Recently, there has been a high distribution rate of malware using abnormal certificates.
Malware often disguise themselves with normal certificates. However, in this case, the malware entered the certificate information randomly, with the Subject Name and Issuer Name fields having unusually long strings.
As a result, the certificate information is not visible in Windows operating systems, and a specific tool or infrastructure is required to inspect the structure of these certificates.
Of course, these certificates fail in signature verification since they are incorrect, and they cannot function as signatures in any way. However, when examining the signature strings, you can see that they include Arabic, Japanese, and other non-English languages, along with special characters and punctuation marks. This diverges from the typical English character string structures. Furthermore, similar samples of this kind have been consistently distributed with slight structural variations for over two months, suggesting a specific intent behind this action.
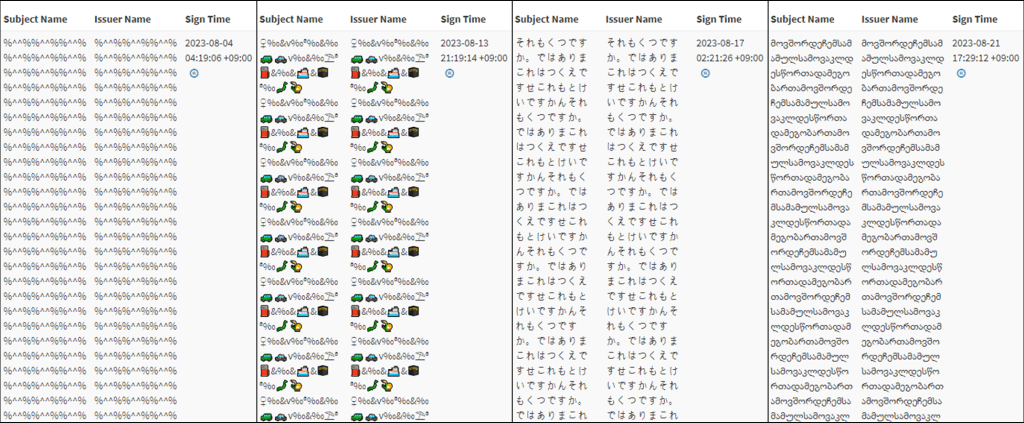
 Figure 1. Malware’s signature information
Figure 1. Malware’s signature informationThe latest sample currently in circulation (bottom right of Figure 1) consists of a string that URL encoded a malicious script. This script is designed to download and execute PowerShell commands from a specific address, but it is currently incapable of downloading. This script does not get executed during the infection process.
 Figure 2. After decoding the signature string (malicious script)
Figure 2. After decoding the signature string (malicious script)Among the malware currently being distributed with this kind of unique form, two strains can be predominantly identified: LummaC2 and RecordBreaker. Both of them are capable of performing various malicious behaviors, but they primarily have a strong focus on infostealing.
Upon infection, they can transmit sensitive user information such as browser-saved account credentials, documents, cryptocurrency wallet files, etc., to the threat actor, potentially resulting in severe secondary damages. Furthermore, an additional piece of malware designated by the threat actor gets installed, enabling continuous malicious behaviors.
These types of malware are distributed via malicious pages that are easily accessible through search engines (SEO poisoning), posing a threat to a wide range of unspecified users. These malicious pages primarily use keywords related to illegal programs such as serials, keygens, and cracks.
 Figure 3. Example distribution page
Figure 3. Example distribution pageRecordBreaker
RecordBreaker is also known as Raccoon Stealer V2, and in addition to the distribution method mentioned above, it is actively being distributed through YouTube and other malware. Its use of meaningful sentences as the User-Agent value when connecting to the C2 server is one of its distinctive characteristics, and it changes this value periodically. The recent sample in distribution uses the string “GeekingToTheMoon”. Functionally, it has not changed significantly from what was described in previous posts.
- RecordBreaker Infostealer Disguised as a .NET Installer
- RecordBreaker Infostealer Disguised as a Well-known Korean Software
- RecordBreaker Stealer Distributed via Hacked YouTube Accounts
LummaC2
LummaC2 is the most actively evolving malware among the ones distributed using the method described in this post.
