This month’s Intezer Analyze community findings include malware employed by two cyber espionage groups linked to the Russian government and an endpoint infected with ServHelper, a remote access trojan (RAT) targeting financial services and retail organizations globally.
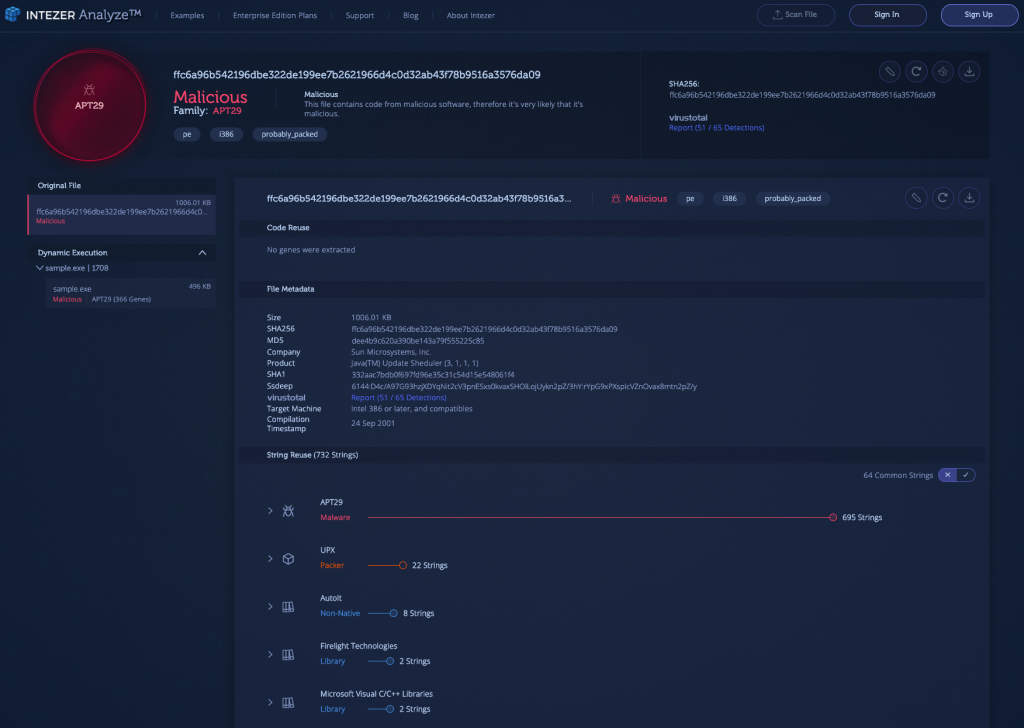
1) Cosmic Duke (APT29) [Link to Analysis]
APT29, also known as Cozy Bear or The Dukes, is a well-resourced cyber espionage group, with alleged ties to the Russian government dating back to at least 2008. The group utilizes a variety of malware tool sets, including remote access trojans (RATs) delivered on seemingly innocuous PDF files. Once installed the malware establishes a connection to remote File Transfer Protocol (FTP) servers to which data is exfiltrated. APT29 has been affiliated with previous attacks on government agencies and political think tanks, primarily members of the Commonwealth of Independent States.
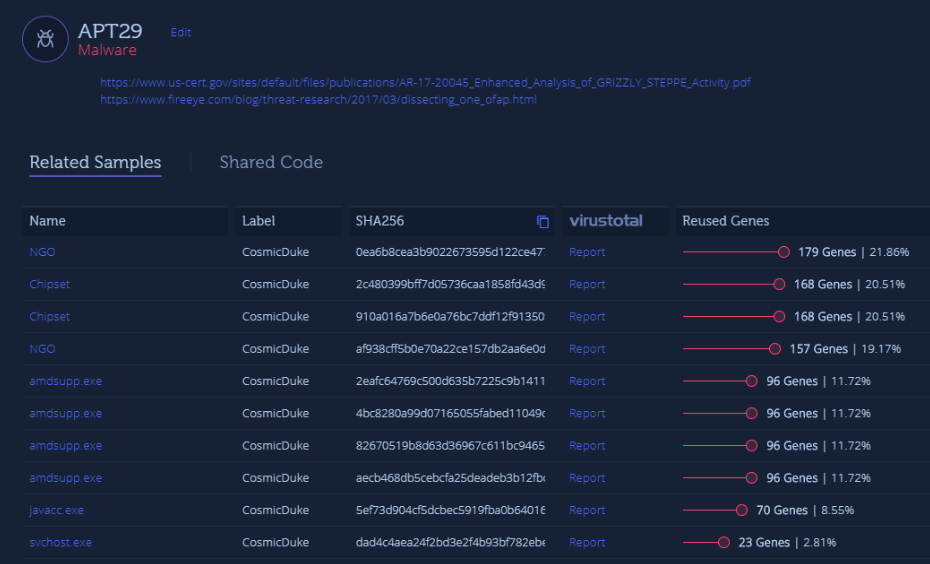
While the packed sample does not appear to contain any genes when analyzed statically, it does share approximately 700 strings with APT29. The sample was automatically unpacked by Intezer Analyze, demonstrating over 40% code reuse between the file and APT29. In viewing the related samples, there are additional files which share a genetic connection to the group, specifically categorized as Cosmic Duke. There are also significant IoCs within the shared and unique strings, including IP addresses, URLs and command lines.
