A Look at the Security Challenges Threatening E-Commerce Websites – Vulnerabilities, Skimmers, Phishing
In the fast-paced world of e-commerce, cyber threats rise as much as the sector’s expanding reach. With over 26.5 million e-commerce websites globally as of 2023, spanning major markets in the US, UK, Brazil, Germany, and Australia, the digital storefronts are not just bustling with customers but also with potential security threats.
While phishing scams and credit card fraud are often the first dangers that come to mind, the threat landscape for e-commerce extends much deeper.
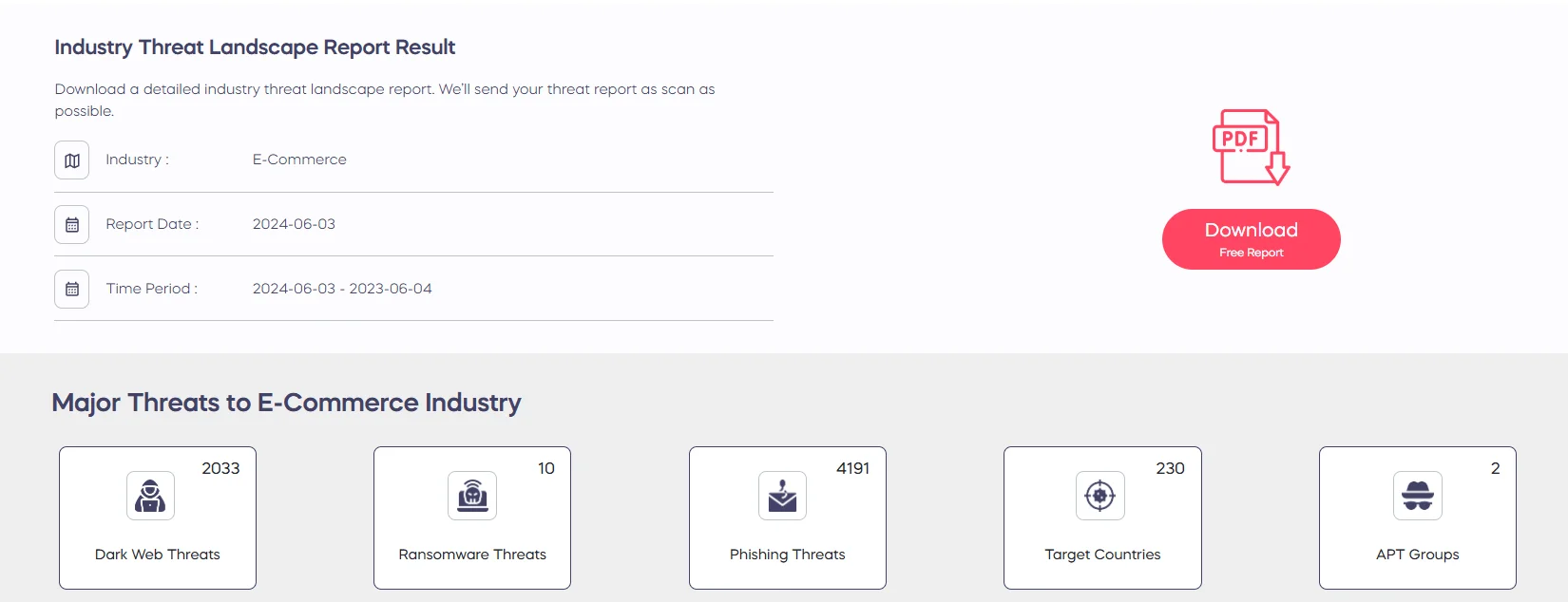
Current Industry Threat Landscape Report for the E-Commerce Industry (SOCRadar LABS)
Vulnerabilities in e-commerce platforms themselves pose significant risks. Common web application vulnerabilities like Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and SQL Injection (SQLi), as well as more disruptive attacks such as Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) threaten the integrity of these digital platforms and their customers.
This blog zooms in on the most common e-commerce cyber threats, especially spotlighting the vulnerabilities that shadow these platforms.
We will explore some of the top e-commerce platforms, the major e-commerce websites that use them, and how certain security vulnerabilities have come to challenge their online security posture. By understanding these risks, businesses can better prepare and protect themselves against the future array of cyber threats they face in the digital marketplace.
Vulnerabilities Across Prominent E-Commerce Platforms: WooCommerce, Shopify, PrestaShop, and Adobe Commerce (Magento)
In exploring digital marketplaces, one quickly realizes that not all e-commerce platforms are created equal, especially in terms of security. While global shopping giants like Amazon, eBay, and AliExpress dominate the scene of e-commerce websites, our focus in this blog post shifts towards brand-centric websites that companies use to establish their online presence. The top 3 platforms they use, according to recent data from BuiltWith, are Shopify, WooCommerce, and Magento.
