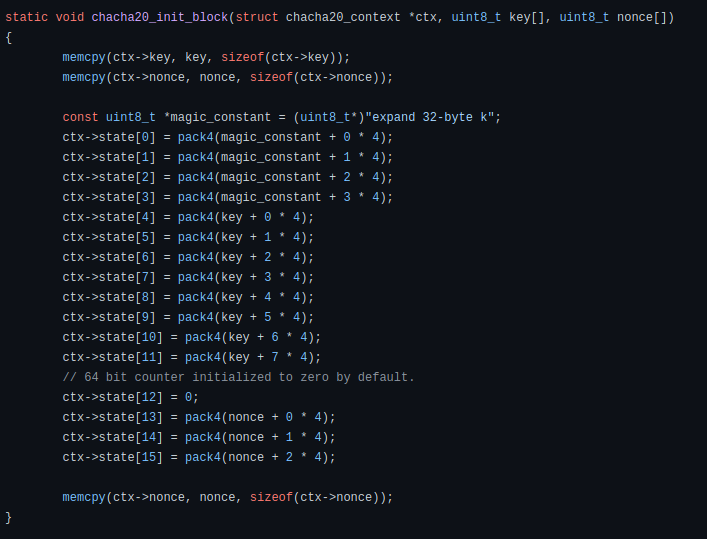 In left: code in sample implemented with ChaCha algo. for encryption key . In right: is the code from github.
In left: code in sample implemented with ChaCha algo. for encryption key . In right: is the code from github.Dynamic Analysis (Basic)
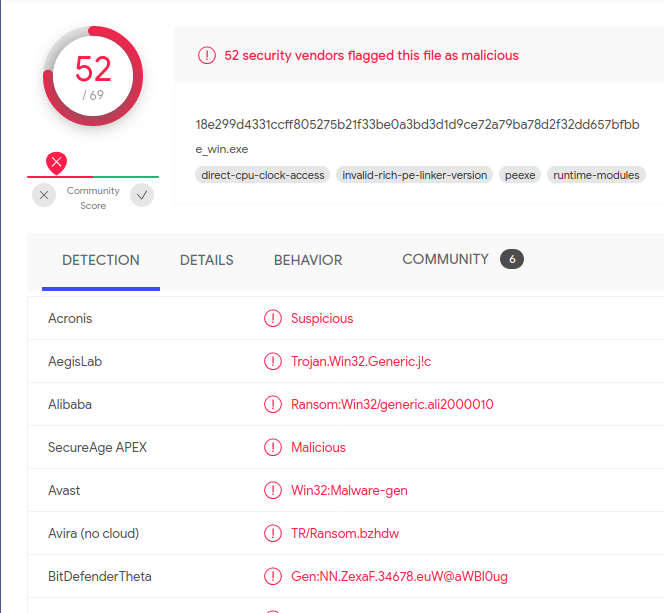 VirusTotal Detection of babuk ransom.
VirusTotal Detection of babuk ransom.Dynamic Analysis (Advanced)
Setting up few breakpoints for carrying out dynamic analysis.
:- extract_heap_info() ;
:- rtrn_ptr_to_handle();
:- save_pub_key_on_disk();
:- service_ops();
:- record_sys_activities();
:- CreateThread();
:- scrambling();
:- check_for_admin_prv();
:- search_file_ops()
:- drive_info_fetch_on_netwk()
:- enum_netwk_resrcs()
:- drive_ops()
:- access_ops()
:- free_up_space()
:- free_heap()
:- CryptReleaseContext() .
On debugging execution, debugger hits at our first breakpoint extract_heap_info() which extracts heap information.