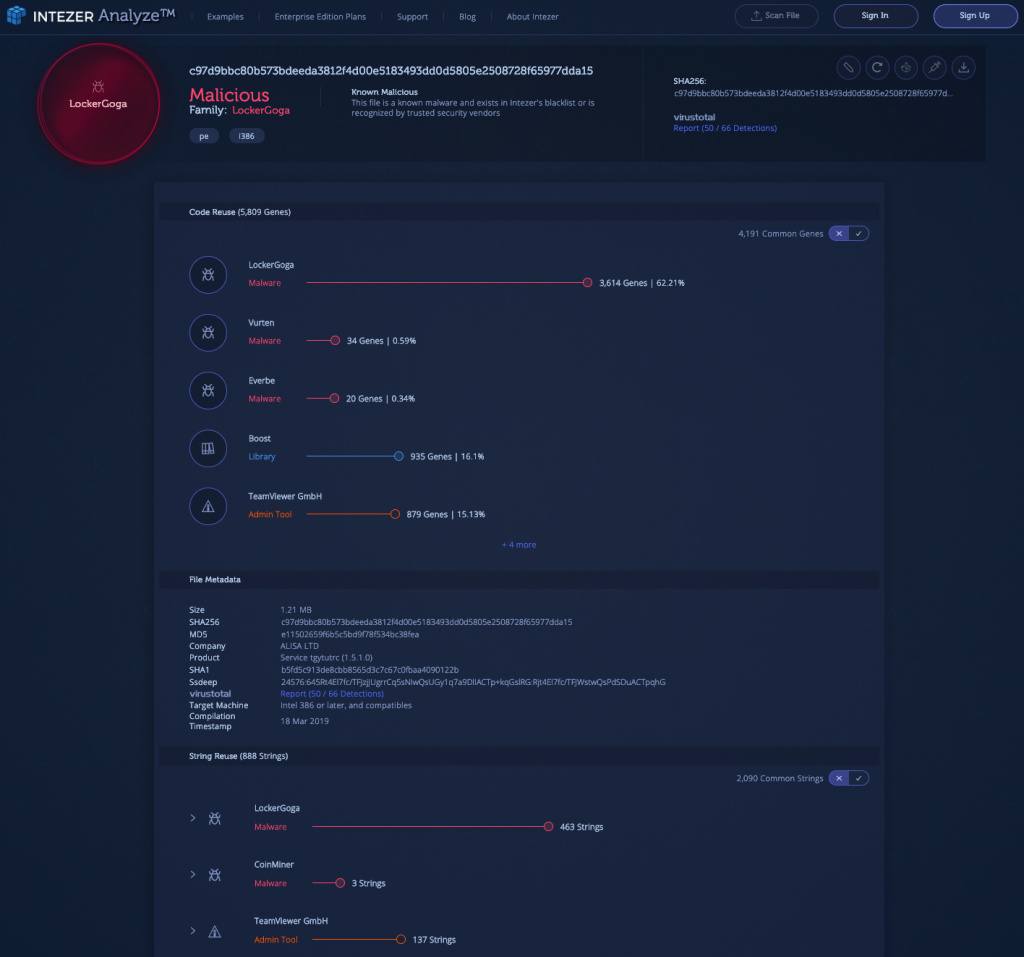
2) LockerGoga Ransomware [Link to Analysis]
LockerGoga is a relatively new ransomware, emerging in January 2019 during an attack against Altran Technologies. Since then the malware has been used to target various manufacturing and industrial organizations in the pursuit of ransom. Once deployed, LockerGoga encrypts files based on a predetermined list of file types, using advanced encryption standard (AES) and RSA encryption algorithms.