The initial sample had the configuration information embedded within the malware itself for its malicious behaviors. However, it later switched to downloading the configuration information from its C2 to perform malicious behaviors. It also shifted to install additional malware like Amadey and Clipbanker in addition to its simple infostealing behavior.
Information regarding the initial distribution sample is detailed in the post below. Following that will be a brief summary of the changes.
– Change of C2 communication method
Since the initial sample had the configuration information embedded, it would promptly collect information and transmit it to the “/c2sock” address upon execution.
Subsequent variants downloaded the configuration information from the “/c2conf” address and transmitted the information to the “/c2sock” address.
Recent samples in circulation use the “/api” address for both downloading the configuration and transmitting the information. Therefore, configuration query connections and information transmission connections are distinguished through the POST parameter upon accessing the C2.
With each significant variation, the “ver” parameter that is sent to the C2 upon execution was increased by 1. The current version is 4.0.
 Figure 4. C2 communication of the most recent LummaC2 sample
Figure 4. C2 communication of the most recent LummaC2 sample“.xyz” was used as the top-level domain (TLD) of the C2 URL for a significant period of time before being switched to the current “.fun”.
 Figure 5. C2 information of LummaC2
Figure 5. C2 information of LummaC2– Downloads additional malware
While earlier samples would simply steal information before terminating, later versions began installing the Amadey malware. Recent versions install both Amadey and Clipbanker.
 Figure 6. URL information of the malware additionally downloaded by LummaC2
Figure 6. URL information of the malware additionally downloaded by LummaC2As a downloader, Amadey enables threat actors to install whatever malware they want through C2 communication. It can even perform infostealing behavior through additional modules depending on the situation. ClipBanker is a type of malware that monitors the clipboard. If it detects the address of a cryptocurrency wallet being copied, it is changed to the threat actor’s address.
LummaC2 is terminated after stealing information and installing additional malware. However, the additionally installed malware remains in the user’s system, allowing for continuous C2 communication (waiting for commands) or wallet address tampering behaviors.
User caution is advised as Infostealers are being actively distributed to unsuspecting users and are evolving continuously.
AhnLab products are actively diagnosing these abnormal certificate structures. Additionally, an automated collection system for samples similar to those described in this post is in operation, enabling swift responses to variants and the blocking of associated C2 connections.
[Detection Name]
- Suspicious/Win.MalPe.X2197 (2023.09.14.00)
- Infostealer/Win.LummaC2.C5482988(2023.09.08.01)
- Infostealer/Win.LummaC2.C5483329(2023.09.08.02)
- Trojan/Win.LummaC2.C5483331(2023.09.08.02)
- Trojan/Win.LummaC2.C5483376(2023.09.08.03)
- Trojan/Win.AGent.C5483377(2023.09.08.03)
- Trojan/Win.Evo-gen.C5481062(2023.09.04.02)
- Trojan/Win.RecordStealer.R604279(2023.09.08.03)
