Goal: Reverse the latest Lethic spambot, shared by Brad from Malware Traffic Analysis with the focus on its plethora of various anti-analysis and anti-virtual machine checks.
Source:
Lethic original spambot (e324c63717a4c2011fde7d1af0d8dbe8ddb0897fe4e7f80f3147a7498e2166fe)
Background
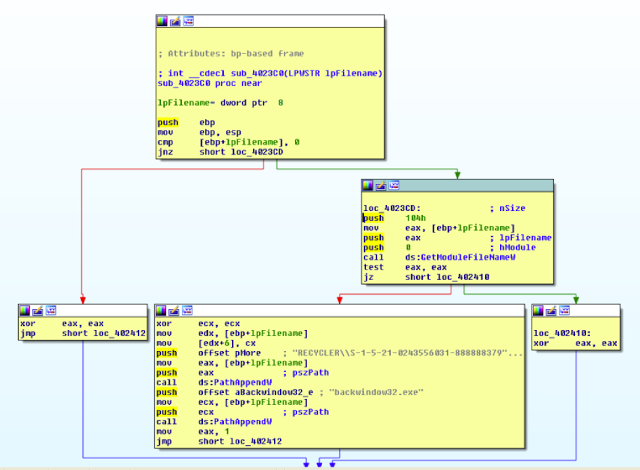
While analyzing the Lethic spambot (thanks to @malware_traffic), unpacked and reviewed some of the bot internals. By and large, the spambot leverages process injection into explorer.exe through usual WriteProcessMemory and CreateRemoteThread. This Lethic hardcoded call back IP is 93[.]190[.]139[.]16. Another unique feature of this Trojan is persistency in C:\RECYCLER\* as “backwindow32.exe” and usual registry RUN keys.
Malware checks:
I. Wine check
II. Anti-analysis process check
III. Anti-analysis DLL check
IV. UserName check
V. Path string check
VI. Virtual Machine (VM) process check
VII. VM registry and VM CreateFile check
VIII. Anti-sleep bypass check
IX. Anti-debugger check
II. Anti-analysis process check
III. Anti-analysis DLL check
IV. UserName check
V. Path string check
VI. Virtual Machine (VM) process check
VII. VM registry and VM CreateFile check
VIII. Anti-sleep bypass check
IX. Anti-debugger check
I. Wine check
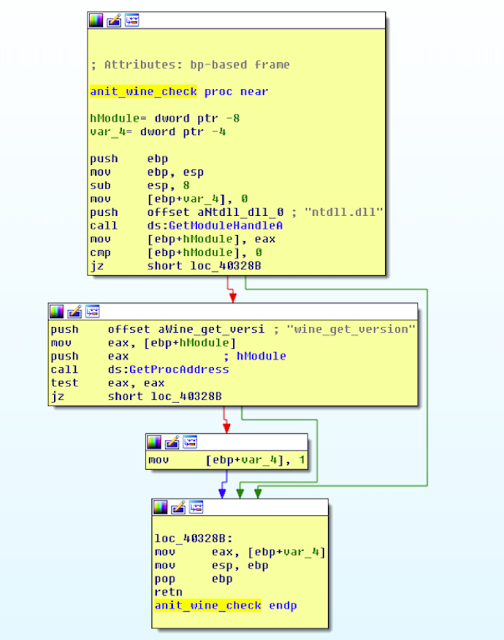
The Lethic spambot checks for the presence of Wine on the victim machine as follows checking the ntdll and kernel32 DLL's for the following functions via GetProcAddress API:
- wine_get_version
- wine_get_unix_file_name
A. wine_get_version
The pseudo-coded C++ function is as follows:
signed int anti_wine_get_version()
{
HMODULE hModule;
signed int v2;
v2 = 0;
hModule = GetModuleHandleA("ntdll.dll");
if ( hModule && GetProcAddress(hModule, "wine_get_version") )
v2 = 1;
return v2;
}
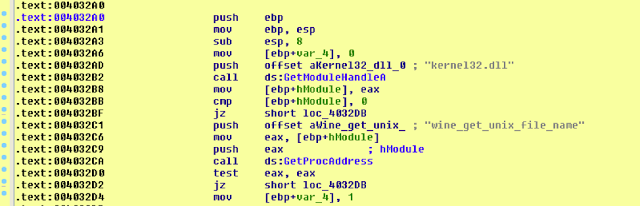
B. wine_get_unix_file_name
The pseudo-coded C++ function is as follows:
signed int wine_get_unix_file_name()
{
HMODULE hModule;
signed int v2;
v2 = 0;
hModule = GetModuleHandleA("kernel32.dll");
if ( hModule && GetProcAddress(hModule, "wine_get_unix_file_name") )
v2 = 1;
return v2;
}
II. Anti-analysis process check
The Trojan checks for the following processes and suspends threads if they exist on the host:
regmon.exe
filemon.exe
procdump.exe
procexp.exe
wireshark.exe
prcview.exe
sysinspector.exe
sniff_hit.exe
proc_watch.exe
apimonitor.exe
tcpview.exe
petools.exe
vmtoolsd.exe
autoruns.exe
The suspend thread function is as follows:
HANDLE __cdecl suspend_thread_function (int a1)
{
HANDLE result;
HANDLE hThread;
THREADENTRY32 te;
HANDLE hSnapshot;
te.dwSize = 0;
te.cntUsage = 0;
te.th32ThreadID = 0;
te.th32OwnerProcessID = 0;
te.tpBasePri = 0;
te.tpDeltaPri = 0;
te.dwFlags = 0;
result = CreateToolhelp32Snapshot(4u, 0);
hSnapshot = result;
if ( result != (HANDLE)-1 )
{
te.dwSize = 28;
if ( Thread32First(hSnapshot, &te) )
{
do
{
if ( te.th32OwnerProcessID == a1 )
{
hThread = OpenThread(2u, 0, te.th32ThreadID);
SuspendThread(hThread);
CloseHandle(hThread);
}
}
while ( Thread32Next(hSnapshot, &te) );
}
result = (HANDLE)CloseHandle(hSnapshot);
}
return result;
}
III. Anti-analysis DLL check
The malware checks for the presence of loaded DLL’s.
