Background
Globalization has been the mantra for years, to bring the best from across the world to the consumer, at the lowest cost and best quality. It is undebatable that globalization has provided a level playing field for commercial stakeholders across the globe and has helped in bringing knowledge and awareness about better supply chain practices as well as the best of consumer products and services to the emerging world and the countries of the third world. While doing this, it has impacted local industries that were prospering over long periods. These industries were built and enhanced through local connections, formed around traditions, adjusted to the societal conditions, hardened through weather, and many other factors. Many thought leaders in global societies and governments of many countries have surfaced some of these issues over the years.
While it is true that consumers of today prefer to enjoy the quality products and services from across the globe, many of them still have emotional and sentimental preferences towards localized, hyperlocal products. Coincidently, some of the regional or local governments want certain products and sectors to be given preference and protection and have enacted compliance regulations to enforce the same. Also, the hyperlocal market needs special ways of treatment throughout the supply chain as well as when the items are made available to consumers.
A global retail organization is expected to bring the best of both the worlds, by providing technology that can enable a level playing field for global players to offer best quality solutions that are optimally priced across the globe, to all the interested consumers. At the same time, it is of paramount importance to provide a secure and trusted means to encourage localized products wherever the government, society and most importantly the customer preference demands so.
In this blog, we will explore how Blockchain technology can be used to achieve this use case and about the various methods that can be employed through which information can flow and be verified across multiple parties involved in the product supply chain.
Solution
As supply chain complexity increases, there is an obvious opportunity to drive efficiency through greater collaboration and transparency across the various constituencies involved, including manufacturers, distributors, shipping carriers, insurers, importers, wholesalers and retailers among others. Knowing in real-time the exact source, location and state of all the inventory in the system could be a game-changer for most businesses, particularly those in perishable or luxury goods category.
Blockchain has been compared with the internet in terms of the impact it can have on business and society. At its core, Blockchain is primarily exciting for its ability to enable greater trust, transparency and collaboration across constituencies that would otherwise struggle to establish the same. Additionally, the use of “smart contracts” offers a never-before-possible means of automating and enforcing promises. For retail, these benefits can be realized across vendors to employees to customers.
Blockchain information flow in Supply Chain with verification capabilityWith the Blockchain at the center of it, the product location information can be captured using various methodologies. The information stored in a Block can be categorized as {Claim, Verification} tuple. Different parties have permission on different attributes in the Blockchain to read, write.
For example, a manufacturer should be allowed to add a location claim attribute and will need write permission on that attribute in the Block. For the verification field associated with location claim, write permission can be given to an auditing authority, who will also have read permission for the location claim.
In supply chain, multiple parties are involved with different information attributes like location. The permission control for different parties on attributes can be achieved using Smart Contract [Reference].
Below are three approaches for location claim verification with a comparative study and a discussion about the industries where each approach will be suitable.
Reactive Approach
Location is claimed by the supply chain stakeholder. Here the record about the product is maintained in the immutable Block in Blockchain. This is a reactive approach and in case of any complaints, the claimed information can be verified.
Pros: There is no explicit verification process. It makes the supply chain process lightweight.
Cons: This is a reactive approach, which means there is still a possibility of error, unless validations are incorporated into each step.
Suitability: This methodology is suitable for low cost items like grocery, where the stakes are comparatively lower.
List Based Approach
The claim about the location is verified by a next party in the supply chain. This is a list approach, where trust is carried through multiple players in the supply chain. For example, the raw material supplier’s claim for location is verified by the manufacturer who purchases the raw material and signs the location claim in the Blockchain.
List based approachPros: This method does not require another party to be involved, other than the next stakeholder in the chain in the supply chain.
Cons: Not all parties involved may agree to, or are capable of performing the verification activity.
Suitability: This approach is applicable for scenarios where less number of stakeholders in the supply chain are involved, and direct interaction is possible between them, without the need for a middle man or arbitrator.
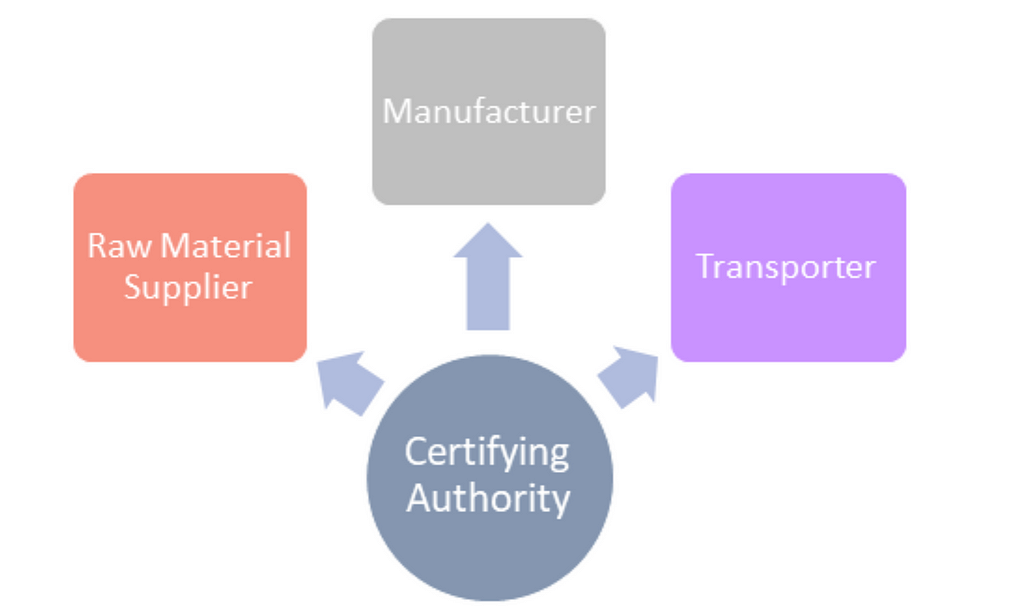
Central Authority
Third approach is where there is an auditing authority, which is responsible for verification of the location claim and signs the claim made by any of the parties in the supply chain, which also gets stored the Blockchain itself.
Central Authority based approachPros: This is the most suitable approach for ensuring that a Supply Chain handles authentic information.
Cons: This requires another party to be involved in the Supply chain (Certification Authority). The verification can be performed either for random samples or for the entire inventory. This approach will add additional cost and processes.
Suitability: This is suitable for high end, premium products like jewelry or expensive garments.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology has started disrupting the traditional ways of working of e-commerce and commerce in general. It has enabled new ways of sharing information in trusted and traceable ways. This can open the doors of opportunity which is more humane in nature and can bring in new ways to make customers happy. In this blog, we have seen how hyperlocal market can be supported by an e-commerce platform using Blockchain.
This is first in a series of blog posts on how Blockchain technology can influence the retail industry by providing an intelligent platform which can go beyond normal demand and supply game. We will get into multiple use cases which are going to reshape the thought process all together.
Blockchain for popularizing localization in eCommerce was originally published in Walmart Global Tech Blog on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Article Link: Blockchain for popularizing localization in eCommerce | by anshuman sinha | Walmart Global Tech Blog | Oct, 2021 | Medium