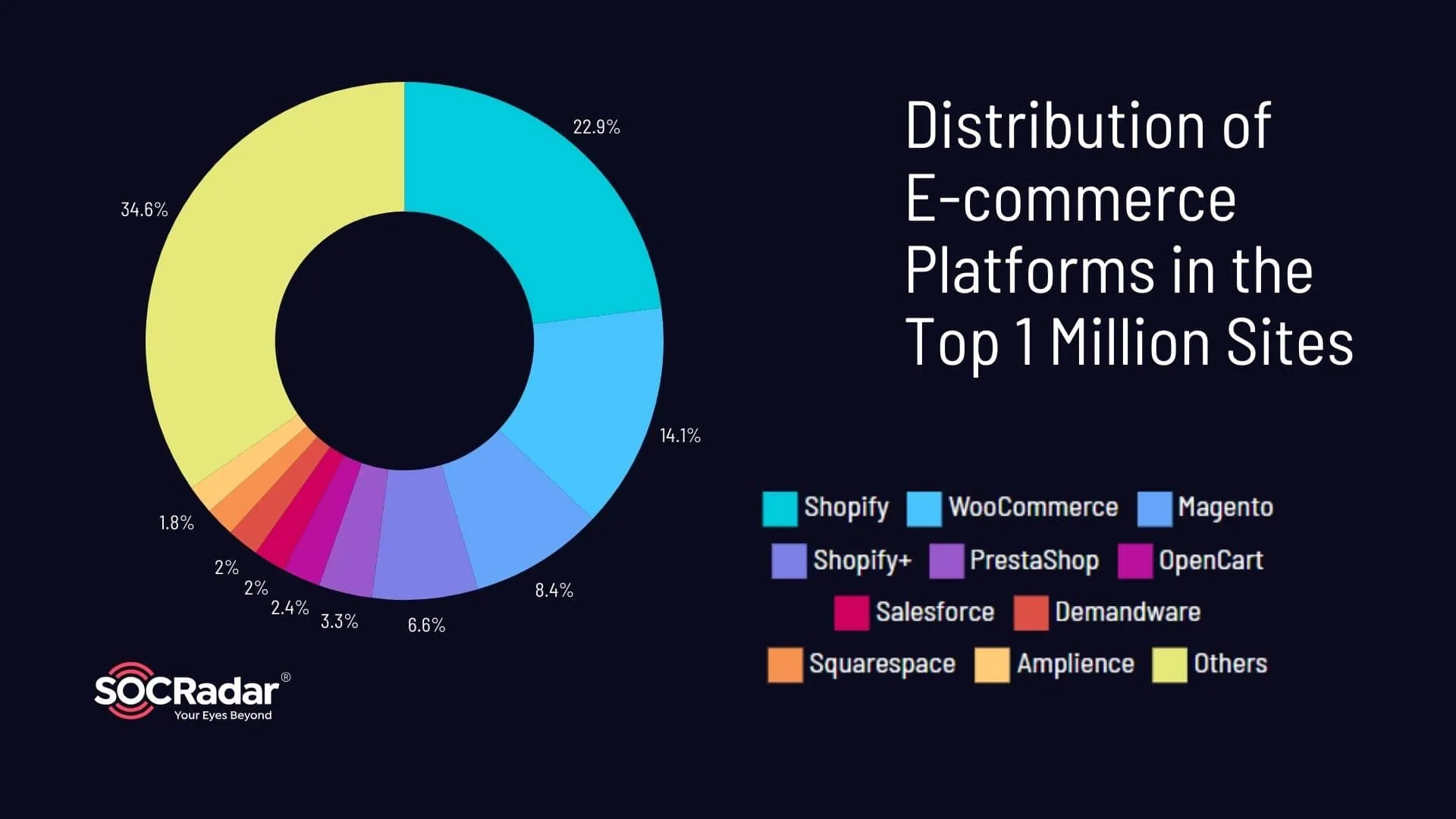
Distribution of e-commerce platforms in the top 1 million e-commerce websites
1. WooCommerce
A powerhouse for e-commerce on WordPress sites, WooCommerce enables users to transform basic websites into expansive commercial hubs. As of April 2024, over 4.7 million active websites owe their retail capabilities to WooCommerce, including brands such as ClickBank, WorthPoint, Holiday World, and Magna-Tiles. This widespread usage, however, brings visibility to its vulnerabilities, such as:
- CVE-2023-52222 (CVSS: 8.8): A critical Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) vulnerability was identified in WooCommerce versions up to 8.2.2, posing a risk that could allow unauthorized actions on behalf of a logged-in user without their knowledge.
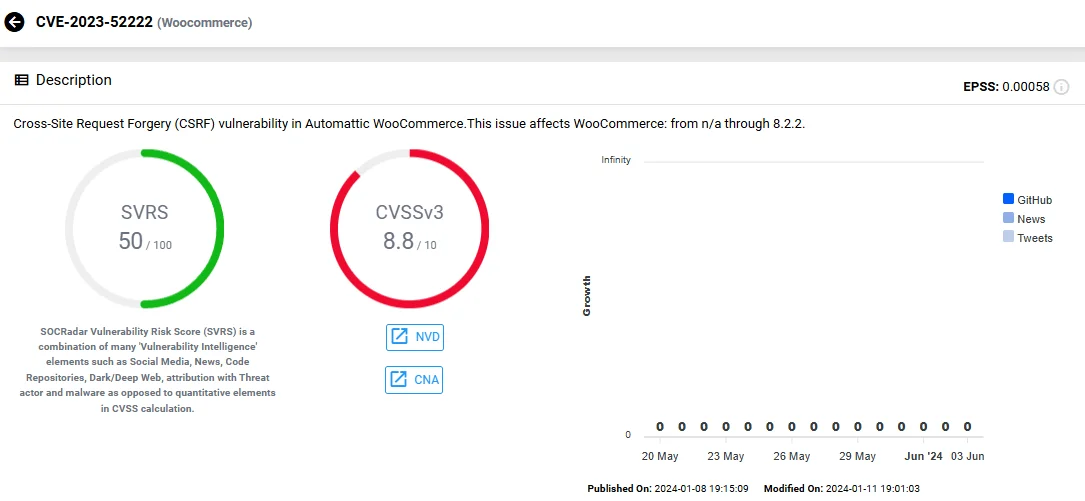
Vulnerability card of CVE-2023-52222 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
- CVE-2023-33318 (CVSS: 8.8): This vulnerability involves the unrestricted upload of files with dangerous types in the popular WooCommerce plugin AutomateWoo, affecting versions up to 4.9.40. It could allow attackers to execute arbitrary code by uploading a malicious file.
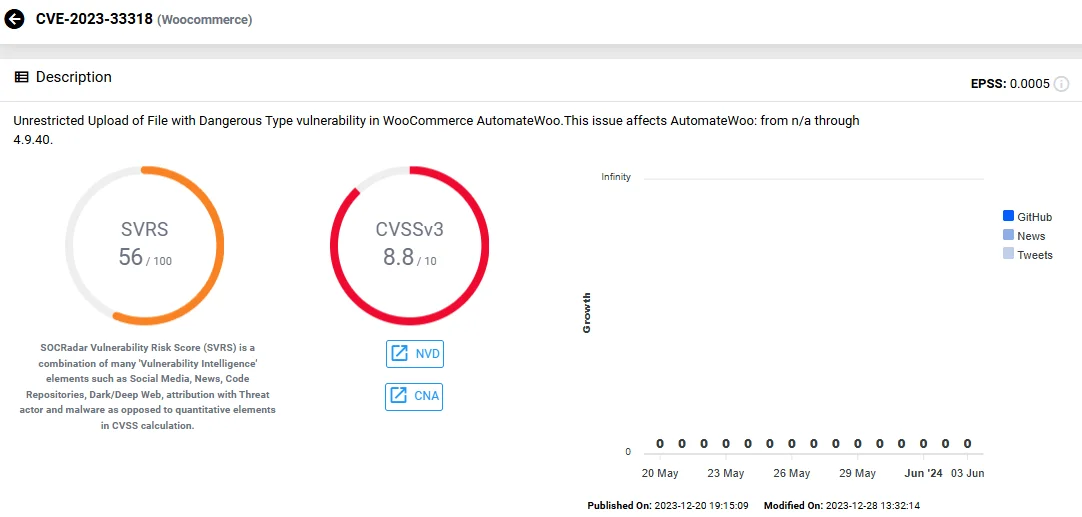
Vulnerability card of CVE-2023-33318 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
2. Shopify
Shopify stands out as a titan in the e-commerce platform arena, rivaling WooCommerce with its vast user base and robust growth metrics. Over 2.35 million live websites currently utilize Shopify, including high-profile names such as:
- Oreo: The iconic cookie brand also takes advantage of Shopify’s features.
- Ring: The home security company known for its smart doorbells and cameras.
- SKIMS: The fashion and shapewear company founded by Kim Kardashian.
- Sanrio: Renowned for its Hello Kitty brand, Sanrio leverages Shopify alongside various technologies to streamline shop operations.
Notably, Shopify hosts a higher transactional value per merchant compared to WooCommerce, underscoring its appeal among high-volume retailers and boutique stores.