The sample above shares the majority of its binary code with LockerGoga, while Intezer Analyze also notes code connections to malware variants Vurten and Everbe and several libraries. There are also indicative strings. There is string reuse between the sample and both LockerGoga and CoinMiner — including email addresses which were successfully used to lock down infected endpoints.
Viewing this file in a hex editor we can quickly identify the string which gave the malware its name.

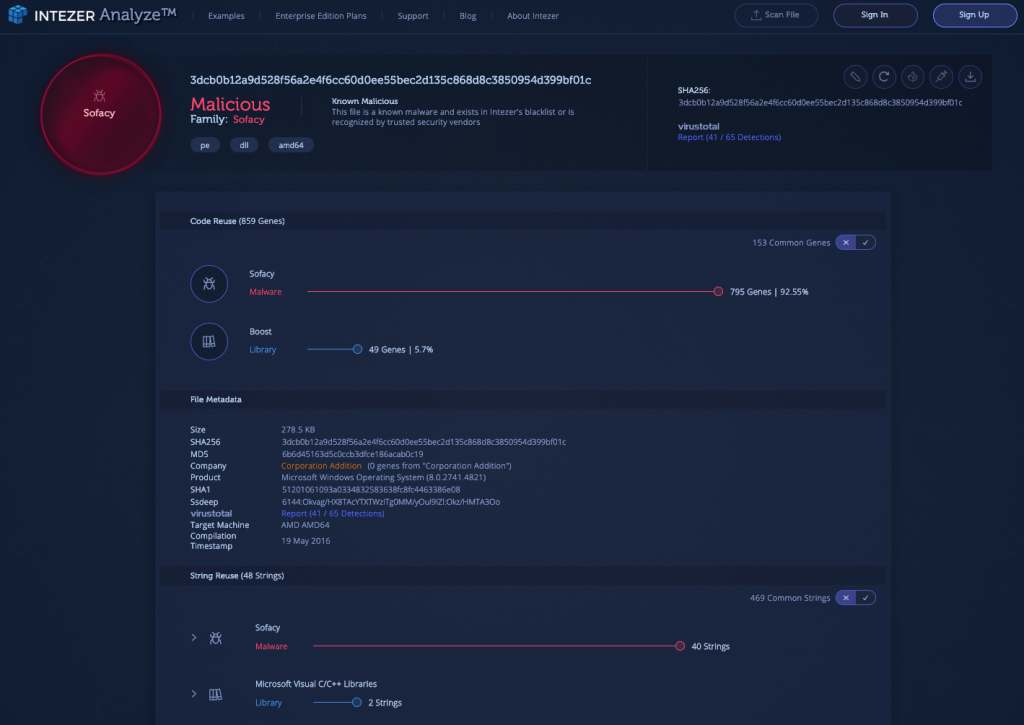
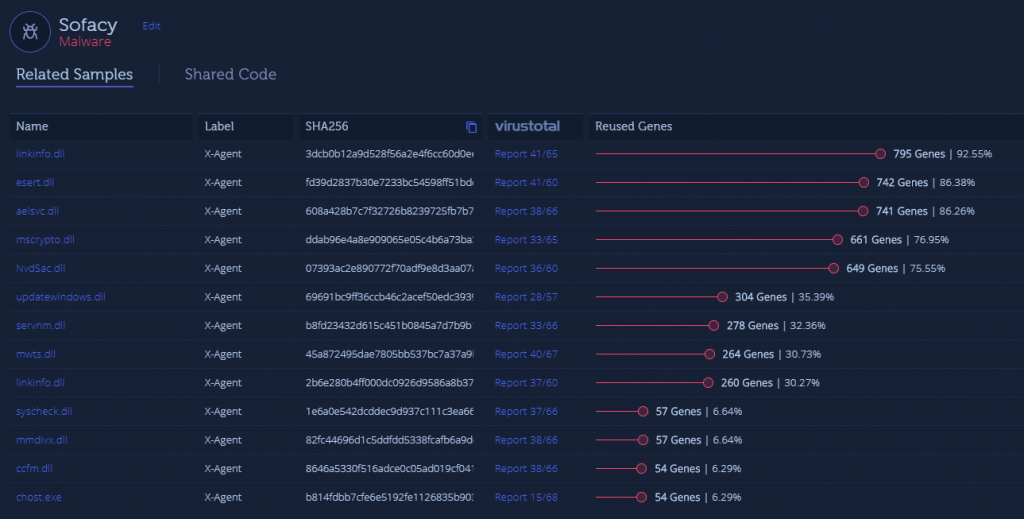
3) Sofacy (APT28) [Link to Analysis]
Sofacy, also known as Fancy Bear, is another cyber espionage group affiliated with the Russian government. The group has likely been active since the mid-2000s and is believed to be responsible for attacks on the German parliament, the White House and NATO. This sample uploaded by an Intezer Analyze community member shares over 90% of its code with Sofacy. In addition, its related samples are specifically related to X-Agent, a tool commonly used by the group to steal information from infected endpoints.