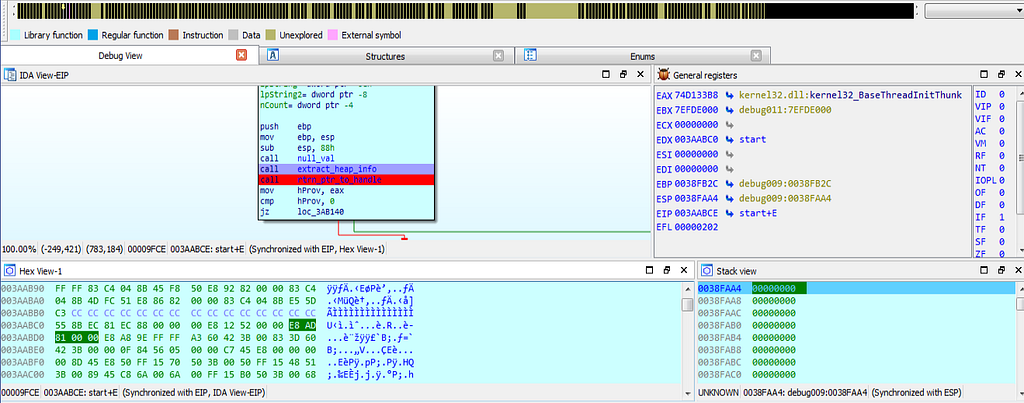 dbg hitting at the first breakpoint.
dbg hitting at the first breakpoint.Soon after that another breakpoint at “rtrn_ptr_to_handle()” is being hit where the using the Crypto APIs handle to CSP and key container is being started.
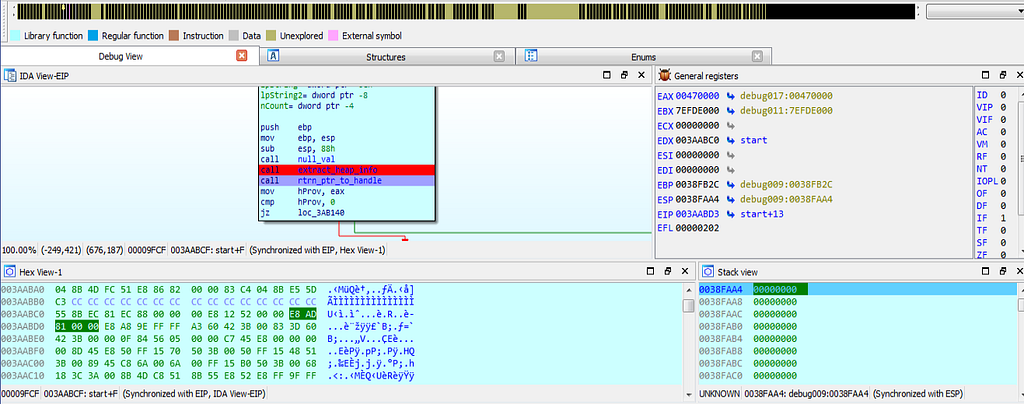 dbg hitting at the rtrn_ptr_to_handle().
dbg hitting at the rtrn_ptr_to_handle().As the debugging continues, debugger hits at the “scrambling” function which scramble up the args passed to scrambling function.
 dbg hits at scrambling function.
dbg hits at scrambling function.Next up the debugger hits at the “service_ops” function where the operations related to starting and stopping services is being carried out.
 dbg hits at service_ops function.
dbg hits at service_ops function.Then after that , debugger hits at the “OpenSCManagerA” for making connection with the SCManager and opening specified SCManager db.
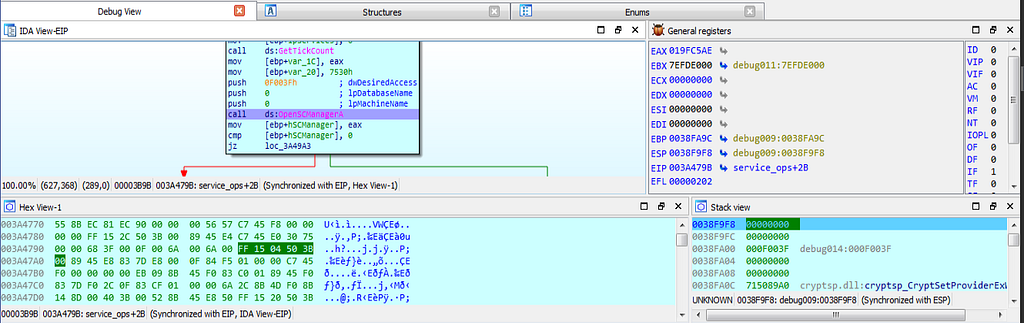 dbg hits at OpenSCManagerA function.
dbg hits at OpenSCManagerA function.Then after that debugger again hits at the “record_sys_activities” function.
 dbg hits at record_sys_activities.
dbg hits at record_sys_activities.After that exception is being raised during debugging.