Among known vulnerabilities affecting the Shopify e-commerce platform are:
- CVE-2021-24105 (CVSS: 7.8): A supply chain vulnerability impacting numerous tech giants including Microsoft, Apple, PayPal, Netflix, Yelp, Tesla, Uber, and Shopify. It involves the potential insertion of malicious packages into repositories used by package managers during development processes. This flaw could lead to remote code execution across various programming environments such as Python/pip, .NET/NuGet, Java/Maven, and JavaScript/npm.
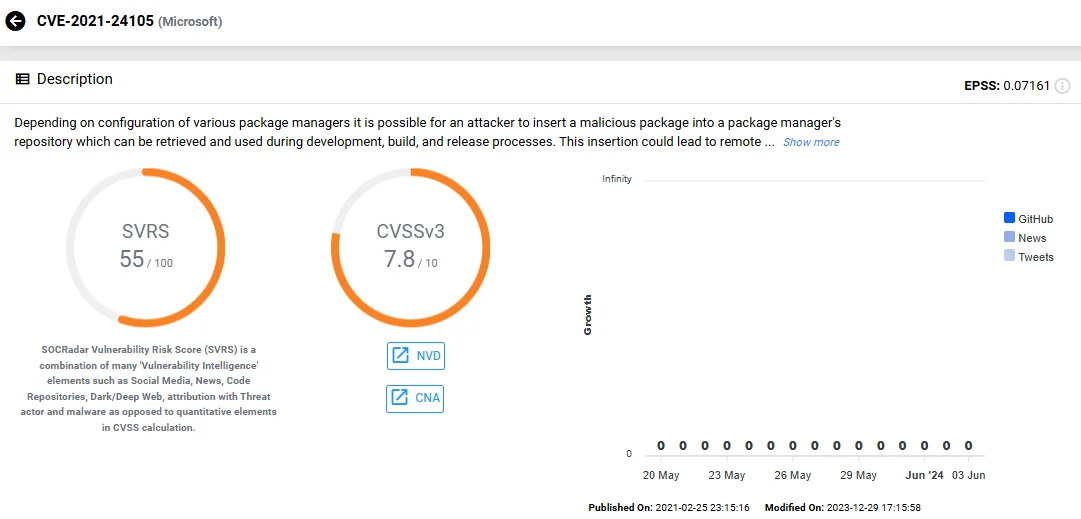
Vulnerability card of CVE-2021-24105 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
- CVE-2022-29230 (CVSS: 5.4): This vulnerability in Hydrogen – a React-based framework for creating custom Shopify storefronts – poses a Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) risk. It affects all versions from 0.10.0 to 0.18.0, allowing script execution on user-controlled pages. The advised mitigation is upgrading to Hydrogen version 0.19.0.
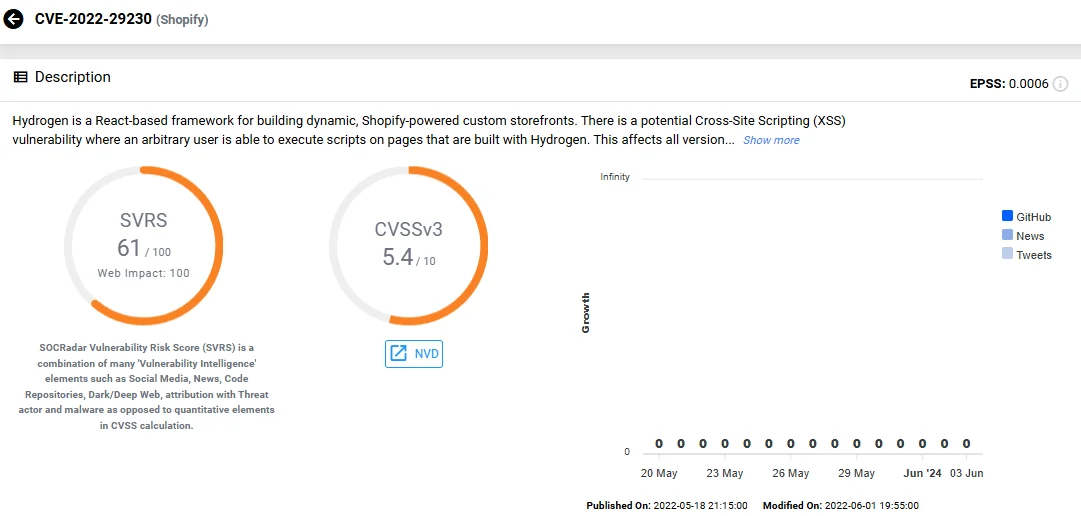
Vulnerability card of CVE-2022-29230 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Although vulnerabilities affecting the Shopify platform have trended relatively rare, its popularity makes it a potential target for threat actors. Continuous monitoring is crucial to combat security vulnerabilities and be prepared when they emerge. SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence offers an extensive overview of emerging CVEs, enabling businesses to swiftly respond to new threats by tracking exploits, mentions, and the overall impact of vulnerabilities on their operations.
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence
3. PrestaShop
PrestaShop, which began its journey in France in 2005, remains a preferred choice among online retailers, claiming about 33% of its user base from France. The platform quickly adapted to global needs by supporting over a dozen languages, emphasizing its commitment to internationalization.
With nearly 209,000 active websites, PrestaShop’s flexibility is showcased across various domains including brands like Palmers, Decathlon Colombia, Jones Snowboards, and Bobbies Paris.
Significant vulnerabilities that have affected this platform include:
- CVE-2024-34716 (CVSS: 9.6): This Cross-site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability arises when the customer-thread feature is enabled. Found in versions starting from 8.1.0 up to before 8.1.6, it can be exploited through the front-office contact form.
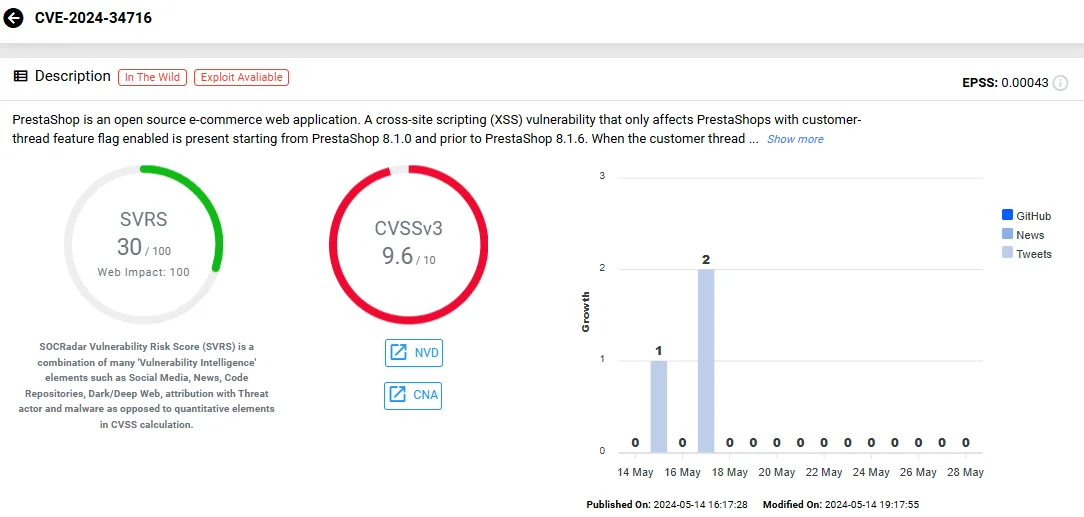
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-34716 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
- CVE-2023-39530 (CVSS: 9.1): Affects versions prior to 8.1.1 and enables file deletion from the server via the CustomerMessage API. Patched in version 8.1.1, there are no effective workarounds for earlier versions.