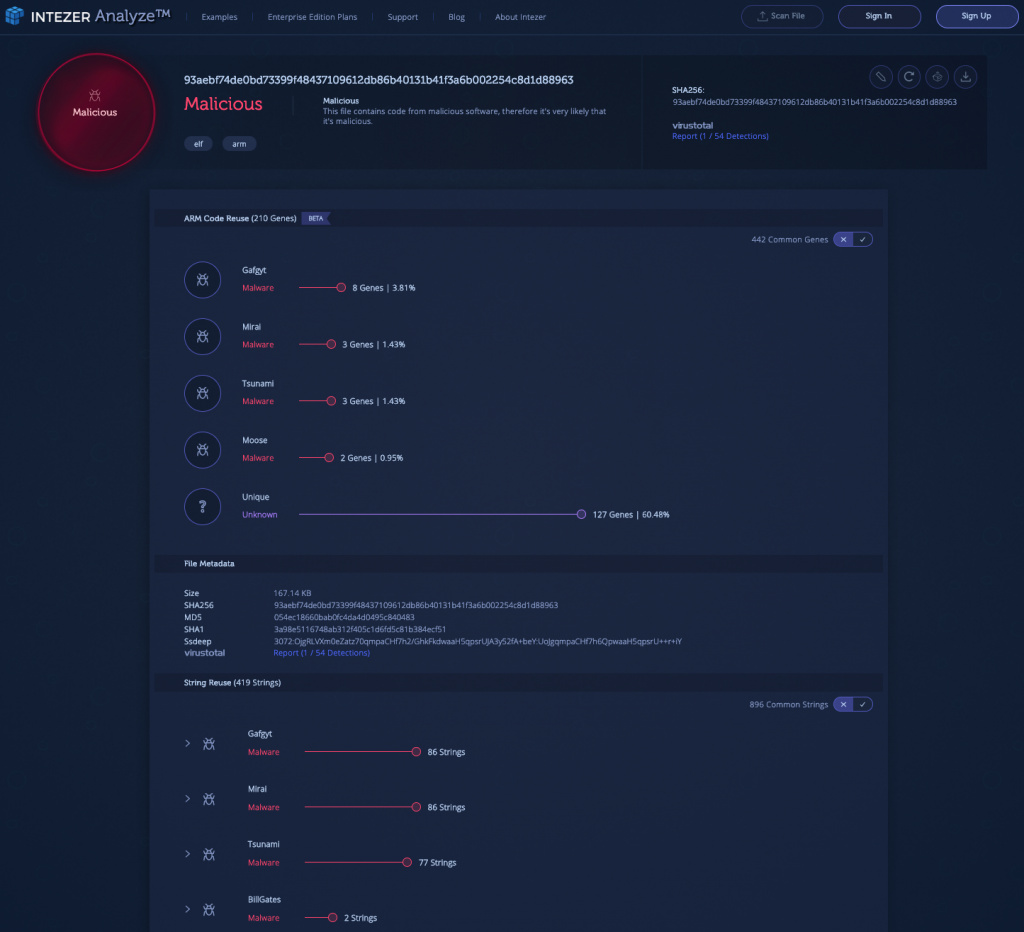
4) Undetected Linux Malware [Link to Analysis]
The sample below is an example of a Linux threat. Many malware detection engines do not support Linux binaries and those that do typically utilize classic methods such as signatures or behavioral analysis.