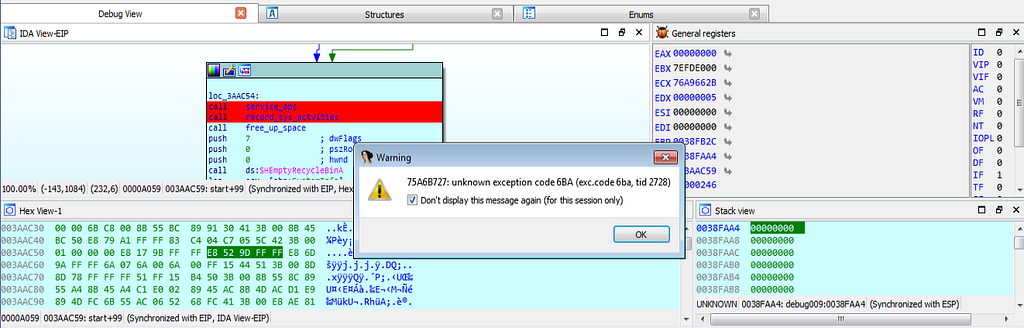 dbg hitting at exception.
dbg hitting at exception.and the debugger stops at 75A6B727 location.
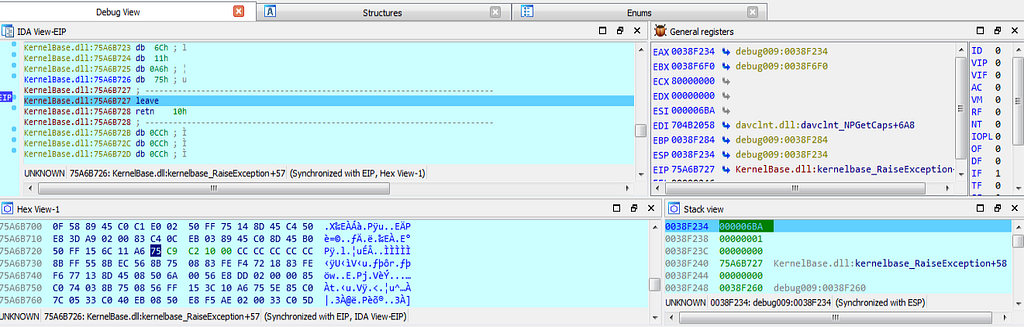 dbg hits at the 75A6B727 location.
dbg hits at the 75A6B727 location.As we move further in debugging “create_access” function is being hit. Where the access is being created for further triage of victim system.
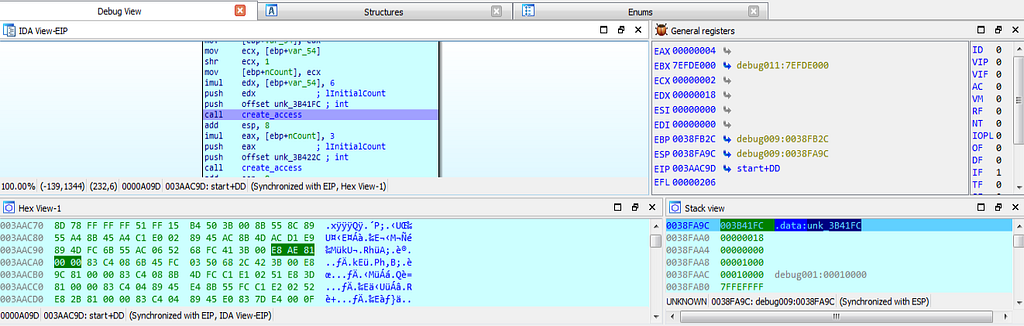 dbg hits at the create_access function.
dbg hits at the create_access function.As the debugging continues, “alloc_heap” is being hit during debugging, by which the allocation of heap happens.