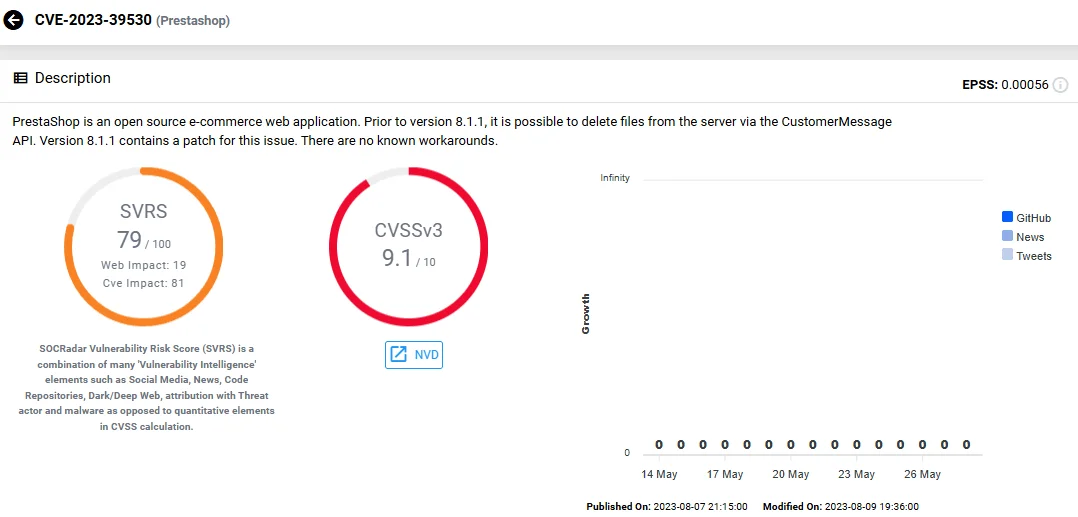
Vulnerability card of CVE-2023-39530 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
4. Adobe Commerce (Magento)
Adobe Commerce, originally known as Magento, stands out as an open-source e-commerce platform renowned for its customization capabilities, allowing merchants to tailor the entire shopping experience. After its acquisition by Adobe in May 2018, the platform has seen enhancements, including Magento Commerce Cloud, though many choose to host their stores independently.
Adobe Commerce boasts nearly 146,000 active sites. Notable brands leveraging its capabilities include ASUS, HP, Volkswagen Classic Parts, Ford, and Canon.
Critical vulnerabilities that are known to affect Adobe Commerce (Magento) include:
- CVE-2024-20719 (CVSS: 9.1): A Stored Cross-site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability that impacts both Adobe Commerce and Magento. This flaw could potentially lead to arbitrary code execution, requiring the attacker to have admin access to exploit.
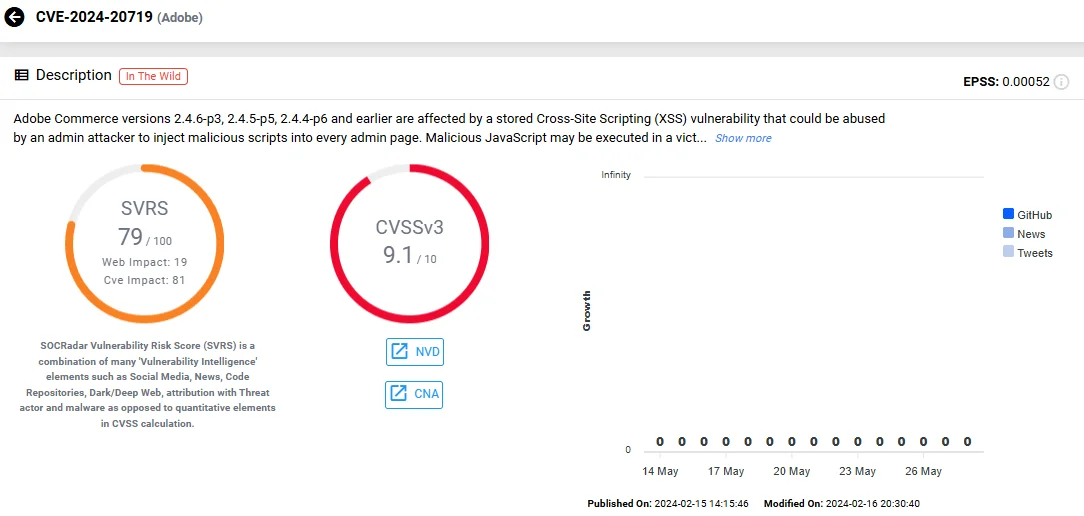
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-20719 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
- CVE-2024-20720 (CVSS: 9.1): This vulnerability arises from the improper neutralization of special elements used in OS Command Injection. Exploitation is contingent on the attacker having authentication and admin privileges.
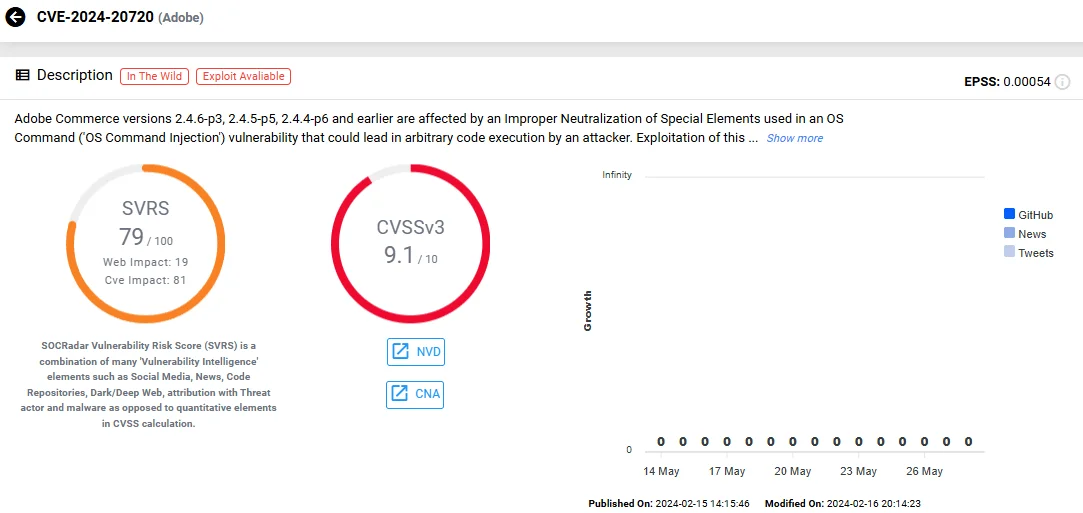
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-20720 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Out-of-Date Dependencies, A Perpetual Challenge in E-Commerce Websites’ Security
One prevalent challenge in securing e-commerce platforms and evading vulnerability exploitation is the organizations’ management of dependencies. Outdated components can introduce severe vulnerabilities, as they often lack the latest security patches and improvements. A substantial portion of cyberattacks exploit such vulnerabilities, leveraging old software to compromise systems.