The sample, having only one detection on VirusTotal to date, does not show a definitive code connection to a specific malware family. However, it does share code with several threats which have a lot in common. Gafgyt, Mirai and Tsunami all share similar methods, spreading throughout networks, infecting IoT devices, collecting data and employing botnets to perform distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. Following the leak of Mirai source code in 2016, Intezer has observed more portions of the code being used in other Linux threats.
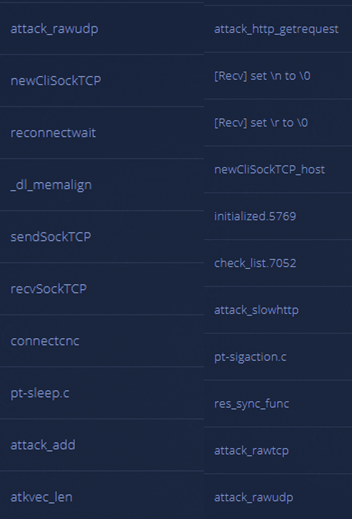
In viewing the unique strings of this sample its functionality becomes clearer, along with the assumption that the malware author did not place a strong emphasis on evasion.
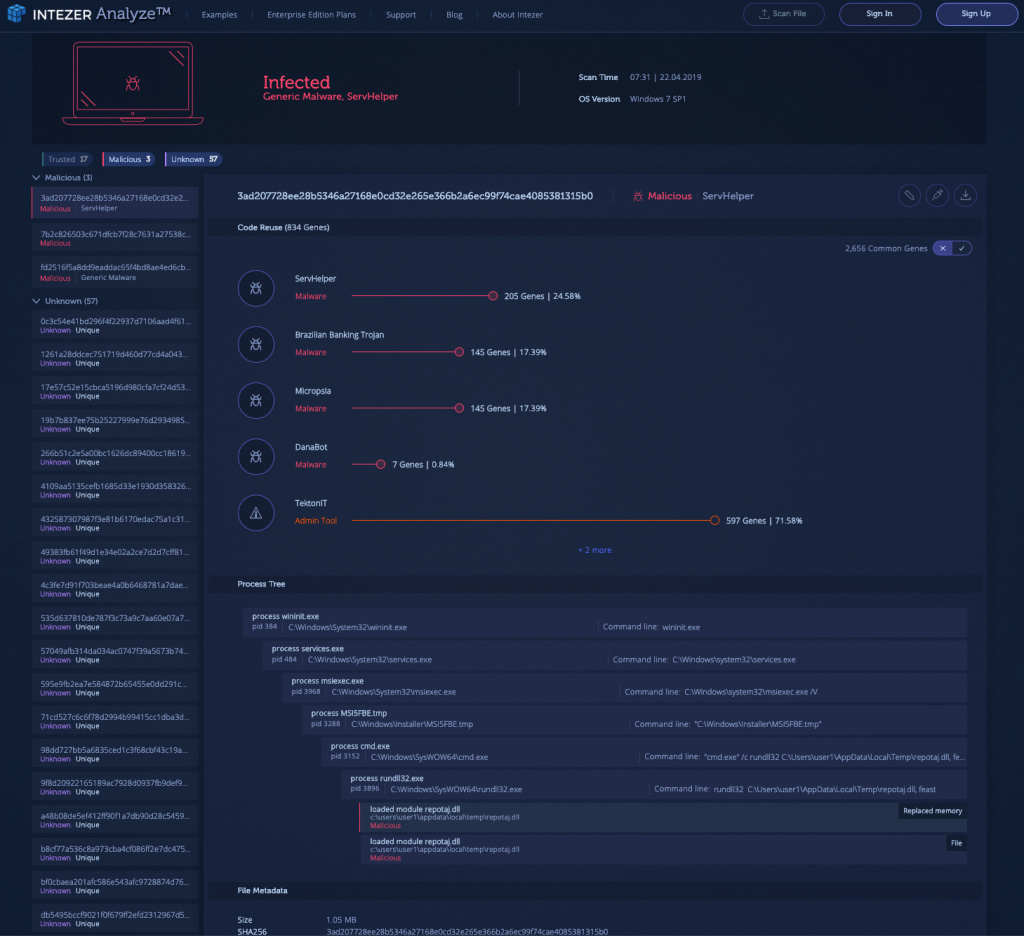
5) Infected Endpoint: ServHelper [Link to Analysis]
ServHelper is a remote access trojan (RAT) commonly used for controlling infected endpoints and enabling the download of additional threats, namely FlawedGrace. According to Proofpoint, FlawedGrace is a financially motivated malware developed by the cybercriminal group TA505. TA505 targets financial services and retail organizations globally, gaining access to networks and stealing user information which can be leveraged to make a profit.