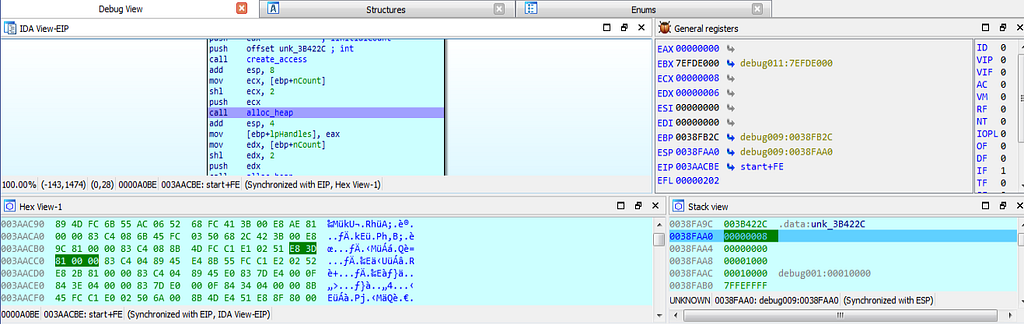 dbg hits at the alloc_heap function.
dbg hits at the alloc_heap function.Now, after hitting at the “alloc_heap” debugger get hits at the CreateThread function by which thread is being created.
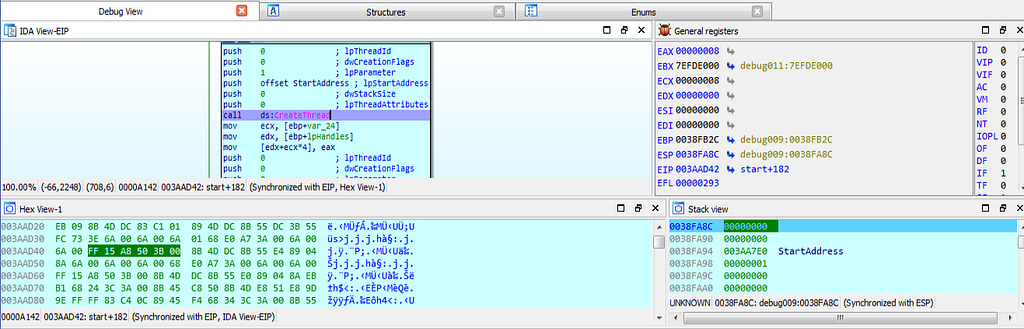 dbg hits at the CreateThread function.
dbg hits at the CreateThread function.Now the further debugging during dynamic analysis “scrambling” function is again hit by debugger.
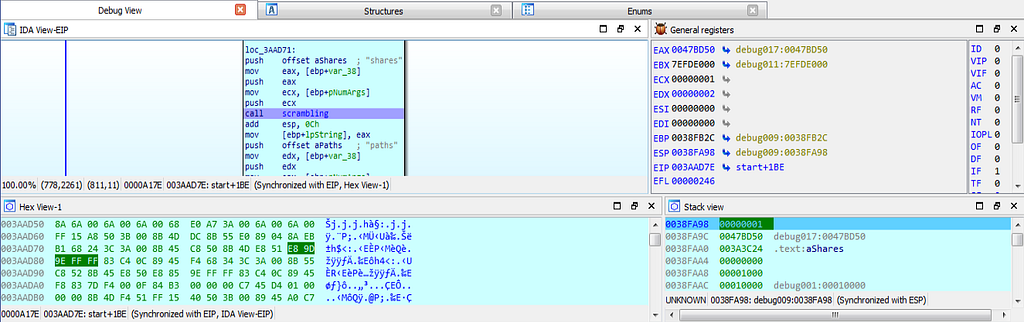 dbg hits at the scrambling scrambling function.
dbg hits at the scrambling scrambling function.Then the debugger gets hit at the “OpenMutexA” by which the handles to differ mutex objects are being handled.
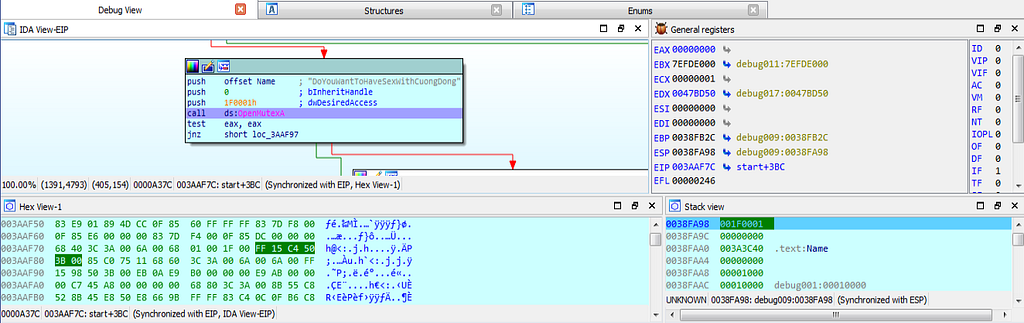 dbg hits at the OpenMutexA function.
dbg hits at the OpenMutexA function.As debugging continues, debugger hits at the function “drive_info_fetch_on_netwrk” which handles fetching of drive information over network.