The list of all checked DLL is as follows:
api_log.dll
log_api32.dll
dir_watch.dll
pstorec.dll
vmcheck.dll
wpespy.dll
snxhk.dll
IV. UserName check
The malware checks for specific host usernames via retrieving them with GetUserName API and converting them to upper case.
The list of the checked usernames is as follows:
MALTEST
TEQUILABOOMBOOM
SANDBOX
VIRUS
MALWARE
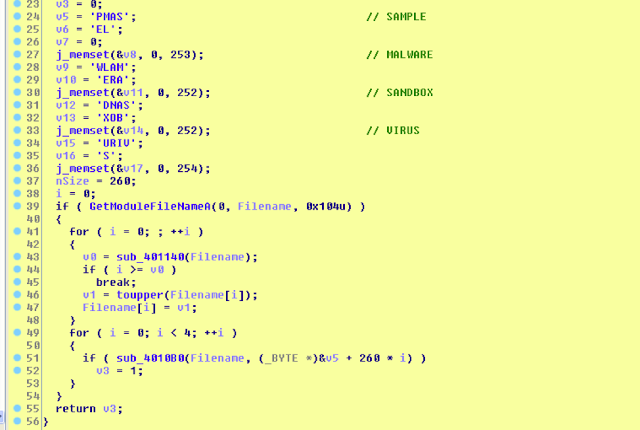
V. Path string check
The malware checks for specific path strings aliases via retrieving them with GetModuleFileName API and converting them to upper case.
The list of the checked path strings is as follows:
SAMPLE
MALWARE
SANDBOX
VIRUS
The malware also checks if it is named “sample.”
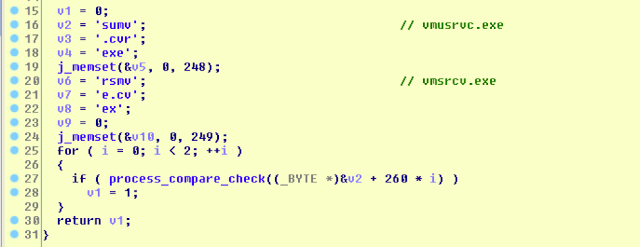
VI. Virtual Machine (VM) process check
Lethic checks for the presence of the VM-related processes.
The full list of all checked processes is as follows:
vmusrvc.exe
vmsrvc.exe
xsvc_depriv.exe
xenservice.exe
VII. VM registry keys check
The malware checks for the registry artefacts associated with VM.
The following registry locations and values are checked:
A. HKLM\HARDWARE\DEVICEMAP\Scsi\Scsi Port 0\Scsi Bus 0\Target Id 0\Logical Unit Id 0\Identifier
- VMWARE
- QEMU
B. HKLM\HARDWARE\Description\System\SystemBiosVersion
- VBOX
- QEMU
C. HKLM\HARDWARE\Description\System\VideoBiosVersion
- VIRTUALBOX
- BOCHS
D. HKLM\SOFTWARE\Oracle\VirtualBox Guest Additions
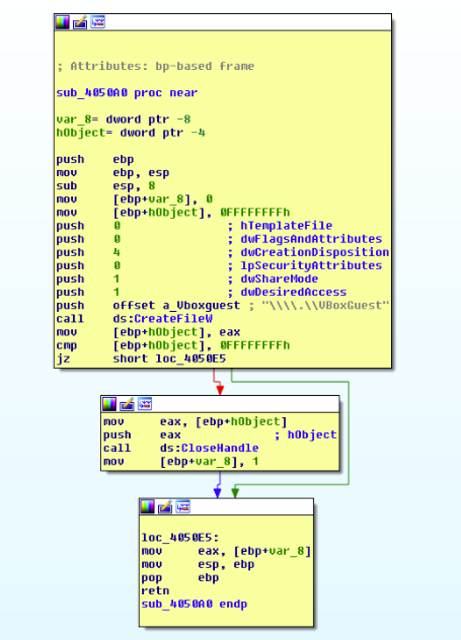
E. The malware tries to create a file “\\\\.\\VBoxGuest” and checks if it exists.
The C++ pseudocode is as follows:
signed int vm_createfile_check()
{
signed int v1;
HANDLE hObject;
v1 = 0;
hObject = CreateFileW(L"\\\\.\\VBoxGuest", 1u, 1u, 0, 4u, 0, 0);
if ( hObject != (HANDLE)-1 )
{
CloseHandle(hObject);
v1 = 1;
}
return v1;
}
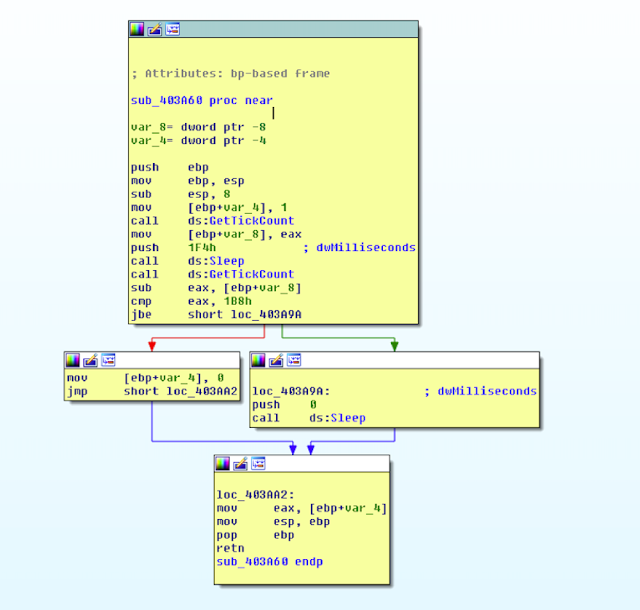
VIII. Anti-sleep bypass check
The malware implements Sleep API patch/hook check preventing the analyst from patching/hooking Sleep to a return.
The routine is as follows:
signed int anti_sleep_hook_check()
{
DWORD v0;
signed int v2;
v2 = 1;
v0 = GetTickCount();
Sleep(500);
if ( GetTickCount() - v0 <= 440 )
Sleep(0);
else
v2 = 0;
return v2;
}
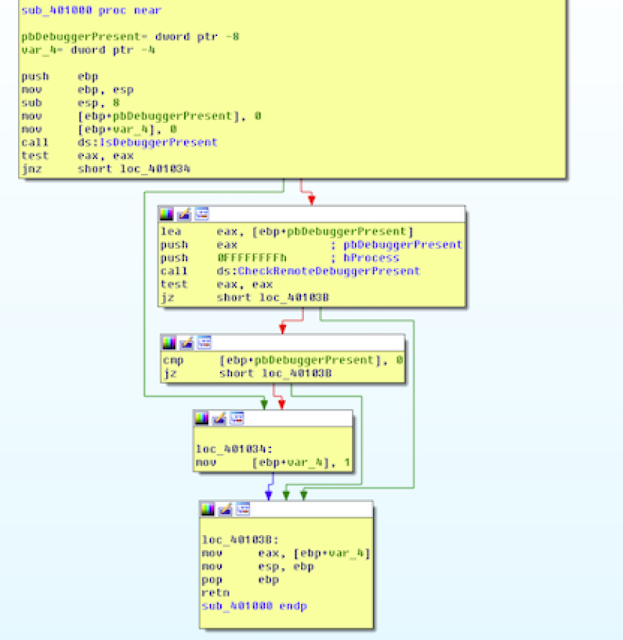
IX. Anti-debugger check
The malware calls IsDebuggerPresent and CheckRemoteDebuggerPresent APIs to check for the debugger presence.
The function in C++ is as follows:
int anti_debugger_check()
{
BOOL pbDebuggerPresent;
int v2;
pbDebuggerPresent = 0;
v2 = 0;
if ( IsDebuggerPresent() || CheckRemoteDebuggerPresent((HANDLE)0xFFFFFFFF, &pbDebuggerPresent) && pbDebuggerPresent )
v2 = 1;
return v2;
}
Article Link: http://www.vkremez.com/2017/11/lets-learn-lethic-spambot-survey-of.html