For instance, a company might use various plugins and additional technologies to enhance its online shopping website – almost all companies do. While each component adds valuable features, they also introduce new responsibilities. Each element must be properly monitored, updated, and secured to ensure the website’s overall security.
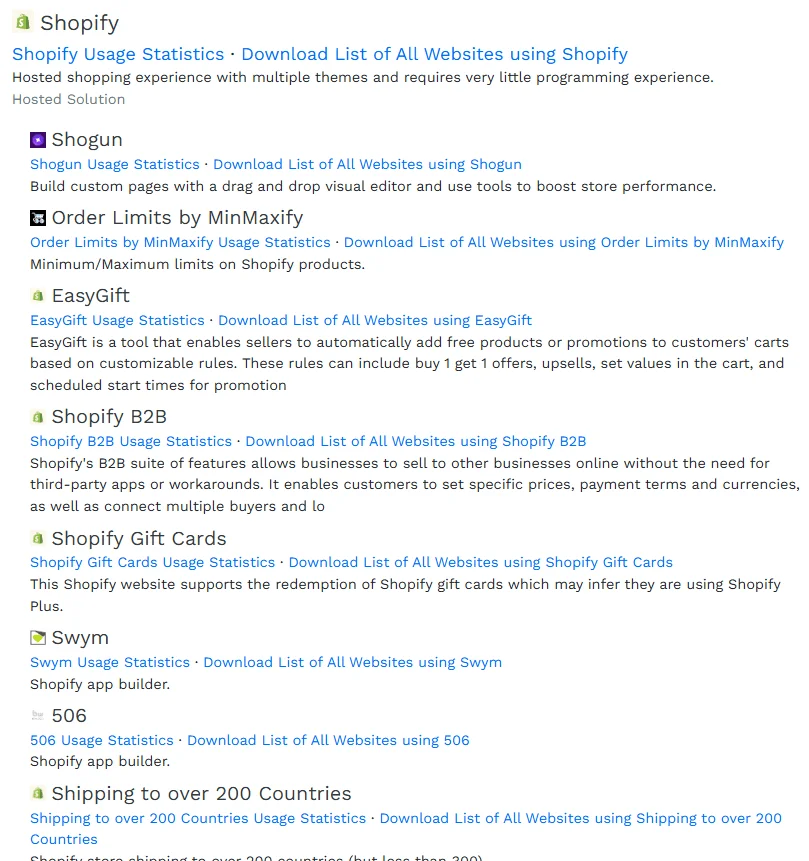
A tech lookup of the e-commerce technologies used by Sanrio; there are several Shopify components. (BuiltWith)
To counteract these threats, companies on the e-commerce scene must maintain a rigorous update and patch management strategy. This approach ensures that all components of the e-commerce platform are up-to-date with the latest security patches.
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module enhances this strategy by continuously monitoring the digital assets within an organization’s ecosystem. It identifies security gaps and provides actionable insights, which are essential for preventing potential exploits and mitigating risks associated with external attack vectors.
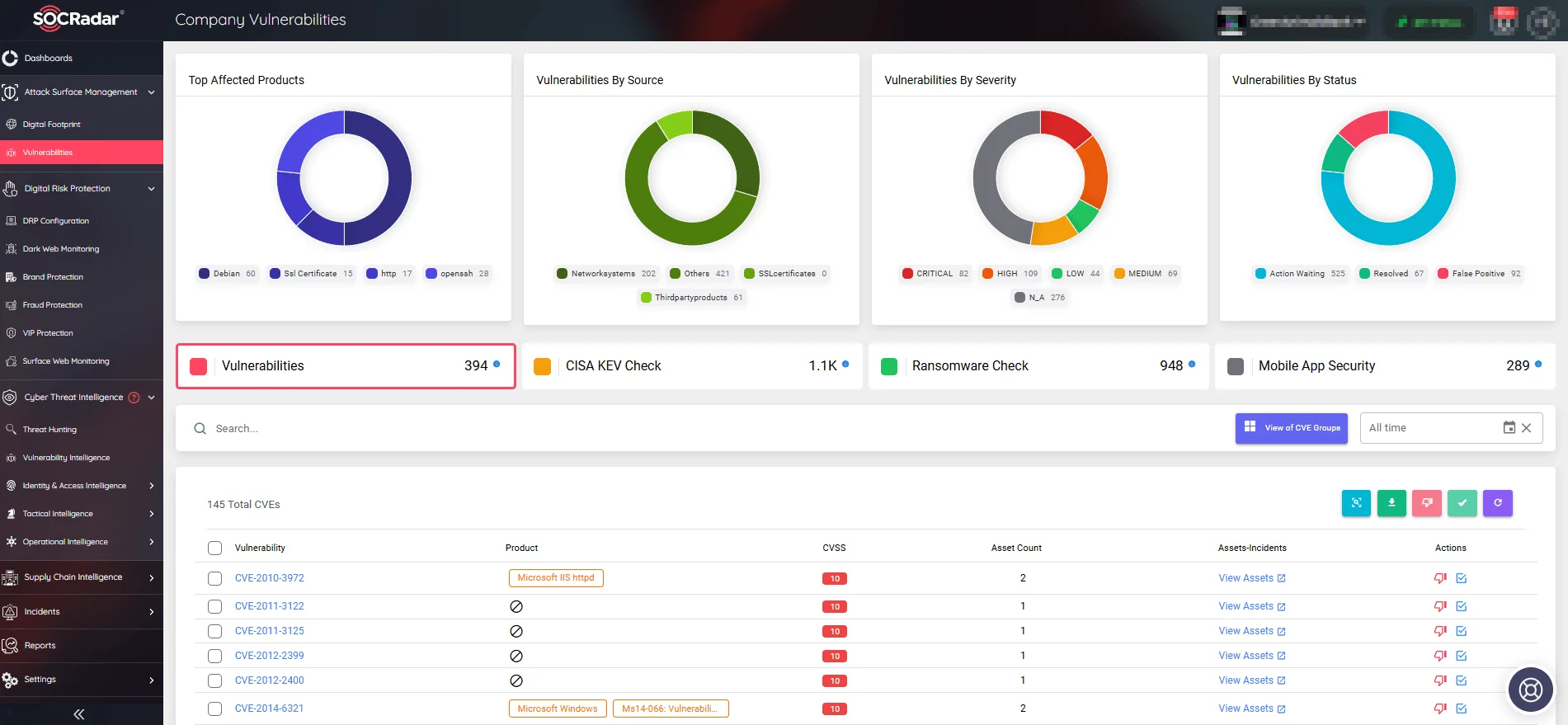
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management
Monitor the Dark Web for Exploits
Moreover, with the expansion of cyber threats, monitoring dark web forums is also essential. These platforms often serve as breeding grounds for threat actors to discuss and trade exploits, including those targeting known vulnerabilities in common e-commerce platforms.