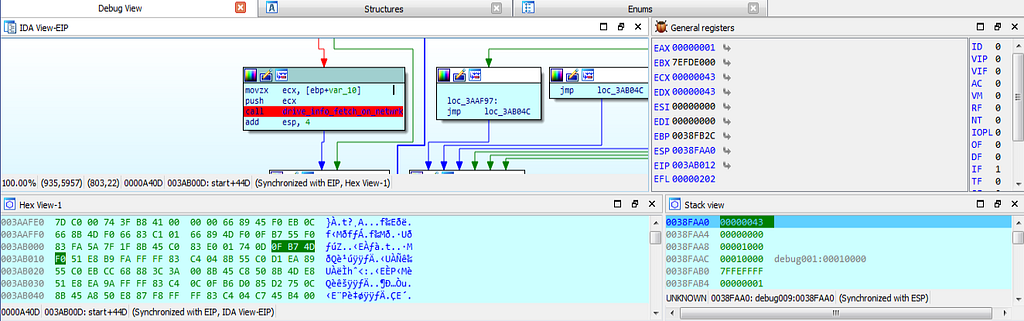
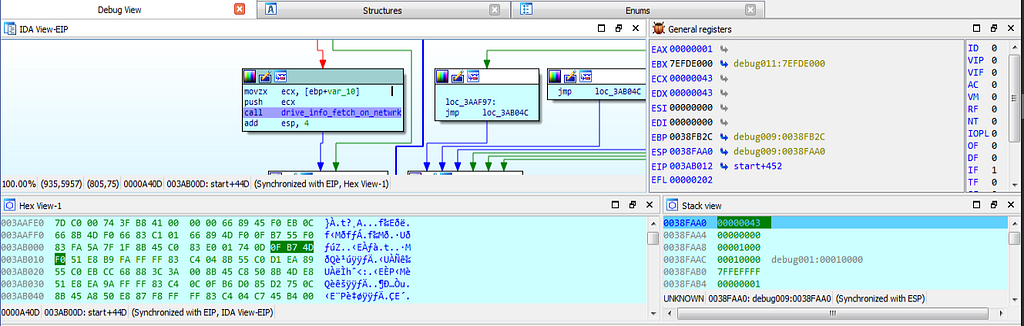 dbg hits at the drive_info_fetch_on_netwrk function.
dbg hits at the drive_info_fetch_on_netwrk function.Lastly debugger hits at the last breakpoint at location 76EE01C4.
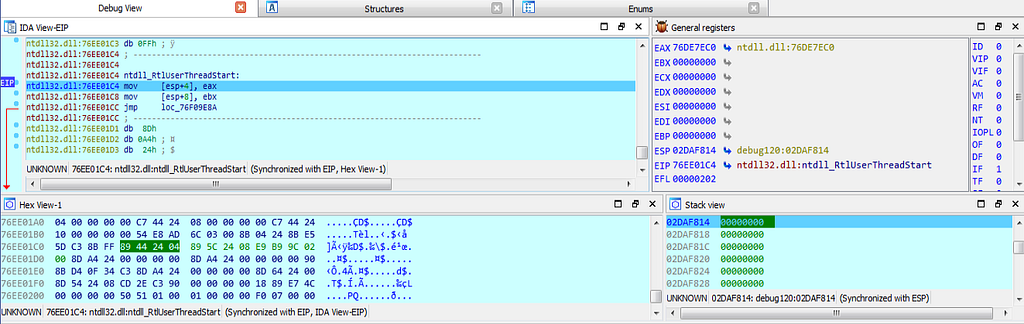 dbg hits at the this 76EE01C4 location at the end.