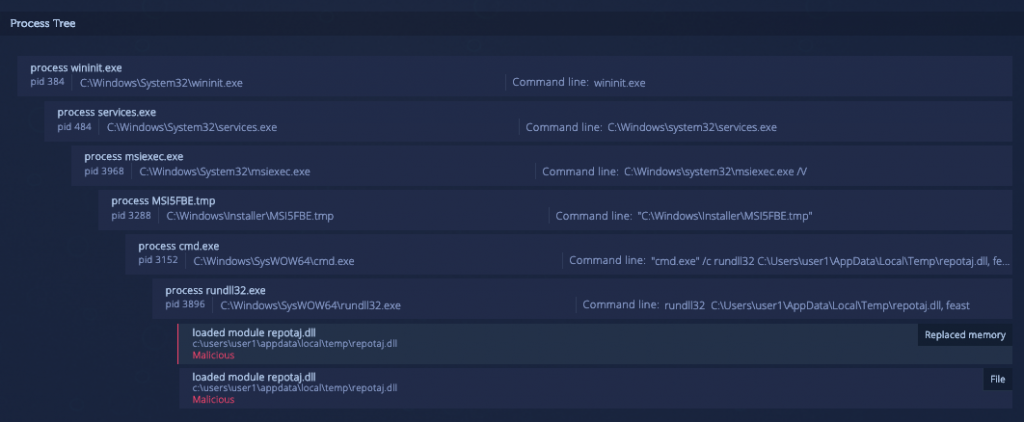
In the endpoint analysis below there are two malicious files which are connected.
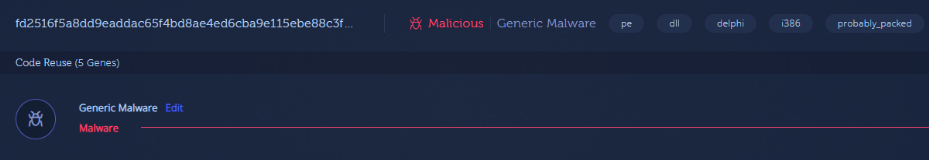
The first file is classified as generic malware but it is also identified as packed.
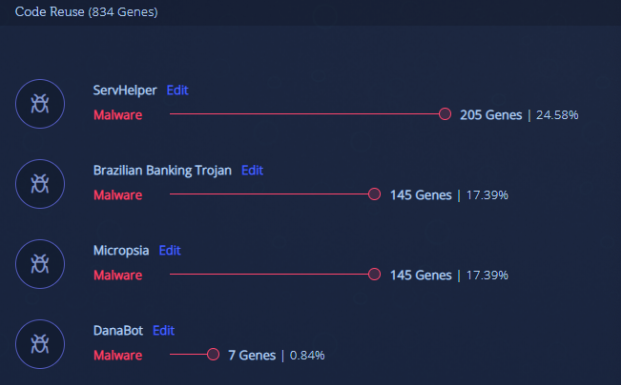
The unpacked payload is located in memory and provides a much clearer classification to ServHelper.
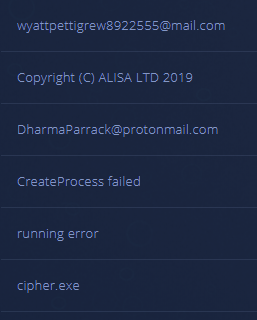
Additional information about the malware’s functionality can be gleaned from the strings.
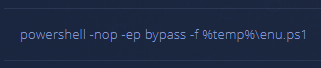
This line leads to an encoded Powershell script which gathers information about the infected endpoint and the currently logged in user.
For more information about the Intezer Analyze community please visit https://www.intezer.com/intezer-analyze/.
The post Top Five Community Uploads | April 2019 appeared first on Intezer.
Article Link: https://www.intezer.com/blog-community-uploads-april-2019/