SOCRadar aids in this area by providing advanced threat intelligence capabilities. It enables organizations to follow emerging threats discussed on the dark web with Dark Web News, significantly reducing the window of opportunity for attackers by keeping companies aware.
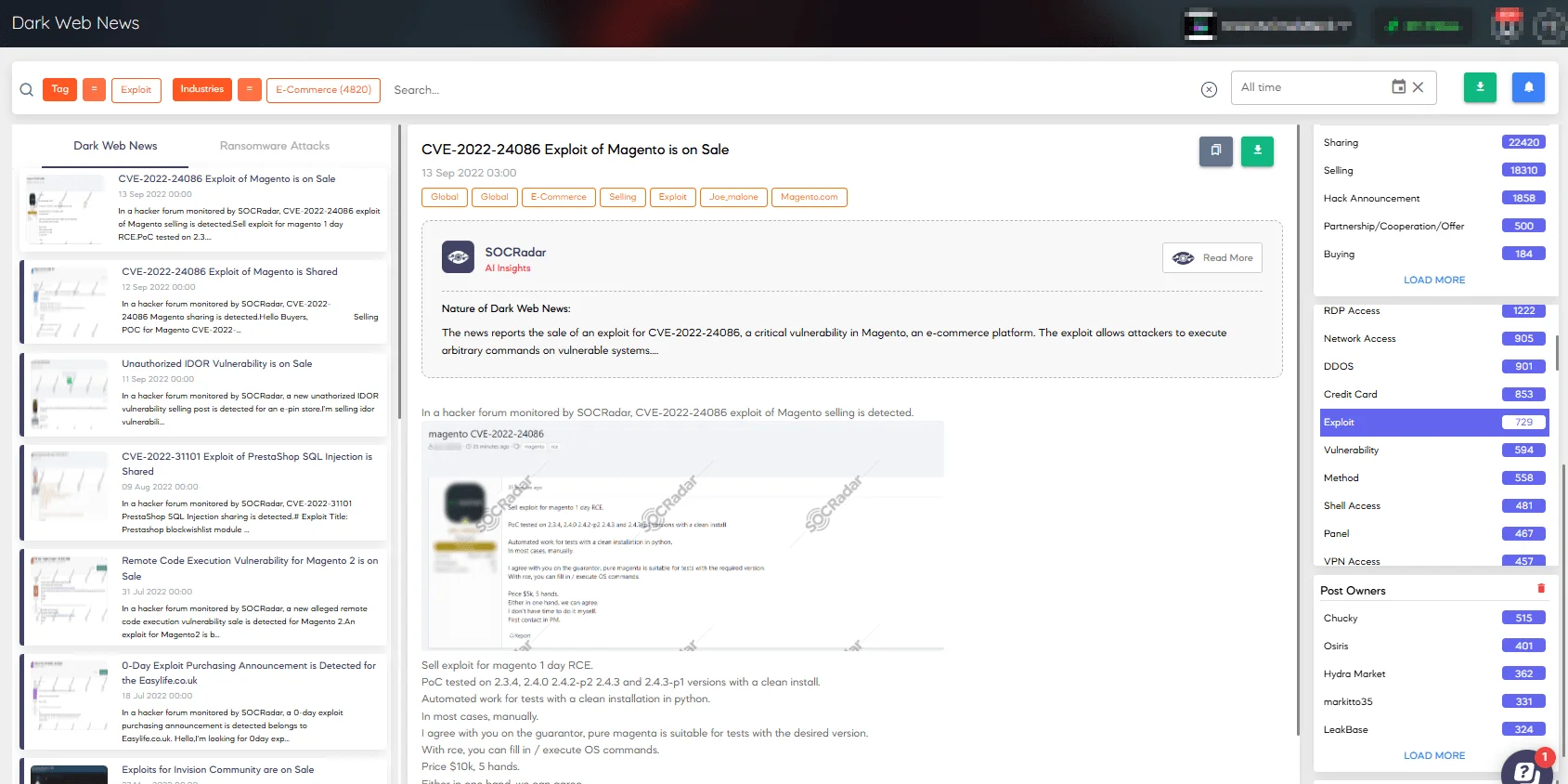
Follow the latest exploits related to the e-commerce landscape with SOCRadar’s Dark Web News
For those aiming to deepen their understanding of cyber threats in the dark web, SOCRadar offers valuable articles, such as “Top 10 Deep Web and Dark Web Forums”.
Threats of Stealer Malware and Stealer Logs to E-commerce Websites
Stealer malware also represents a significant threat to e-commerce websites, capitalizing on vulnerabilities to infiltrate systems and pilfer sensitive information. These malicious programs are adept at infecting legitimate or spoof websites, then capturing and transmitting user data, including login credentials, and from time to time, even payment card details, back to cybercriminals.
Once stolen by stealer malware, information is often compiled into what are known as stealer logs. These logs are then sold or traded on dark web forums, serving as a goldmine for fraudsters and other cybercriminals. The presence of this stolen data on the dark web can lead to widespread financial fraud for customers and significant reputational damage for the affected organizations.
Vulnerable e-commerce websites may be compromised through various methods such as Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks or other forms of code injection, facilitating the deployment of stealer malware. Once installed, this malware can harvest an extensive array of user data, creating logs that cybercriminals eagerly exploit.
For a deeper dive into how these threats operate, explore SOCRadar’s comprehensive analysis in the blog post: The Anatomy of Stealers: How They’re Stealing Our Information & Where They’re Taking It.
Credit Card Skimmers and Magecart Attacks
Magecart attacks represent a significant cybersecurity threat to e-commerce sites, primarily involving the use of malicious scripts known as skimmers – which operate similarly to stealer malware, but directly on the payment service.
Shortly put, these attacks target online payment forms to steal customer payment information directly from the checkout pages.
What Exactly Is “Magecart”?
Magecart is an umbrella term for attacks or cybercriminal groups that specialize in injecting payment card skimmers into websites.
Once a site is compromised, every transaction processed by the site can potentially have payment data skimmed and transmitted to servers controlled by attackers. This method is particularly insidious because it can go undetected for extended periods, allowing cybercriminals to gather massive amounts of data.
And how do skimmers operate? Skimmers are typically JavaScript code snippets that are covertly installed on e-commerce payment pages. When customers enter their payment information during checkout, the skimmer secretly captures the data and sends it to the attacker’s server. This process is seamless from the user’s perspective, making it extremely difficult for customers to detect that their information has been compromised.
You can read our previous blog posts related to web skimming and a Magecart campaign for more context on this matter.