dbg hits at the this 76EE01C4 location at the end.Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) & Detection
Att&ck IDs
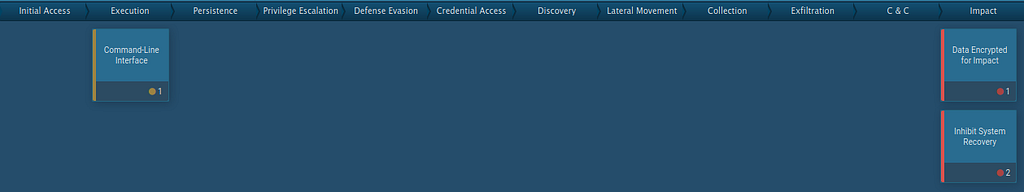 Att&ck Matrix from Any.Run Sandbox.
Att&ck Matrix from Any.Run Sandbox.Att&ck Techniques (Static TTPs)
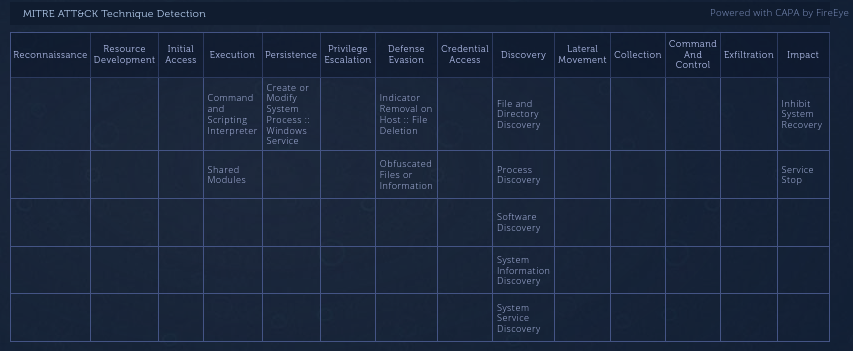 Mitre Att&ck Techniques Projected by CAPA(FireEye).
Mitre Att&ck Techniques Projected by CAPA(FireEye).Sample from Report
MD5 16c7212928b23a170cebb12935a933fa
SHA1 5d316698dfe20b8fcdc881dbf68632b13af11d0f
SHA256 18e299d4331ccff805275b21f33be0a3bd3d1d9ce72a79ba78d2f32dd657bfbb
YARA Signature
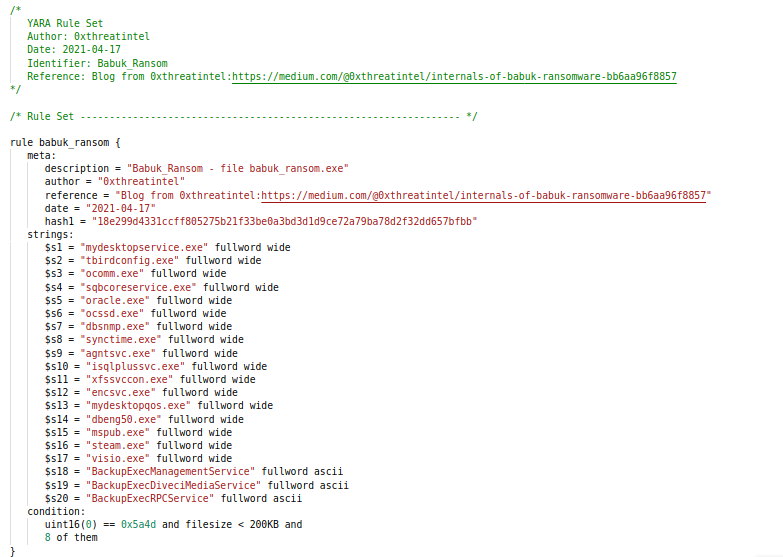 Yara Signature for detection of Babuk Ransom from Report.
Yara Signature for detection of Babuk Ransom from Report.References
Samples from Abuse.ch : https://bazaar.abuse.ch/browse/tag/Babuk/
Blogs from Community:
https://www.mcafee.com/blogs/other-blogs/mcafee-labs/babuk-ransomware/
Babuk Locker is the first new enterprise ransomware of 2021
Thanks for reading.
Article Link: https://0xthreatintel.medium.com/internals-of-babuk-ransomware-bb6aa96f8857?source=rss-a15183055fd6------2