- Trojan/Win.RecordStealer.R604282(2023.09.08.03)
- Infostealer/Win.Agent.C5475457(2023.08.24.03)
- Trojan/Win.LummaC2.R606862(2023.09.23.00)
- Trojan/Win.MSIL.C5475827(2023.08.25.03)
- Trojan/Win.Injection.C5472888(2023.08.19.01)
- Infostealer/Win.LummaC2.C5474761(2023.08.23.00)
- Trojan/Win.Injection.C5472889(2023.08.19.01)
- Trojan/Win.PWSX-gen.C5469716(2023.08.12.00)
- Trojan/Win.Injection.C5468781(2023.08.10.01)
- Trojan/Win.Injection.C5468508(2023.08.09.02)
- Downloader/Win.Amadey.R596666(2023.08.11.00)
- Trojan/Win.Generic.R596332(2023.08.09.00)
- Trojan/Win.Injection.C5467711(2023.08.07.01)
- Trojan/Win.Injection.C5467418(2023.08.06.01)
- Infostealer/Win.LummaC2.C5467423(2023.08.06.01)
- Downloader/Win.StealWallet.R596060(2023.08.07.03)
- Infostealer/Win.LummaC2.C5466555(2023.08.04.02)
[IOC Info]
eae39f18a51c151601eaf430245d3cb4
3c39098b93eb02c664d09e0f94736d95
89644b879046b97dccf71c68c88bcf42
bb2147e536ba06511ca8ea0b43a38ef7
e584f749b3b06d328001f0dea7a45617
331c7d351bc39efb36fd53c74c12c3a5
d8518e4fcbdbcc056a72a495430f37b6
2667f726136c0c848b30ec93cbd488b7
a0caecafa32e88f363942945f759b799
5dfe53ca9cd218a0ed129ebecc107cf0
7ed43c0f2093707f65369ad87832599c
dabe6f3ac23858a353c53382f92a217b
fa371f301369b16a7a379008cc1b4f64
6b5ad8f456dc6704638d5b3e38135a2b
dbee35748bd993f3bd4a822d362f309d
331031e51a9816db6aa48a7dcff41c28
32b4703cc03286e610094704925ca5e4
e5f82461f276bfb9150ab253b3474aa1
e6facedba218387d24d6908a59f1730b
8329b54e5b8921825579c3eae37ee8b4
6260a3ea150744248ed0a155d079d2c8
a998f8d64d6953e1fdaafba655c84120
cbc06399af416c6b5a5aec73890a15a1
613425d8623f118e45fb65619f71c387
5d2359723a3acac158320a48f1930e08
05ab72ab29765fa803a9a88e940cc826
b484fdc3953f4d84e24ba8dd309accf2
7974df61d5906ca20e146c1b8b8b3aaa
0970196d074cbf7221f5be8208c7cba3
63a0789d8bfa599da31a7620947d7a24
d8b5732afb4897035043ea05ad84f928
a82d9b679c0df2a62939ee21939e7e7a
4cf108debe0314357431525f01376a56
de9cb5f942d9f73a1a5659172372b099
aa4fb8876b89288a015fbf945da98d87
b64c3663718228679df20e9282727110
0ece25acd98b2cd0beebd20d3fc11fd1
[C2]
-
RecordBreaker
hxxp://49.13.59.137/
hxxp://95.216.166.188/
hxxp://49.13.51.185/
-
LummaC2
blockigro.xyz
programmbox.xyz
cvadrobox.xyz
stormwumen.xyz
fullppc.xyz
holdbox.xyz
scoollovers.xyz
beerword.xyz
fisholl.xyz
survviv.xyz
checkgoods.xyz
singlesfree.xyz
acexoss.xyz
freeace.xyz
glowesbrons.xyz
usdseancer.xyz
phonevronlene.xyz
seobrokerstv.xyz
reconphotocolor.xyz
sonyabest.xyz
seobrokerstv.fun
welcometv.fun
equestrianjumpingfrog.fun
seededraisinlilinglov.fun
gougeflying.fun
-
Additionally Downloaded Malware
hxxp://imagebengalnews.com/amday.exe
hxxp://enfantfoundation.com/amday.exe
hxxp://vbglimited.com/Amdays.exe
hxxp://moshito-marketing.com/Amda.exe
hxxp://sms.vbglimited.com/Amda.exe
hxxp://lungalungaenergyltd.co.ke/Adayn.exe
hxxp://vrecepte.com.ua/Blazerstreetavenu.exe
hxxp://erp.fastgas.co.ke/Bitmodertorent.exe
hxxp://marrakechfolkloredays.com/clips.exe
hxxp://africatechs.com/55aa5e.exe
hxxp://rusticironstore.com/clip.exe
hxxp://tinsignsnmore.com/5ea275.exe
hxxp://ezisystem.com/clip.exe
hxxp://portmarine.co.tz/5ea275.exe
hxxp://mediterraneanshippingllc.com/clip.exe
hxxp://toolstechs.com/5ea275.exe
hxxp://justentertainer.us/5ea275.exe
The post Infostealer with Abnormal Certificate Being Distributed appeared first on ASEC BLOG.
Article Link: Infostealer with Abnormal Certificate Being Distributed - ASEC BLOG