Incorporating tools such as SOCRadar’s Threat Hunting and Dark Web Monitoring can significantly enhance an organization’s defense mechanisms against Magecart attacks, as well as stealer malware threats. By providing timely intelligence and comprehensive threat analysis, these tools equip security teams with the necessary resources to effectively respond to and mitigate the impacts of stealer malware and other cyber threats.
The Threat Hunting module allows defenders to proactively sift through stealer logs to detect and neutralize threats before they escalate. This capability is valuable for identifying compromised data early and taking the necessary steps to mitigate further damage.
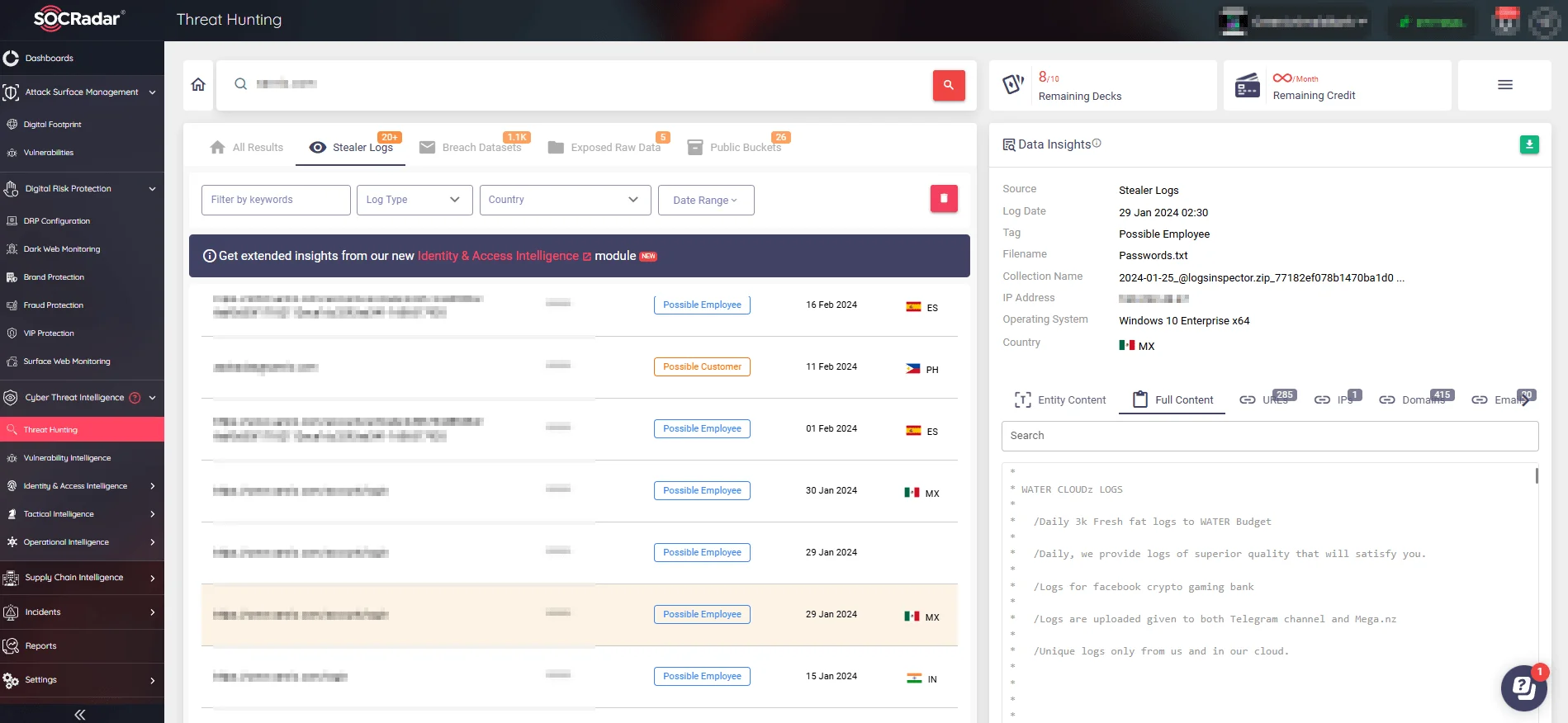
Searching for an e-commerce domain with SOCRadar’s Threat Hunting
With the Dark Web Monitoring tool, encompassing data from black markets and various other channels, you can track potentially compromised information related to your organization, including corporate, employee, and customer information, whether PII or financial.
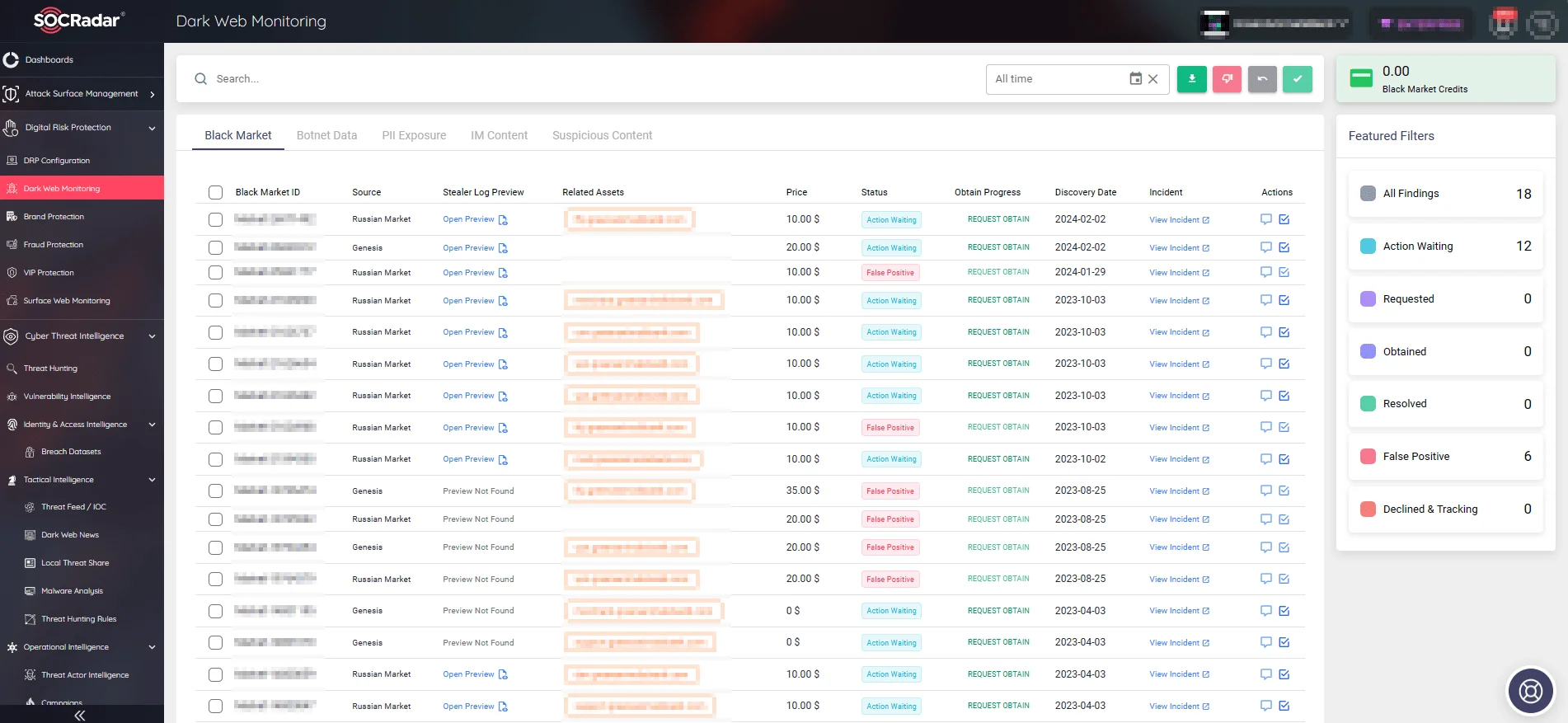
SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring
Social Engineering Tactics
Social engineering also remains a potent threat, with tactics such as phishing and website impersonation becoming increasingly sophisticated, especially with the advancements of GenAI.
These methods compromise transaction security and pose a significant risk to customer trust and data integrity.
Phishing attacks often leverage stolen customer data, obtained either through direct breaches of e-commerce sites or via third-party leaks. Attackers use this information to craft convincing emails and messages that mimic legitimate communications from the e-commerce provider, tricking customers into divulging sensitive information such as credit card numbers and login credentials.
The entry level for such attacks has become quite low, due to threat actors’ use of LLMs and the vulnerability of some models to cyberattack helpfulness.
Beyond phishing, cybercriminals also employ tactics like typosquatting, also known as domain squatting. By registering domains that are visually similar to legitimate e-commerce sites, attackers create deceptive websites that can fool customers into believing they are making purchases or logging into their accounts on the genuine site. This not only leads to financial fraud but also damages the reputation of the real e-commerce platforms.
SOCRadar’s Brand Protection module provides monitoring against such threats, detecting and alerting organizations to potential impersonations, from spoofed domains and social media profiles to rogue mobile apps. By identifying these threats early, companies can take swift action to takedown malicious activities and protect their customers from fraud.
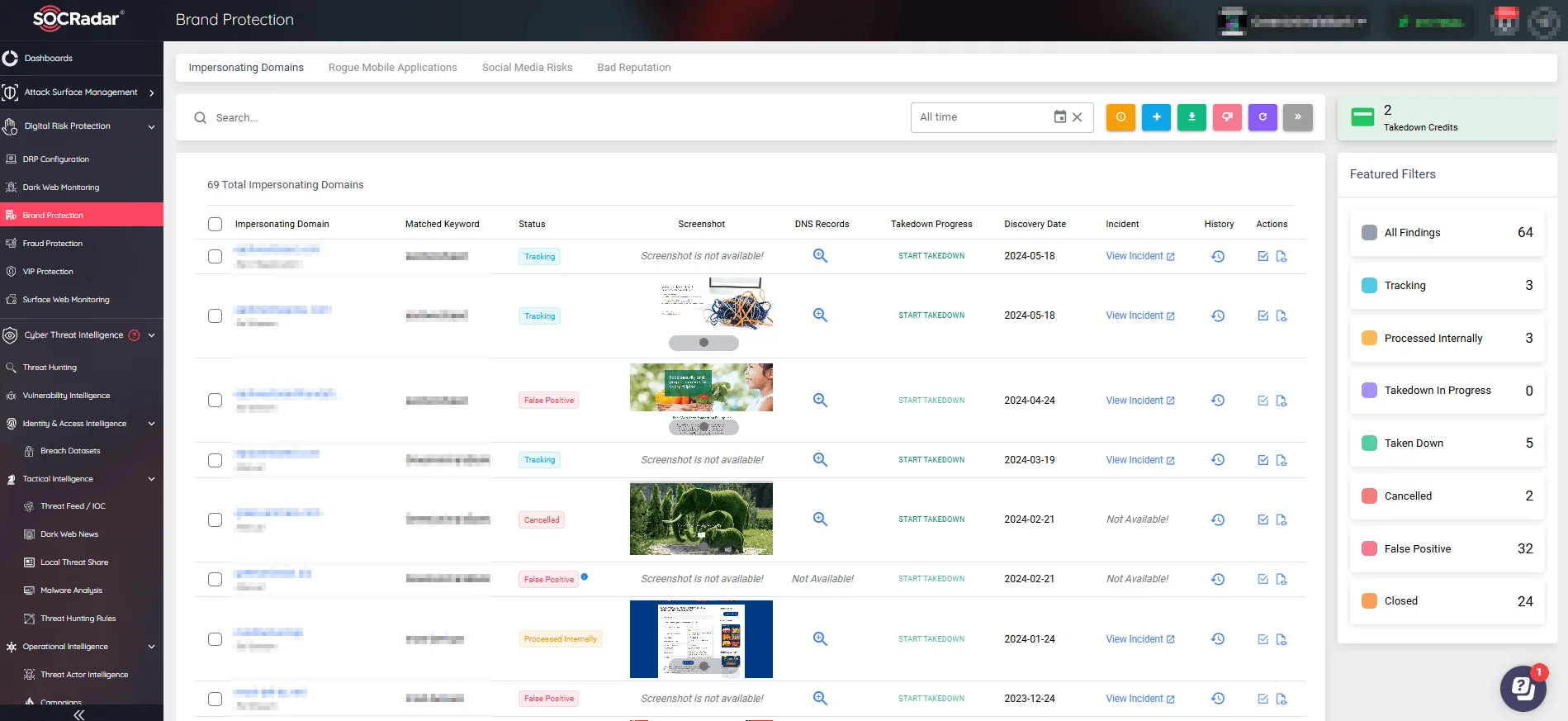
Through SOCRadar’s Brand Protection, you can start takedown actions on impersonators. Check out the Integrated Takedown module.
Conclusion
The world of e-commerce is vast and vibrant but not without its vulnerabilities. From critical security flaws in platforms like WooCommerce, Shopify, PrestaShop, and Magento to the covert dangers of Magecart attacks, the threats are as varied as they are severe.
As we have explored in this blog, these cyber threats can lead to direct financial losses and erode customer trust, potentially tarnishing a brand’s reputation irreversibly.
The persistence of outdated dependencies, the risk of social engineering, and the sophisticated tactics of stealer malware underline the need for an exhaustive approach to cybersecurity. In response, e-commerce businesses must employ proper defense strategies that include regular updates, comprehensive monitoring, and proactive threat hunting.
SOCRadar, with its suite of cybersecurity tools, offers an all-in-one platform to support companies in this context. With features ranging from Attack Surface Management to Brand Protection, businesses can gain critical insights and actionable intelligence to protect their digital assets. By leveraging SOCRadar’s capabilities, companies can detect and react to threats in real time, and anticipate and prevent future attacks.
In conclusion, while the digital transformation has expanded the horizons of retail, it has also broadened the attack surface, and it is a must for businesses to continuously evolve their cybersecurity measures to safeguard their e-commerce websites.
